- Draw a line from point A to B - using parallel rules, from starting mark to next mark.
- Check the line for safety - if not, move end mark until you get a safe leg.
- Measure and mark the heading - transfer the leg to compass.
- Measure and mark the distance - measure the legs.
How to plot a course on a chart?
Dec 24, 2021 · How do you plot a sailing course on a chart? When shaping a sailing course , plot a line on the chart joining the departure point ( A ) and the destination (B). The navigation chart symbol is signified by marking two arrowheads on the line and called the [ Ground Track ] and is the course to be followed, over the ground, to the destination.
How do you determine a course on a boat?
Nov 15, 2020 · How to plot a course to steer on a nautical chart Draw your ground track (COG)from start point (A) through and beyond your end point (B). Measure the distance of your ground track from A to B using your dividers, measure this against the scale on your chart to determine the distance.
How do you plot a boat Start Point?
Oct 17, 2021 · I have been unable to figure out how to plot a course for a sailing rout on either platform. What must I do to unlock this feature? Than you. 1 Reply Last reply Reply Quote 0. idefix37 Sailor Moderator @mickey171 last edited by . @mickey171 Windy.app has nothing to do with windy.com, only the name is similar.
What nautical charts do I need to sail a sailboat?
Plan your course right up to the edge of the current. Then do a CTS calculation to get a heading to steer through the current, and drop a mark on the other side of the current on that range and bearing. When you get to the current zone out on the water you will point to the correct amount up current to sail the CTS.
How do you plot a course to steer?
0:313:49RYA Day Skipper: Plotting a course to steer - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe begin by marking the start position for our passage on the chart. We mark this with a symbol forMoreWe begin by marking the start position for our passage on the chart. We mark this with a symbol for a fix a dot. And a circle.
What do navigators need to consider when plotting a course?
8 Things to Consider While Doing Nautical Chart Plotting On ShipsScale of the Chart. The Scale of the chart is the first thing to check before commencing Chart work. ... Notes of the Chart. ... Chart Symbols. ... Chart Corrections. ... GPS Positions. ... Radar Fixes. ... Visual Fixes. ... Position Circle and Position Line.
How do you plot in navigation?
Plotting is the process of keeping track of the position of a vessel over time. This is done by recording the successive positions of the vessel in the nautical chart. The position can be obtained by dead reckoning or by taking bearings from prominent charted landmarks and constructing Lines-of-Position.
How do you plot a course with a compass?
0:022:49How to plot a course with map and compass - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo first I want to make sure my map is oriented to true north to north here is at three four fiveMoreSo first I want to make sure my map is oriented to true north to north here is at three four five degrees. So I just make sure that when I run my compass along here I'm still at three four five.
What are the main purpose of plotting Maritime?
It provides water depths, locations of dangers to navigation, locations and characteristics of aids to navigation, anchorages, and other features. The nautical chart is essential for safe navigation. Mariners use charts to plan voyages and navigate ships safely and economically.Oct 13, 2021
What is the best position fixing method?
Primary method of position fixing There should always be at least two method of position fixing. Now at open sea, the primary method is GPS and secondary method would be “celestial fix”. If there is a radar conspicuous object, the primary method of position fixing becomes the “radar fix”.May 6, 2017
How do you plot your position?
0:191:25Plot Simple Position - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTake the parallel rule. Place one side on a nearby fixed longitude line on the chart. And move theMoreTake the parallel rule. Place one side on a nearby fixed longitude line on the chart. And move the other side to your mark on the scale use the rule to transfer that coordinate to your chart.
What are the 4 stages of voyage planning?
There are four stages of Voyage Planning that are, Appraisal, Planning, Execution and Monitoring that logically follow each other.Jan 21, 2019
What does it mean to plot a course?
Verb. To obtain or provide directions, usually by reading a map.
How do you navigate a map and compass?
1:516:35How to Use a Map and Compass - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhat direction we need to travel in to start let your map out on a flat surface. And put yourMoreWhat direction we need to travel in to start let your map out on a flat surface. And put your compass on top of the map. Make a marking of where you're going to start and then where you want to end.
How do I plot a route on Google Maps?
Plot a route on a map To start drawing your route simply doubleclick on the map to set the starting pinpoint, then continue to click each of the points along the route you wish to follow. You can change the map view to satellite, hybrid or terrain using the selector on the top left corner of the route map.
How do you use orienteer with a map and a compass?
Place the compass flat on the map. Rotate the map until the "north lines" on the map (a series of evenly spaced parallel lines drawn across the map, all pointing to magnetic north) are aligned with the compass needle. The map should now be oriented to the terrain.
What is nautical chart?
A nautical chart is like a road map. It shows you the expected lay of the land and gives references for finding your way to somewhere when don't know the path.
What can you see on a land chart?
When land shows on a chart, it may show standpipes, towers, flagpoles and other permanent structures if they may be helpful to navigation. You can sight these with a compass to get your position and use them to get your bearings. In the sample below, you can find a monument, a tower, and a chimney as visible landmarks from the water.
What is the most important information on a chart?
The most useful information on the chart is the various marks and symbols. Every sailor should have a copy of U.S. Chart Number 1, the master list of all symbols, signs and objects you will see on any U.S. government chart. Some details may vary on charts from other countries, but most of the symbols and abbreviations are used on almost all English language charts. It's a great reference to learn chart reading and is available as a free download. You can also order a paper copy for your nav station.
How to read a chart?
In order to read a chart, you interpret longitude and latitude lines to determine your coordinates, which is your position. You have to understand and interpret different symbols like depth, scale, and navigation marks. Using these symbols, you find a safe course and plot it on the chart.
Where do latitude and longitude run?
Lines of latitude range from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles and run parallel to the equator. Lines of longitude run from the north to the south start at 0° in Greenwich, England and run to 180° West and East.
Can you use dividers to measure leg length?
There are several was to use dividers to measure your leg lengths, you'll figure out which works best for you and some techniques work better in some situations than others.
What is somewhere on a chart?
Somewhere on the chart will be a bit of text describing in some detail what the chart is. Not all of this applies to plotting a basic route, but it's good to know things like how old the chart is.
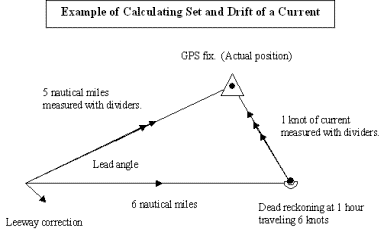
How long does it take to sail from A to B?
Draw a line from A to be, and measure and note it’s length (8 miles) and direction. If your boat speed is eight knots, it will take you an hour to sail from A to B normally. This means you will be exposed to one hour of current - so the current will sweep you 2.5nm in that time.
What happens if your autopilot isn't integrated with your GPS?
If your autopilot isn't integrated with your GPS, you will adjust it step by step to the course to steer as your GPS changes waypoints. You're all set if you put in the CTS calculation in the course, just follow the numbers.
What is CTE in autopilot?
Many autopilots have a Cross Track Error (or "CTE") mode of navigation. In normal course mode, most autopilots point at the next programmed mark, which works well enough without big currents.
Navigation Basics
- To start, we'll do a route from a single point to another - a one leg trip. A full course is just a series of plotted legs from point to point, starting where you are end ending where you wish to go.
Reading A Chart
Using A Chart - Plotting A Course
- A nautical chart is like a road map. It shows you the expected lay of the land and gives references for finding your way to somewhere when don't know the path. On land you've got roads, which limit where you can drive and how much trouble you can get into. If you're on Interstate 95 and you know the next exit number, you're good for figuring out where you are and how to get where you'r…
Dead Reckoning - Pulling It All Together
- This article teaches reading paper charts, since paper charts are the basis of navigation for chart plotters and electronic charts. There are variations in how electronic charts may display information, especially vector charts, but once you know paper charts e-charts are easy. We’ll take you through each part of the chart, explaining the key information needed for basic navigation. R…
Popular Posts:
- 1. get percentage of students who failed course
- 2. which one is the course title
- 3. what pieces are in thompson's adult piano course
- 4. the course networking how to upload documents
- 5. what percentage of those applicants who are interviewed are offered a job? course hero
- 6. crash course that's why carbon is a tramp
- 7. which of the following is true about short-term memory course hero
- 8. where can i take a bible course that begins in the old testament genesis
- 9. which of the following entry modes into a foreign market best serves a high-tech firm? course hero
- 10. fundamental analysis looks at which of the following? course hero