The U.S. has an ecological footprint of 8.04 gha per capita, one of the highest in the world, with a biocapacity per capita of only 3.45 hectares. This leads to a total ecological deficit of -1.49 billion hectares, a biocapacity reserve of -4.59 gha per capita.
Full Answer
What is the ecological deficit of the United States?
The U.S. has an ecological deficit of -1,416.05. Its ecological footprint per capita is 8.04 hectares and its biocapacity per capita is 3.45 hectares. The average US ecological footprint is about 50% larger than the average person in most European countries.
What is the difference between ecological footprint and biocapacity?
Individuals. Both the Ecological Footprint and biocapacity are expressed in global hectares —globally comparable, standardized hectares with world average productivity. Each city, state or nation’s Ecological Footprint can be compared to its biocapacity. If a population’s Ecological Footprint exceeds the region’s biocapacity,...
What is biocapacity deficit and why does it matter?
If a population’s Ecological Footprint exceeds the region’s biocapacity, that region runs a biocapacity deficit. Its demand for the goods and services that its land and seas can provide—fruits and vegetables, meat, fish, wood, cotton for clothing, and carbon dioxide absorption—exceeds what the region’s ecosystems can regenerate.
What is a biocapacity reserve?
A region in ecological deficit meets demand by importing, liquidating its own ecological assets (such as overfishing), and/or emitting carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. If a region’s biocapacity exceeds its Ecological Footprint, it has a biocapacity reserve.
What percentage of the world's population lives in countries that are running ecological deficits?
What happens when a population's ecological footprint exceeds the region's biocapacity?
How are ecological footprints and biocapacity expressed?
What is ecological footprint accounting?
What is the Global Footprint Network?
What are the areas of biocapacity?
Who created the Ecological Footprint?
See 4 more
About this website
What was the per capita biocapacity deficit in the US in 2010?
Ecological footprint, biocapacity and biocapacity deficit per person, 1961-2014YearEcological footprint per personBiocapacity per person20105.192.1420115.042.1120124.782.0620134.722.1250 more rows
What is a biocapacity deficit of the United States?
A biocapacity deficit occurs when the Footprint of a population exceeds the biocapacity of the area available to that population. Conversely, a biocapacity remainder exists when the biocapacity of a region exceeds its population's Footprint.
What is the biocapacity per capita for the United States?
The U.S. has an ecological footprint of 8.04 gha per capita, one of the highest in the world, with a biocapacity per capita of only 3.45 hectares.
What is the average biocapacity per person?
The world average biocapacity was 1.6 global hectares per person. In contrast, the world average Ecological Footprint was 2.8 global hectares per person.
What is biocapacity biological capacity quizlet?
Biocapacity. The capacity of a given biologically productive area to generate an on-going supply of renewable resources and to absorb its spillover waste.
How is biocapacity calculated?
The amount of biocapacity available per person globally is calculated by dividing the 11.2 billion global hectares of biologically productive area by the number of people on Earth (6.3 billion in 2003). This ratio gives the average amount of biocapacity available on the planet per person - 1.8 global hectares.
What country has the highest biocapacity deficit?
Countries and regionsRankCountry/regionBiocapacity deficit or reserve(gha/person)World-1.121Luxembourg−14.142Aruba−11.3152 more rows
Why does the United States have the largest ecological deficit?
In summary, the U.S. Ecological Footprint is larger than that of other countries because per capita consumption of energy and a wide range of goods of all kinds is greater. Wastes, including carbon dioxide, are greater as well, adding to the relative size of the footprint.
What is the average ecological footprint in the United States?
8.1 gha per personHere's how we calculate that, using the United States as an example: The Ecological Footprint for the United States is 8.1 gha per person (in 2018) and global biocapacity is 1.6 gha per person (in 2018). Therefore, we would need (8.1/ 1.6) = 5.1 Earths if everyone lived like Americans.
What are the top 4 countries for total biocapacity per person?
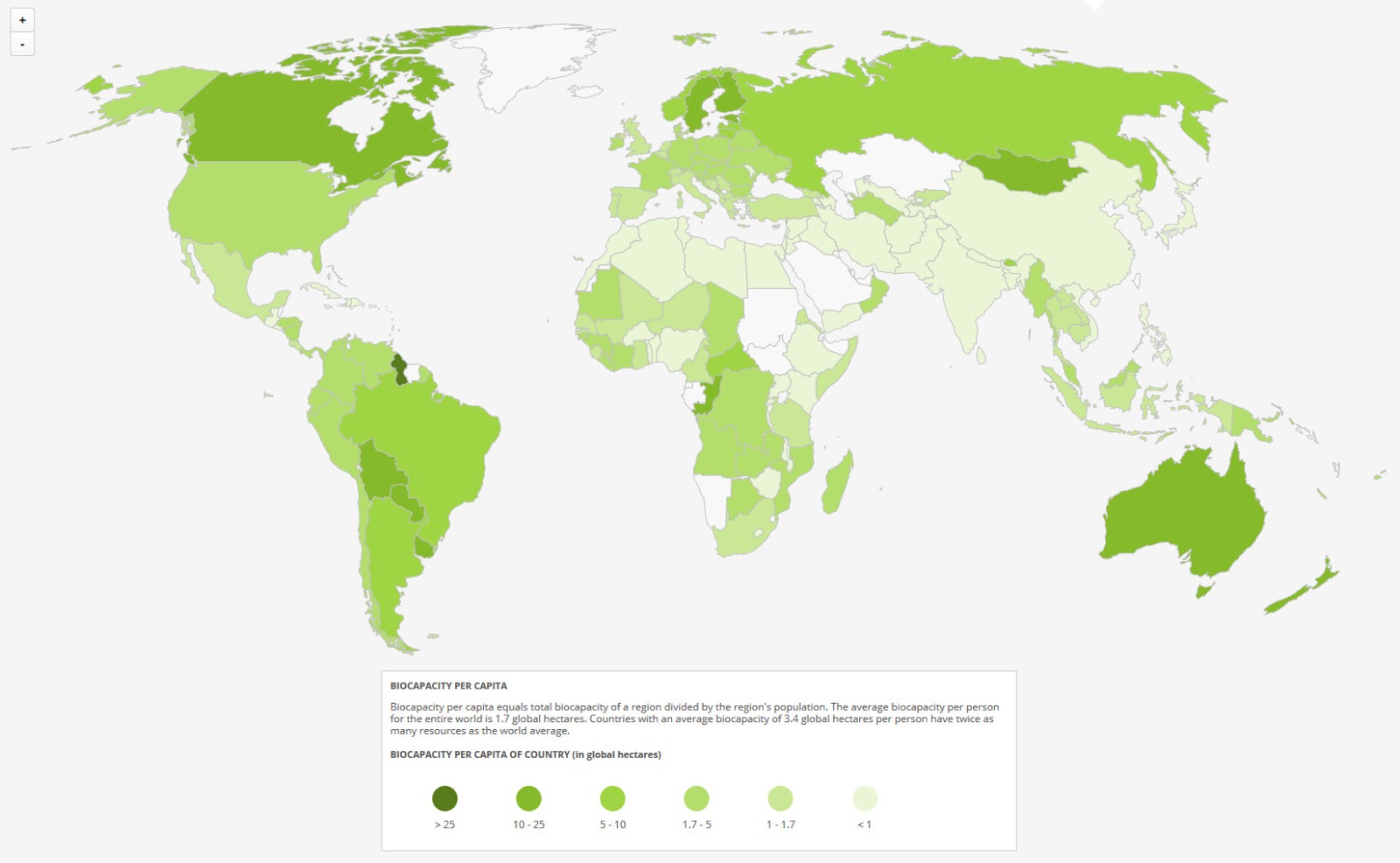
COUNTRIES WITH BIOCAPACITY RESERVEFrench Guiana4,810%Suriname2,520%Guyana2,030%Gabon869%Congo754%Uruguay641%Central African Republic524%Bolivia358%More items...
What are the top 3 countries for total biocapacity?
The top five countries with a positive biocapacity reserve are led by Finland (with 6.37 global hectares per capita), followed by Sweden (with 3.9 global hectares per capita), Norway, and the Baltic countries.
What does the term biocapacity mean?
biological capacity or biocapacity. The capacity of ecosystems to regenerate what people demand from those surfaces. Life, including human life, competes for space. The biocapacity of a particular surface represents its ability to regenerate what people demand.
Why does the US have a large ecological deficit?
An ecological deficit is possible because states can import goods, overuse their resources (for instance by overfishing and overharvesting forests), and emit more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than can be absorbed by their own forests. Alaska, South Dakota, and Montana have the greatest ecological reserves.
Why does the United States have the largest ecological deficit?
In summary, the U.S. Ecological Footprint is larger than that of other countries because per capita consumption of energy and a wide range of goods of all kinds is greater. Wastes, including carbon dioxide, are greater as well, adding to the relative size of the footprint.
Which country has highest biocapacity?
Countries and regionsRankCountry/regionPopulation (millions) for biocapacity to equal ecological footprint*World25001Luxembourg0.0552212Aruba0.00479853 more rows
What is biocapacity in simple terms?
biological capacity or biocapacity. The capacity of ecosystems to regenerate what people demand from those surfaces. Life, including human life, competes for space. The biocapacity of a particular surface represents its ability to regenerate what people demand.
List of countries by ecological footprint - Wikipedia
This is a list of countries by ecological footprint.The table is based on data spanning from 1961 to 2013 from the Global Footprint Network's National Footprint Accounts published in 2016. Numbers are given in global hectares per capita. The world-average ecological footprint in 2016 was 2.75 global hectares per person (22.6 billion in total).
Ecological Footprint: What Is It and How to Calculate It - Ecobnb
When was it introduced? British Columbia University professor William Rees first mentioned this term, together with his then student Mathis Wackernagel, founder and current president of the Global Footprint Network (sounds familiar?).In 1996, they published a book titled Our Ecological Footprint: Reducing Human Impact on the Earth, in which they introduced this new notion.
What is biocapacity
The Biocapacity, or biological capacity , is the term used to define the availability of biologically productive area within a given territory.
Biocapacity and ecological footprint
We have already defined the term biocapacity in the previous section, now let’s talk about the definition of the ecological footprint in order to distinguish between the two concepts easily. It is a biophysical indicator of sustainability in which different impacts of human communities on their environment are considered.
Biocapacity: examples
In this last section we will see some examples of the value of biocapacity per capita (hectares / inhabitants) of different countries in the world, to analyze in an illustrative way, the consumption that different countries make of their available natural resources within their total surfaces.
Which state has the least biocapacity?
The states with the least biocapacity are Rhode Island, Delaware, and Arizona. California, Texas, and Florida have the highest ecological deficits. Alaska, South Dakota, and Montana have the greatest ecological reserves.
When is Ecological Deficit Day?
In 2015, the Ecological Deficit Day of the United States landed on July 14, according to our new report, “State of the States: A New Perspective on the Wealth of Our Nation,” co-authored by Earth Economics.
Which state has the smallest ecological footprint?
The states with the smallest per-person Ecological Footprints are New York, Idaho, and Arkansas. Alaska, Texas, and Michigan are the most resource-abundant states based on biocapacity, a measure of bioproductive land. The states with the least biocapacity are Rhode Island, Delaware, and Arizona.
What percentage of the world's population lives in countries that are running ecological deficits?
Today, more than 80 percent of the world’s population lives in countries that are running ecological deficits, using more resources than what their ecosystems can regenerate. How does your country compare? Visit our Ecological Footprint Explorer open data platform to find the answer.
What happens when a population's ecological footprint exceeds the region's biocapacity?
If a population’s Ecological Footprint exceeds the region’s biocapacity, that region runs a biocapacity deficit. Its demand for the goods and services that its land and seas can provide—fruits and vegetables, meat, fish, wood, cotton for clothing, and carbon dioxide absorption—exceeds what the region’s ecosystems can regenerate.
How are ecological footprints and biocapacity expressed?
Both the Ecological Footprint and biocapacity are expressed in global hectares —global ly comparable, standardized hectares with world average productivity.
What is ecological footprint accounting?
Ecological Footprint accounting measures the demand on and supply of nature. On the demand side, the Ecological Footprint adds up all the productive areas for which a population, a person or a product competes. It measures the ecological assets that a given population or product requires to produce the natural resources it consumes ...
What is the Global Footprint Network?
Together with York University, Toronto, Global Footprint Network has established an independent organization, Footprint Data Foundation (FoDaFo), to be the steward of the National Footprint and Biocapacity Accounts. This organization independently owns and produces the Accounts, with the goal to provide them with highest reliability, so they can inform public and private decision-making in an unbiased way. It also has the ambition to build a coalition of countries, supported by a rigorous global academic network, to advance its work.
What are the areas of biocapacity?
Typically these areas are: cropland, grazing land, fishing grounds, built-up land, forest area, and carbon demand on land. On the supply side, a city, state or nation’s biocapacity represents the productivity of its ecological assets (including cropland, grazing land, forest land, fishing grounds, and built-up land).
Who created the Ecological Footprint?
Conceived in 1990 by Mathis Wackernagel and William Rees at the University of British Columbia, the Ecological Footprint launched the broader Footprint movement, including the carbon Footprint, and is now widely used by scientists, businesses, governments, individuals, and institutions working to monitor ecological resource use ...
How big is the ecological deficit in the US?
United States. The U.S. has an ecological deficit of -1,416.05. Its ecological footprint per capita is 8.04 hectares and its biocapacity per capita is 3.45 hectares. The average US ecological footprint is about 50% larger than the average person in most European countries.
What happens if a population's ecological footprint exceeds its biocapacity?
If a given population’s ecological footprint exceeds its biocapacity, that population has an ecological deficit. This means that the population’s demand for natural resources exceeds its supply, which can lead to depletion and high emissions of carbon dioxide into the air. If a given population’s biocapacity exceeds its ecological footprint, ...
What is biocapacity in ecology?
Biocapacity is the capacity of a given biologically productive area to generate a supply of renewable resources and to absorb its wastes. The ecological footprint and biocapacity are expressed in global hectares. Global hectares are comparable and standardized with world average productivity.
How much is India's ecological footprint?
India’s ecological footprint per capita is 1.19 and its biocapacity per capita is 0.43 hectares. India’s total ecological deficit is -878.05 hectares. India represents about 6% of the world’s ecological footprint. India, like China, has a population of over 1 billion people. While India’s ecological footprint is relatively low, its biocapacity is much lower, leading to its large deficit.
What is biocapacity in ecological footprint?
Biocapacity is the capacity of a given biologically productive area to generate a supply of renewable resources and to absorb its wastes.
What is Japan's ecological deficit?
Japan’s ecological deficit is -547.18 hectares, the fourth-highest in the world. A majority of Japan’s ecological footprint is made up of Japan’s carbon footprint. If everyone lived based on the Japanese standard of living, we would require the equivalent of 2.3 Earths to support the world population. 5. United Kingdom.
What is the ecological footprint of a country?
The ecological footprint is a metric that measures human demand on natural capital or the quantity of nature it takes to support a given population or economy. The ecological footprint is the demand on and the supply of nature.
Why is GDP the best measure of economic growth?
Change in per capita real gross domestic product (GDP) is the best measure of economic growth because: it adjusts changes in nominal GDP for changes in the price level and population growth.
How much did Poland's GDP grow in 2010?
From 2006 to 2010, per capita real gross domestic product (GDP) in Poland grew an average of 4.71% per year. At that rate, according to the Rule of 70, in roughly how many years will the Polish economy double in size?
What was the GDP of Canada in 2011?
Given that Canada's population was roughly 33.4 million people, per capita GDP in Canada in 2011 was roughly: $41,796. Access to lifesaving medicine is very limited in parts of Africa; as a result, over 10% of children do not reach the age of five.
Is Liberia a poor country?
Liberia, a very poor nation in West Africa, is relatively abundant in resources such as mahogany and rubber tree forests, iron-ore deposits, and diamonds. If Liberia is so rich in valuable resources, why is it still so impoverished?
Is there evidence of catching up with the poor?
there is no evidence of catching up by the poor countries or of the slowing down of growth in the wealthy countries.
Who created economic growth theory?
a boost in population growth. Economic growth theory originated about 60 years ago as a result of contributions by: Robert Solow. Consider a country that suffered through five years of civil war, but now has a stable government that has the support of the majority of the people.
Does Liberia have the institutions to make productive use of resources?
Liberia lacks the institutions necessary to make productive use of those resources.
Popular Posts:
- 1. how will this course help you in the future
- 2. who advocated research on the actions the mind performs, rather than the ideas it has course hero
- 3. which of the following is a true statement about closing the books of a proprietorship? course hero
- 4. how to change senior course college ap ux
- 5. how to build a drone course
- 6. how to lower your car insurance defensive driving course
- 7. his tax preferences total $51,000. what is chuck’s amti for 2016? course hero
- 8. how to appeal for driving course in va without court
- 9. what is an oral disclosure course albany
- 10. how to drop a course in udemy