Vostok is a cold, cold desert and the very slow ice accumulation rate introduces significant uncertainties to the data. In addition to ice cores, Vostok is famous for the sub-glacial lake that lies beneath that has been mapped as one of the largest lakes in the world covering 14,000 sq kms.
Full Answer
Why is there an ice core at Vostok?
Snow accumulates very slowly there, and an ice core contains a long, accurate record of the temperature at Vostok, and of the atmospheric composition, because air bubbles trapped in the ice are little samples of the old atmosphere.
What happened to the temperature of the Earth at Vostok?
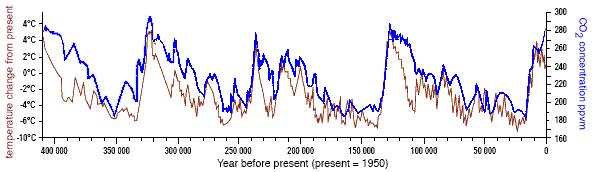
The temperature record, from the isotopic composition of the ice, is what happened in the Vostok region, not the whole world. But, if you take records from elsewhere, and smooth them a good bit, they all look similar to Vostok; the whole world cooled and warmed together through the ice-age cycles.
Where is Vostok Antarctica?
The Russian Vostok Antarctic base lies 1300 km from the S pole, close to the centre of the Antarctica continent at an elevation of 3488 m. It currently receives 2.6 mm precipitation per year. Average temperature is -55˚C and the record low is -89.2˚C which is below the freezing point of CO2. Vostok is one of the most hostile places on Earth.
Why does the earth look like Vostok?
But, if you take records from elsewhere, and smooth them a good bit, they all look similar to Vostok; the whole world cooled and warmed together through the ice-age cycles. And as explained in the next clip, this is primarily because of changes in CO 2.
What happened at Lake Vostok?
Russian scientists breached Lake Vostok in February 2012, after years of drilling. The lake lies beneath 3.5 kilometres of ice, and has been cut off from the rest of the world since Antarctica froze 14 million years ago.
What are the problems with ice cores?
The most commonly encountered ice-core drilling problems are the following: lost objects in the borehole, sticking drills, disorder cable spooling, cable damages, breakdown of surface and downhole equipment, casing leaking, and inability for penetration.
What was the significance of the Vostok ice shelf data?
Vostok. One of the primary results of paleoclimate research over the past decade has been strong evidence for human-influenced (anthropogenic) global warming. Results have been based on ice cores taken from undisturbed ice sheets, such as those in Antarctica .
What is the Vostok ice core and why is it important for us to look at it?
Vostok is a cold, cold desert and the very slow ice accumulation rate introduces significant uncertainties to the data. In addition to ice cores, Vostok is famous for the sub-glacial lake that lies beneath that has been mapped as one of the largest lakes in the world covering 14,000 sq kms.
Why are ice cores not reliable?
Cores with extensive melting are avoided for studies of past atmospheric composition, and even small amounts of meltwater are problematic for highly soluble gases such as CO2. However, the high CO2 concentration in the melt layers provides a tracer for diffusion.
What does the Vostok ice core reveal?
Ice cores are unique with their entrapped air inclusions enabling direct records of past changes in atmospheric trace-gas composition. Preliminary data indicate the Vostok ice-core record extends through four climate cycles, with ice slightly older than 400 kyr (Petit et al. 1997, 1999).
What is Vostok ice?
Abstract. The Antarctic Vostok ice core provided compelling evidence of the nature of climate, and of climate feedbacks, over the past 420,000 years. Marine records suggest that the amplitude of climate variability was smaller before that time, but such records are often poorly resolved.
What was the Vostok ice core?
Vostok is in proper stratigraphic order to about 3350 m depth. From 3350-3536 m depth, the ice is clean glacial/refrozen lake ice and is not in stratigraphic order. Discontinuous sections are available in the NSF-ICF archive. Several sections from other cores drilled at Vostok are also in the NSF-ICF archive.
What do ice core data taken from the Vostok site in Antarctica show?
historical carbon dioxide levelsThe Dataset Ice core samples taken at the Vostok station are used to collect data on historical carbon dioxide levels. The data consist of measurements of the percentage of atmospheric gasses, such as CO2 in fossil air bubbles that have been trapped in snow flakes and compressed into ice over 400,000 years old.
What was one of the most important discoveries made by scientists studying the Vostok ice core from Antarctica?
And the levels of CO2 and methane in the atmosphere today are unprecedented in the past 420,000 years. The study was published in Nature in 1999. “[The Vostok core] stands to this day as the most important record demonstrating the relationship between temperature and greenhouse gases,” Mayewski said.
What is the importance of the place Vostok station Russia?
Vostok Research Station is around 1,301 kilometres (808 mi) from the Geographic South Pole, at the middle of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet. Vostok is located near the Southern Pole of Inaccessibility and the South Geomagnetic Pole, making it one of the optimal places to observe changes in the Earth's magnetosphere.
Is there life in lake Vostok?
The embayment contained the most biological activity with the largest number of species identified. After two years of computer analysis, the team determined that Vostok Lake contains a diverse set of microbes, as well as some multicellular organisms.
How much precipitation does Vostok receive?
It currently receives 2.6 mm precipitation per year. Average temperature is -55˚C and the record low is -89.2˚C which is below the freezing point of CO2.
What is the rapid cooling of an interglacial?
The rapid warming that marks the beginning of an interglacial is normally followed in short order by rapid cooling. One can imagine the permafrost gradually freezing again, resulting in a reduction of the methane flux, the rate of destruction overtakes the rate of release and the concentration falls.
Is Vostok a desert?
Vostok is a cold, cold desert and the very slow ice accumulation rate introduces significant uncertainties to the data. In addition to ice cores, Vostok is famous for the sub-glacial lake that lies beneath that has been mapped as one of the largest lakes in the world covering 14,000 sq kms.
Introduction
The Vostok Ice core is one of the finest geochemical data sets ever assembled. I first visited this topic in December 2014 in a post called The Vostok Ice Core: Temperature, CO2 and CH4 [1]. For background information on Vostok, readers are directed to that post.
Data
In order to make my points, the data are presented in stages via a series of charts that hopefully makes my argument easier to follow.
Discussion
In attempting to combine these various bits of information into a coherent model, the following factors need to be taken into account:
Popular Posts:
- 1. how to write a rating for a online college course
- 2. course hero which statement best describes the spring backlog as outcome of the sprint
- 3. in diablo 3 which quest is the bridge of course it found
- 4. how to register to a new course in connect
- 5. where is moon valley golf course, phoenix
- 6. how to be a 3 percent man home study course
- 7. how to add a course page to wordpress
- 8. which course is best for data analyst
- 9. how to care for course asian hair
- 10. what happened to sugarloaf mtn golf course