You can use a E6B or similar flight computer and forecast winds aloft to correct your true course to determine a true heading. To answer your other question, Forecast Winds and Temperature Aloft charts (FD) are given in reference to true north.
What is true course and true heading?
· You can use a E6B or similar flight computer and forecast winds aloft to correct your true course to determine a true heading. To answer your other question, Forecast Winds and Temperature Aloft charts (FD) are given in reference to true north. 3) Magnetic Heading (MH): The difference between true north and magnetic north is known as variation.
What is true course (TC)?
· Let’s say you need to know the true bearing of Bruin Channel. The relative bearing is 325°. Your course is 135° T. According to the calculation relative bearing + heading = true bearing so 325 + 135 = 460. But is that right? Not exactly! Compass heading works in a …
What's the difference between true heading and magnetic heading?
View Course Converting True Course To Magnetic Heading - BestOfCourses Top www.bestofcourses.com · Add or subtract the magnetic deviation from the magnetic course. If the magnetic deviation is 1 degree west, for example, add 1 degree to the magnetic course. If it is 1 degree east, subtract 1 degree. The result is the true course . More Courses ››
How to determine the true heading of a plane?
· The steps for converting your heading from either True Heading to Ship's Compass Heading or from Ship's Compass Heading to True Heading.Looking to become a l...
How do you calculate true heading from true course?
To get the true heading, you need to first read the magnetic compass, then either add an Easterly, or subtract a Westerly, magnetic variation; based on the isogonic lines. When converting true to magnetic heading, you'd do the opposite and subtract an Easterly, or add a Westerly, magnetic variation.
Is true heading and true course the same?
True Course: The aircraft's course over the ground relative to true north. True course is measured with a navigation plotter and a sectional map. True Heading: True course corrected for wind.
How do you convert course angles to true course?
To convert a compass course into a true course we can use the original equation. If we have steered a compass course of 200°, we have to plot a true course of 203° in the chart if the variation is 3° East , or a true course of 190° if the variation is 10° West .
How do you calculate course headings?
1:063:48How to Calculate Magnetic Heading with Wind Correction Angle FormulaYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo just make sure you get your signs right so if your wing correction angle is negative 5 and yourMoreSo just make sure you get your signs right so if your wing correction angle is negative 5 and your magnetic course is 60. This is gonna be 60 plus a negative 5 okay.
Do pilots use magnetic or true north?
Since the beginning of flight, pilots have been using the magnetic compass for navigation. It doesn't matter if you're flying a Piper Cub or a Boeing 747, you'll find a magnetic compass in the cockpits of almost any aircraft.
What does DTK mean in aviation?
Desired TrackThe Basics. Most GPS navigators present a function called DTK—Desired Track.
What is the formula of true bearing?
(i) True Bearing = (Magnetic Bearing + Declination) = (89°45՛ + 5°30՛) = 95°15՛.
How do you convert true bearing to compass bearing?
3:299:40Conversion between True and Compass Bearings - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's the one in the brown. I want to convert that to a compass bearing. So all I really need to doMoreIt's the one in the brown. I want to convert that to a compass bearing. So all I really need to do here is say well am I in the north or the south will appear I'm certainly in the north.
How do you calculate true bearing and compass bearing?
Procedure for converting compass bearings When converting a compass bearing to a true bearing one must first remove the deviation. This will provide one with a magnetic bearing. By next applying the variation correction one will finally arrive at the true bearing.
What is a true heading?
Definition of true heading : the heading measured clockwise from true north.True heading Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Websterhttps://www.merriam-webster.com › dictionaryhttps://www.merriam-webster.com › dictionary
What is difference between course and heading?
In navigation, the course of a watercraft or aircraft is the cardinal direction in which the craft is to be steered. The course is to be distinguished from the heading, which is the compass direction in which the craft's bow or nose is pointed.Course (navigation) - Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Course_(navigation)https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Course_(navigation)
How does aviation calculate true course?
2:486:18Measuring True Course - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThere is a small hole. The hole is a reference point and we are going to place it over theMoreThere is a small hole. The hole is a reference point and we are going to place it over the intersection of the route and a line of longitude any.Measuring True Course - YouTubehttps://www.youtube.com › watchhttps://www.youtube.com › watch
What is the difference between a track and a heading?
Heading is the direction the airplane is pointed, whereas track is the actual direction of the airplane tracking across the ground. Bearing is the angle between any two points, whereas course is your intended path of travel to your destination. In the rest of this post we’ll elaborate on each of these points and then also provide ...
What is the meaning of heading in airplanes?
By definition though, heading is actually just the direction that the nose is pointed. This does not factor for wind, or the actual movement of the airplane across the ground.
Why do you have to head 080?
Due to wind correction angles you might have to be heading something different than 090 in order to track 090. If you have a northerly wind, you might have to head 080 in order to track along the 090 bearing off of the VOR.
What happens to your bearing when you fly from one airport to another?
If you are going directly from one airport to the other, your course and bearing will be the same along the route of flight. If you are flying from an airport to a VOR to another airport, your course will change in each leg, as will your bearing.
Does GPS RNAV use the same ground track?
However, both methods of navigation should produce the same desired ground track when using approved, IFR navigation system. Should significant differences between the approach chart and the GPS avionics’ application of the navigation database arise, the published approach chart, supplemented by NOTAMs, holds precedence.
Can you be headed north?
So you can be “heading” due north but if you have an incredible wind from the west, you might still be pointed (heading) due north but actually tracking over the ground to the northeast. Magnetic variation and deviation of the compass also impacts what heading you’ll need to be pointed to maintain a given track. Speaking of track, let’s cover that next.
Is "on course heading" a misleading word?
It’s confusing because they are often (incorrectly) used interchangeably in conversation: Heading, bearing, course, and track. Even correctly used by ATC, “on course heading” is still a little misleading because below you’ll see they’re practically referring to “course” and not “heading”.
How to convert from true course to magnetic heading?
1. The correct answer is B. Converting from true course to magnetic heading is a two-step process. The pilot would first subtract left or add right wind correction angle, then subtract easterly or add westerly variation. (Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge, Chapter 15) 2.
When converting a true course to a true heading, what angle to subtract?
When converting a true course to a true heading, subtract a left wind correction angle or add a right wind correction angle. When converting from a true heading to a magnetic heading, add westerly variation or subtract easterly variation. Answer (A) is incorrect because right wind correction is added.
How to switch to real course?
To switch to the real course, we first obtain the magnetic course and then add the magnetic declination to the east or subtract the one to the west. Then the average annual change of the magnetic declination is taken into account (it's multiplied by the number of years and then added or subtracted).
How to convert a true course to a compass?
Conversion of directions from True to Compass courses thus involves two steps: 1. K nowing the true course Tto be followed by the boat, as measured on the chart from the True North, the navigator subtracts the magnetic variation V if it is east (East is Least) or adds it if the Variation is west (West is Best) to obtain M, the Magnetic course.
What is a course heading?
A course, heading or bearing taken from a hand-held compass is a magnetic reading. And when navigating you have to be able to convert magnetic to true. In the conversion between true and magnetic, the variation, as indicated in the compass rose, is added or subtracted depending on whether the variation is east or west.
What is the difference between true and magnetic north?
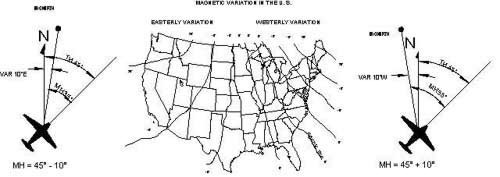
The magnetic compass points to magnetic north. The angular difference between true and magnetic north is known as variation and it changes for different locations on the earth . Variation must be considered when converting true course, true headings, or true winds to magnetic direction.
How many degrees is the declination of the North Pole?
However, the actual declination at that longitude is between 10 and 20 degrees on the equator. In practice, following a compass to the magnetic North Pole will get you there - but not via the shortest route. Converting True North Heading to Compass Heading. All horizontal directions, or azimuths, displayed on timeanddate.com refer to true north.
How to find the true heading of a compass?
To get the true heading, you need to first read the magnetic compass, then either add an Easterly, or subtract a Westerly, magnetic variation; based on the isogonic lines.
Why do we use magnetic and true headings?
The simple reason that we use both true and magnetic headings, is because we have two Norths: true north and magnetic north.
How does a compass work?
Without getting into exactly how a compass works, it’s basically like this: The compass contains certain metals (magnets) that are attracted to metals inside Earth’s crust and thus the magnetic compass orients itself to magnetic north. To find true north, you need to know the nearby variation.
How to find variation on a VFR sectional?
In order to find the variation on a VFR sectional, look for the lines of variation, or isogonic lines. On the sectional look for the dashed magenta lines with a number nearby.
What is magnetic heading?
Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole and geographic north pole being hundreds of miles apart. There are some interesting reasons why these poles are not in ...
What is the difference between true and magnetic directions?
According to the PHAK, “The difference between true and magnetic directions is called variation. This same angular difference in surveying and land navigation is called declination.”
Where is the true north?
Simply put: true north is at the top of the giant sphere we call Earth.
How did Negoro set off course?
Those who read Jules Verne will remember that the cook Negoro had sinister plans for the ship Pilgrim and its 15-year-old captain and deliberately set them off course by place an axe under the compass binnacle. There are a lot of things on a ship that can affect a magnetic compass. To eliminate this effect, there are deviation charts for each compass that show the deviation for various courses. Over time, the deviation may be changed due to the installation of new equipment or the magnetization of the old iron parts, so tables are regularly updated. Using the value of the deviation table, it is possible to bring the compass course to the magnetic course. To do so, the deviation value for this compass course is added to the compass course if it's deviating east, or subtracted if it's deviating west.
What are the factors that influence a compass course?
There are two factors that influence your course ( compass course) from the course you drew on a map ( true course ): Compass readings deviations – magnetic deviation. Discrepancy of magnetic and true poles – magnetic declination. To calculate the compass course by the true course, or vice versa, you should set the values ...
Can you draw a direct line from the point of origin to the point of destination?
However, if you draw a direct line from the point of origin to the point of destination and without deviating a single degree follow the plotted course, you will hardly reach your desired destination, especially if the distance is big. There are two factors that influence your course ( compass course) from the course you drew on a map ...
How to Use an E6B Flight Computer for True and Magnetic Heading – Video Transcript
Today what we’re going to do is learn how to use the E6B to calculate a Magnetic Heading and this comes from a question specific in the FAA knowledge test bank. We’re going to use that example to help us figure out how to use this E6B. So, the question we’re going to use today is this:
How to Use the E6B Flight Computer
So over to the E6B and our first step is to set our wind direction under the true index. Our wind direction from the question was 215˚ and next it’s going to ask us to mark the wind velocity up from the center point. In this case, I have the center point resting on 100. I chose that just because it makes the math easier for me.
Heading
Track
- Track is the easiest of these four to understand in my mind,because it simply refers to how you are actually tracking over the ground. Whennavigating in the air, your track is really all that matters in terms ofgetting to where you want to go. If you need to go northeast to yourdestination, and have a significant wind from the west, your heading might beto the north in order to achieve a tr…
Bearing
- Bearing can be confusing sometimes because has some overlap with course. Bearing is simply the angle or direction between two points. A practical application of this is in VOR navigation. It’s a common thing to hear someone say “we are bearing 090 from the station”. This simply means that off of the VOR they are tracking on the 090 radial outbound from the station. In relation to th…
Course
- Course is very similar to bearing in that it’s the desireddirection for your route of flight. If you are going directly from one airportto the other, your course and bearing will be the same along the route of flight.If you are flying from an airport to a VOR to another airport, your course willchange in each leg, as will your bearing.
Example
- For this example we’re going to work backwards through the above mentioned directions. Assume you are departing an airport and your destination is directly eastbound. When you take off the course between the departing airport and destination airport is 090. In this instance the bearing of the destination airport off of your departing airport is also 090. This is also the direction you wan…
Does A GPS Use True Or Magnetic Heading?
- The above example assumes you are using the compass in yourairplane (hence why it requires so many steps to calibrate the differencebetween your true course all the way down to your actual compass heading). Butwhat about a GPS? By definition it’s not using earth’s magnetic fields as a wayof navigation, but rather positioning information provided by satellites. So ifit shows your “de…
Popular Posts:
- 1. how to get in the canifis agility course
- 2. explain why wind speeds are greatest when the slope of the pressure curve is steepest course hero
- 3. how do you get on the state bar of texas advanced real estate course.
- 4. what ia kaplan course track
- 5. how to enter course title and number
- 6. where can i get a course on nails at home
- 7. how much should you adjust for a golf course home
- 8. which of the following are considered to be key innovations in the course of animal evolution?
- 9. which two cultures merged and influence one another over the course of the early middle ages?
- 10. how to make a dog agility course out of household items for tiny dogs