Full Answer
What do all amino acids have in common?
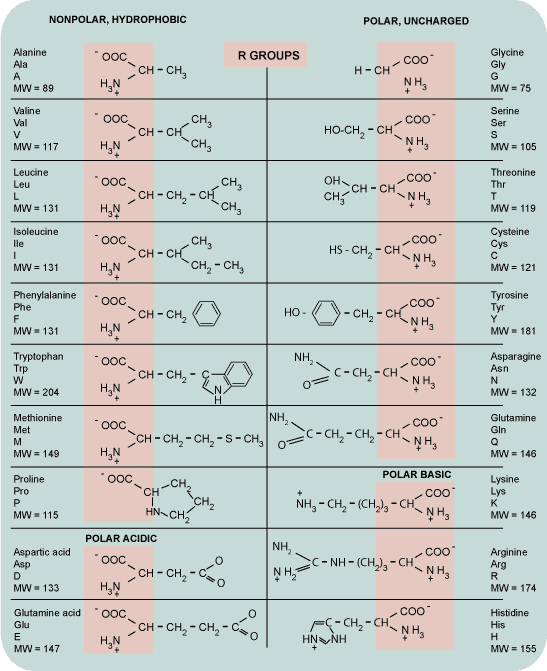
All amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group. The "R" group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers. The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code.
What is the structure of amino acids?
Each amino acid contains a central C atom, an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and a specific R group. The R group determines the characteristics (size, polarity, and pH) for each type of amino acid. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another through dehydration synthesis.
Which of the following is a non essential amino acid?
These nonessential amino acids are alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine. With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino acids are synthesized from products or intermediates of crucial metabolic pathways.
What is the function of amino acids?
Amino acids are organic molecules that, when linked together with other amino acids, form a protein. Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Some proteins function as enzymes, some as antibodies, while others provide structural support.
What class are amino acids?
There are 2 IMGT 'Polarity' classes, based on the presence or absence of hydrogen donor and/or acceptor atoms. Amino acids in each class are in the order of Table 2: Polar: R, N, D, Q, E, H, K, S, T, Y.
What is amino acids job?
The main function of amino acids is to serve as building blocks for proteins. Proteins tend to be typically comprised of between 50 to 2000 amino acids joined end-to-end in many different combinations. Each protein has unique sequences of amino acids in its own twisted and folded configuration.
How many amino acid classes are there?
four different classesThere are basically four different classes of amino acids determined by different side chains: (1) non-polar and neutral, (2) polar and neutral, (3) acidic and polar, (4) basic and polar.
How do you study amino acids?
3:509:08Memorize the 20 Amino Acids in 9 Minutes - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHere's a way to remember them. Basically as lost kid always returned. The basic amino acids areMoreHere's a way to remember them. Basically as lost kid always returned. The basic amino acids are histidine lysine and arginine and the one letter abbreviations.
What food has amino acids?
Foods that contain all nine essential amino acids are called complete proteins. These foods include beef, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, soy, quinoa and buckwheat. Foods that contain some but not all the essential amino acids are called incomplete proteins. These foods include nuts, seeds, beans and some grains.
What is amino acid in zoology?
“Amino Acids are the organic compounds that combine to form proteins, hence they are referred to as the building components of proteins. These biomolecules are involved in several biological and chemical functions in the human body and are the necessary ingredients for the growth and development of human beings.
What are the 3 most important amino acids?
BCAAs are considered essential because, unlike nonessential amino acids, your body cannot make them. Therefore, it is essential to get them from your diet. The three BCAAs are leucine, isoleucine, and valine. All have a branched molecular structure and are considered essential to the human body.
Which foods have all 9 essential amino acids?
Foods that contain all nine essential acids are called complete proteins. These include eggs, fish, beef, pork, poultry, and whole sources of soy (tofu, edamame, tempeh, and miso). Generally speaking, plant proteins have lower essential amino acid contents when compared to animal proteins.
What are essential amino acids Class 12?
Those amino acids which need to be obtained from the diet are known as essential amino acids. -The nine essential amino acids are valine, phenylalanine, lysine, histidine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, threonine and tryptophan and all of these amino acids must be obtained from various dietary sources.
Do I need to memorize amino acids for MCAT?
The MCAT may test your knowledge of all three, so be sure to memorize each form. There are 8 nonpolar amino acids: alanine, phenylalanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, tyrosine, tryptophan, and methionine.
Do amino acids help your brain?
Amino acids both act as neurotransmitters and help stabilize levels of neurotransmitters, making them a key nutritional therapy for brain and mental health.
Can amino acids give you anxiety?
In this study, a significant inverse association was found between BCAAs intake and odds of depression and anxiety; however, there was no significant association between BCAAs intake and odds of psychological distress.
What are amino acids made of?
From a structural perspective, amino acids are typically composed of a carbon atom, a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group along with an amino group and a variable group.
Which amino acids are considered conditionally essential?
Six of the nonessential amino acids (arginine, cysteine, glutamine, glycine, proline, and tyrosine) are considered conditionally essential as dietary supplementation may be required during the course of an illness or in children. Amino acids that can not be produced naturally are called essential amino acids.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
While amino acids are necessary for life, not all of them can be produced naturally in the body. Of the 20 amino acids, 11 can be produced naturally. These nonessential amino acids are alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine. With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino ...
What are nonessential amino acids?
With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino acids are synthesized from products or intermediates of crucial metabolic pathways. For example, alanine and aspartate are derived from substances produced during cellular respiration. Alanine is synthesized from pyruvate, a product of glycolysis.
What are the structural properties of amino acids?
Generally, amino acids have the following structural properties: All amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group. The "R" group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers.
How are amino acids joined together?
The resulting amino acids are joined together through dehydration synthesis, a process in which a peptide bond is formed between the amino acids. A polypeptide chain is formed when a number of amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds.
How many amino acids are in proteins?
Although there are hundreds of amino acids found in nature, proteins are constructed from a set of 20 amino acids.
Amino Acids and Proteins
In the human organism, proteins undertake multiple and vital functions. Structural proteins are found in each and every cellular compartment. Intracellularly, motor proteins power the energy-dependent transportation of vesicles. Signal proteins receive and transmit information.
Free Certification
Academy Europe presents high-quality formal diplomas, certificates and e-certificates which are formal proof and recognition of accredited online courses. It shows all student’s abilities to learn and achieve high results and is very useful to promote personal career including with CVs, job applications and self improvements.
Audience
The medical course by Academy Europe aims at imparting quality education and training to students to help contribute to the growing sector of health and medicine.
Prerequisites
Before you start proceeding with this course, we are assuming that you have a good aptitude and can think logically. You should want to help patients and want to try something different.
The Syllabus on Medical Education
Pre-Clinical >> Anatomy, Bio-Chemistry, and Physiology: Basic knowledge to understand the various structures in the body; the molecular organization of the cell; and the functioning of the organs in the body.
Job Profiles for Medical Education
Candidates who wish to work can opt for any of the below-mentioned job profiles:
What Are Amino Acids?
When protein is digested it is once again broken down into specific amino acids, that are then selectively put together for different uses. These new proteins formed in the body are what make up most solid matter in the body: skin, eyes, heart, intestines, bones and, of course, muscle.
What are the three most important amino acids?
Branched-chain amino acids are held in high regard in bodybuilding circles and justly so. They are the three most important amino acids in the manufacture, maintenance and repair of muscle-tissue. All three exert a strong synergistic effect.
How many amino acids are needed for bodybuilding?
A complete spectrum of amino acids and optimum health can only be brought forth by gearing your protein intake to these 8 aminos.
Why is protein important in the body?
Not only does it improve the use of free amino acids in the body, it also prevents the use of engaged amino acids by minimizing protein breakdown.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
Depending on who you talk to, there are around 20 to 22 standard amino acids. Of those 20-22, 8 to 10 of them are considered essential, which means that you need to get a certain amount of them in your diet to function properly - our bodies cannot synthesize them from other materials, so we only get them from food.
What are amino acids? What are their functions?
Once you learn what they do in the body, you're almost struck with amazement. They fulfill the basic foundations of well-being like vitamins and minerals whilst also optimizing those micronutrients and providing the fuel for growth, health, good functioning of the body and genetic transcription.
Why is it important to get enough vitamins and minerals?
To counter potential harmful effects, getting enough vitamins and minerals is important because they insure proper conversion of protein to amino and vice versa.
Why do we need amino acids?
Why You Need Amino Acids. Amino acids are known as the building blocks of protein, which is an important component of every cell in your body. Here are a few roles that amino acids play in your overall health:
What amino acids are used in muscle?
Athletes commonly use leucine, isoleucine, and valine to improve their performance. These amino acids can be metabolized in muscle to provide extra energy during exercise.
What is the best source of amino acids?
These five foods are some of the best sources of dietary amino acids available: Quinoa. Quinoa is one of the most nutritious grains available today. In addition to being a good source of fiber, it contains all nine essential amino acids that your body needs from food.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
Amino acids are organic compounds that come together to form proteins in your body. There are 20 amino acids overall, and they each fall into one of three categories: Because your body cannot make the nine essential amino acids itself, you need to get them from the foods you eat. The essential amino acids include:
How many amino acids are in cottage cheese?
Mushrooms contain a total of 17 amino acids, including all of the essential ones.
Can amino acids improve liver function?
Evidence suggests that taking branched-chain amino acids by mouth can improve liver function in people with poor brain function due to liver disease.
Why are amino acids classified as basic amino acids?
These basic amino acids are so classified because they have basic side chains containing nitrogen, which resemble ammonia (a base). The pKa values of basic amino acids are high enough to bind protons and give them a positive charge.
Why do amino acids matter?
Though some are essential and some nonessential, the reason amino acids matter, and the reason that all these tiny permutations matter, is because without each of them working together, our health and well-being would fail. We at Amino Co. have developed amino acid supplements specifically because we understand their vital importance to human life. The chemistry behind each person's daily concert of amino acids is the science that drives our passion.
What is the difference between acidic and basic amino acids?
In conclusion and to summarize: the difference between acidic and basic amino acids is the same as between any acid and base in chemistry and chemical substances. Their similarities still include being polar amino acids, as well as hydrophilic amino acids, and, of course, the biggest thing they have in common is that they're all still amino acids, ...
What are the nonessential amino acids?
Your nonessential amino acids are the amino acids your body can create on its own as a byproduct of normal functioning. There are 11 of these amino acids, and they include the following: Alanine (ala) Arginine (arg) Asparagine (asn) Aspartic acid (asp) Cysteine (cys) Glutamic acid (glu) Glutamine (gln)
What are the three molecular structures of amino acids?
Each amino acid is made of a central alpha carbon atom (Cα), and attached to that central atom are three molecular structures, also known as functional groups: one is a carboxyl group (-COOH), the second is an amino group (-NH2), and the third is a single hydrogen atom (H). This is the same structure of all amino acids, ...
How are amino acids delivered?
Amino acids can be delivered either by intravenous infusion or oral ingestion. Both routes support protein metabolism in the body, as well as provide amino acids for other purposes. But what are the advantages and disadvantag ...
What are the building blocks of protein?
Amino acids are the buildings blocks of protein in your body. In short, when it comes to protein synthesis and literally building new muscle, you cannot do it without your amino acids.
Free Certification
Audience
- The medical course by Academy Europe aims at imparting quality education and training to students to help contribute to the growing sector of health and medicine. Different institutes have different cut off marks, however, the selection is made on the basis of the entrance exams conducted either on the national level or by individual institutes. After completing this medical c…
Prerequisites
- Before you start proceeding with this course, we are assuming that you have a good aptitude and can think logically. You should want to help patients and want to try something different. Students who have a keen interest in learning the basics of the Medical Sciences, its workings and also the diagnosis of human bodies, should opt for this course. This course has a structure which develo…
The Syllabus on Medical Education
- Pre-Clinical >> Anatomy, Bio-Chemistry, and Physiology:Basic knowledge to understand the various structures in the body; the molecular organization of the cell; and the functioning of the organs in the body. Para-Clinical >> Community Medicine, Forensic Medicine, Pathology, Pharmacology, Microbiology, Clinical postings inwards and OPDs:Awareness of...
Job Profiles For Medical Education
- Candidates who wish to work can opt for any of the below-mentioned job profiles: Doctor:Doctors are responsible for performing health tests, running diagnosis, treating patients and prescribing medicines to them. Private Practitioner:Private practitioners provide private services to their patients related to health, mental issues, and many other things. Public Health Specialist:They a…
Popular Posts:
- 1. college what is blended course
- 2. what golf course where a pga event is played has a witch logo
- 3. how much calories does a strength course burn
- 4. what is data structure course in college
- 5. how to convert long course to short course
- 6. for the lease which is attached as a word document, please answer the following course hero
- 7. where to take driving safety course
- 8. what course is rnsg 2301
- 9. autoimmune diseases occur when course hero
- 10. how do i access my course als three materials