Do cells divide during the G0 phase of the cell cycle?
The G0 phase is a period in the cell cycle in which cells exist in a quiescent state. G0 phase is viewed as either an extended G1 phase, where the cell is neither dividing nor preparing to divide, or a distinct quiescent stage that occurs outside of the cell cycle. So, yes, the answer is yes. (4 votes)
What is the key process of the cell cycle?
Gap 1 Key process: the cell grows Time interval (hours): 11 Sets of DNA present in each cell at end of phase: 1 Number of organelles in each cell at end of phase: 560 Synthesis Key process: DNA replication
What is the last part of the cell cycle?
Cytokinesis- Cytokenisis is the last part of the cell cycle, this stage is when the whole cell is divided into two new cells. Speedway High School.
What happens during the G phase of mitosis?
G phase. During the second gap phase, or G phase, the cell grows more, makes proteins and organelles, and begins to reorganize its contents in preparation for mitosis. G phase ends when mitosis begins. The G, S, and G phases together are known as interphase.
Where does the G1 phase take place?
G1 phase. G1 is an intermediate phase occupying the time between the end of cell division in mitosis and the beginning of DNA replication during S phase. During this time, the cell grows in preparation for DNA replication, and certain intracellular components, such as the centrosomes undergo replication.
What happens in G1 phase?
Initially in G1 phase, the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles. In S phase, the cell copies its DNA to produce two sister chromatids and replicates its nucleosomes. Finally, G2 phase involves further cell growth and organisation of cellular contents.
What occurs during interphase G1, S and G2 of the cell cycle?
During interphase, G1 involves cell growth and protein synthesis, the S phase involves DNA replication and the replication of the centrosome, and G2 involves further growth and protein synthesis.
Which of the following occurs during G1 and G2 of interphase?
Interphase is composed of G1 phase (cell growth), followed by S phase (DNA synthesis), followed by G2 phase (cell growth). At the end of interphase comes the mitotic phase, which is made up of mitosis and cytokinesis and leads to the formation of two daughter cells.
Is G1 part of interphase?
Interphase is defined by three stages: the first gap phase (G1), the synthesis (S) phase, and the second gap (G2) phase.
What is the G1 checkpoint?
The G1 checkpoint. The G1 checkpoint is located at the end of G1 phase, before the transition to S phase. If cells don't pass the G1 checkpoint, they may "loop out" of the cell cycle and into a resting state called G0, from which they may subsequently re-enter G1 under the appropriate conditions.
What does G1 stand for and what occurs in this cell cycle checkpoint?
The G1 stage stands for "GAP 1". The S stage stands for "Synthesis". This is the stage when DNA replication occurs. The G2 stage stands for "GAP 2". The M stage stands for "mitosis", and is when nuclear (chromosomes separate) and cytoplasmic (cytokinesis) division occur.
What cell structures are made in G1?
In G1, cells accomplish most of their growth; they get bigger in size and make proteins and organelles needed for normal functions of DNA synthesis. Here, proteins and RNAs are synthesized, and, more especially the centromere and the other components of the centrosomes are made.
Why is G1 phase important?
The G1 phase is often referred to as the growth phase, because this is the time in which a cell grows. During this phase, the cell synthesizes various enzymes and nutrients that are needed later on for DNA replication and cell division.
Which is synthesized in G1 phase?
During the G1 phase, the cell grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and protein that are required for DNA synthesis and for this process, DNA polymerase is needed.
Which of the following is correct for G1 phase?
G1 belong to interphase of cell cycle which is metabolically active stage. During G1 synthesis of ATP nucleotides,amino acids,RNAs and protein synthesis occur and growth of nucleus is observed. DNA replicates in S- phase of the cell cycle.
How are G1 and G2 different?
G1 phase is the first phase of the interphase of the cell cycle in which cell shows a growth by synthesizing proteins and other molecules. G2 phase is the third phase of interphase of the cell cycle in which cell prepares for nuclear division by making necessary proteins and other components.
Description
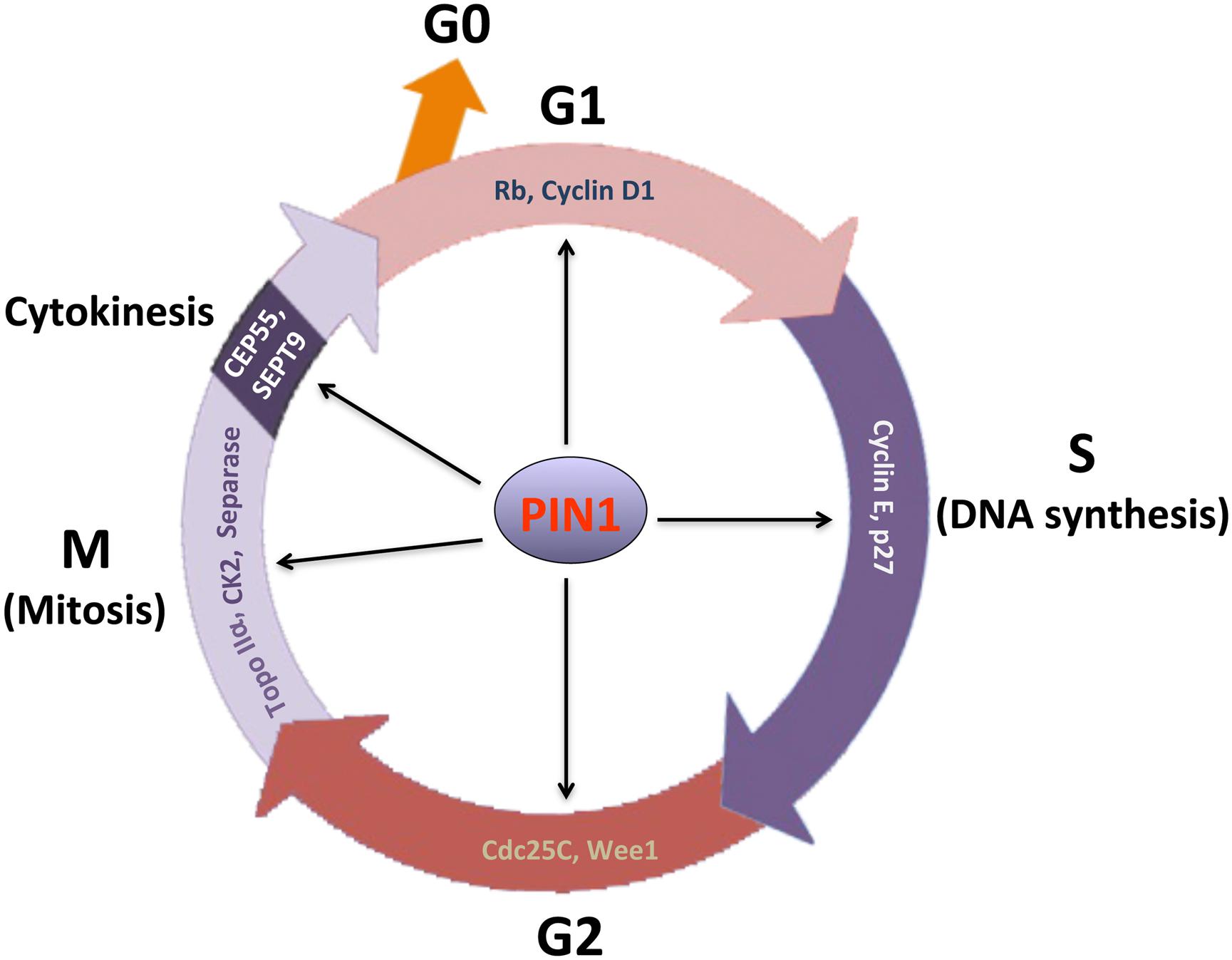
The cell cycle is the process by which cells grow, replicate their genetic material, and divide. In eukaryotes, cell division is known as mitosis. The entire cell cycle is divided into four phases: G 1, S, G 2, and M. The G 1, S, and G 2 phases are collectively known as interphase.
At A Glance
The cell cycle is the continuum of cell growth and division in the life of a cell. Cell division in eukaryotes is called mitosis.
Where does cytokinesis take place?
Importantly, cytokinesis takes place differently in animal and plant cells. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells. In an animal cell, a contractile ring of cytoskeletal fibers forms at the middle of the cell and contracts inward, producing an indentation called the cleavage furrow. Eventually, the contractile ring pinches the mother cell in two, ...
What is the life cycle of a cell?
Other organisms, from humans to plants to bacteria, also have a life cycle: a series of developmental steps that an individual goes through from the time it is born until the time it reproduces. The cell cycle can be thought of as the life cycle of a cell.
What is the M phase?
M phase involves two distinct division-related processes: mitosis and cytokinesis. In mitosis, the nuclear DNA of the cell condenses into visible chromosomes and is pulled apart by the mitotic spindle, a specialized structure made out of microtubules.
How many stages of mitosis are there?
Mitosis takes place in four stages: prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. You can learn more about these stages in the video on mitosis. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of the cell is split in two, making two new cells.
How many steps does mitosis go through?
The cell goes through 4 steps (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.) The cells at the end of the process also have the same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end, 2 cells are produced. Mitosis is used to make body cells, and occurs in the body.
How long does it take for a cell to divide?
A typical human cell might take about 24 hours to divide, but fast-cycling mammalian cells, like the ones that line the intestine, can complete a cycle every 9-10 hours when they're grown in culture. Different types of cells also split their time between cell cycle phases in different ways.
How do plant cells divide?
Because of this, plant cells divide in two by building a new structure down the middle of the cell. This structure, known as the cell plate, is made up of plasma membrane and cell wall components delivered in vesicles, and it partitions the cell in two.
What is the second part of the cell cycle?
Mitosis- Mitosis is the second part of the cell cycle, it is a type of cell division that makes in two daughter cells, both with the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus.
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is split into three stages- interphase, metaphase, and cytokinesis. Interphase- interphase is the first and longest part of the cell cycle, Interphase is split into three parts- G1,S,G2.
Popular Posts:
- 1. • to what group of mammals do whales belong? course hero
- 2. a character who does not change during the course of a story is called a character
- 3. what is a full time course load college
- 4. how to upload documents to course hero
- 5. why is canning salt course
- 6. how to be funny college course
- 7. when a second firm enters a monopolist's market course hero
- 8. how much time outside class for three-credit course
- 9. which of the following is a good example of a process breakdown structure? course hero
- 10. how long should a urinary tract infection last after starting a course of cipro