Definition of Positive Externality: This occurs when the consumption or production of a good causes a benefit to a third party. For example: When you consume education you get a private benefit.
Full Answer
What are the benefits of positive externalities?
Positive Externalities 1 With positive externalities, the benefit to society is greater than your personal benefit. 2 Therefore with a positive externality the Social Benefit > Private Benefit 3 Remember Social Benefit = private benefit + external benefit.
How do you teach the principle of positive externalities?
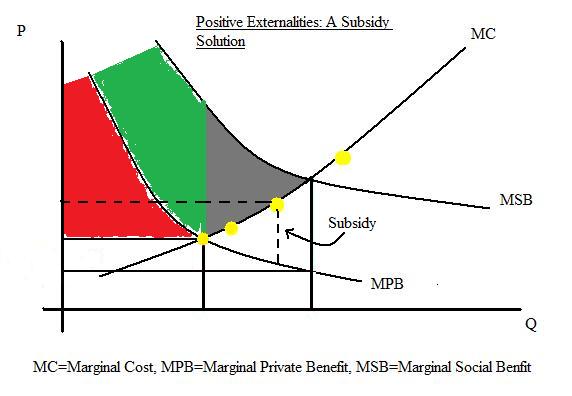
Either (production or consumption externality) is acceptable to show the principle of positive externalities. Generally, I advise using the positive externalities of consumption. To simply economics for some students (who often get confused by these diagrams), I will only teach one positive externality diagram.
What is a positive production externality?
In a positive production externality situation, the producing company's action gives a benefit to another party, but the company does not receive any form of compensation for this occurrence and the party receiving the benefit doesn't solicit it.
What is a positive consumption externality?
In a positive consumption externality, an individual's or entity's consumption benefits another party, and they also do not receive compensation for their role in providing the benefit. There are two types of positive externalities: production and consumption. Here are some details about both of them:
When there is a positive externalities benefit?
A positive externality exists when a benefit spills over to a third-party. Government can discourage negative externalities by taxing goods and services that generate spillover costs. Government can encourage positive externalities by subsidizing goods and services that generate spillover benefits.
What's an example of a positive externality?
Positive externalities occur when a third party benefits at no direct cost. For example, there are hundreds of shops in the mall, but the average consumer doesn't go to see them all. Instead, they go to a few specific shops that they want to buy from.
What is the positive externality of education?
One example of a positive externality is the market for education. The more education a person receives, the greater the social benefit since more educated people tend to be more enterprising, meaning they bring greater economic value to their community.
What is a benefit of externality?
A positive externality (also called "external benefit" or "external economy" or "beneficial externality") is the positive effect an activity imposes on an unrelated third party. Similar to a negative externality, it can arise either on the production side, or on the consumption side.
What is positive externality quizlet?
Positive externalities. a benefit obtained without compensation by third parties from the production or consumption of sellers or buyers. Example: A beekeeper benefits when a neighboring farmer plants clover. An external benefit or a spillover benefit. Cost benefit analysis.
What is an example of a positive externality quizlet?
consumers will consume the good at a level at which their individual marginal benefits exceed the marginal costs borne by the firm producing the good. the cost borne by a third party not involved in the trade is not reflected in the market price. The best example of a positive externality is: roller coaster rides.
What are the benefits of education?
10 Benefits Showing Why Education Is Important to Our SocietyCreating More Employment Opportunities. ... Securing a Higher Income. ... Developing Problem-solving Skills. ... Improving the Economy. ... Providing a Prosperous and Happy Life. ... Giving Back to the Community. ... Creating Modern Society. ... Bridging the Borders.More items...
Is education a positive externality of consumption to production?
A positive externality is a benefit of producing or consuming a product. For example, education is a positive externality of school because people learn and develop skills for careers and their lives. In comparison, negative externalities are a cost of production or consumption.
What are the indirect benefits of education?
INDIRECT CONTRIBUTIONS OF EDUCATION TO DEVELOPMENT Some of these spillover benefits include: Reduced need for other services, e.g. increased investment in education will tend to reduce the necessity of placing more public revenue into health, welfare, and penal system.
How do you find the positive externality?
Positive ExternalitiesThe market surplus at Q1 is equal to total private benefits – total private costs, in this case b. [(b+c) – (c)].The social surplus at Q1 is equal to total social benefits – total social costs, in this case a+b. ... The market surplus at Q2 is equal to b-f. ... The social surplus at Q2 is equal to a+b+d.
How do positive externalities affect demand curves?
A positive externality increases the social benefits of economic activity, so an adjusted demand/benefit curve would lie farther left on the diagram, reflecting a lower social price at each quantity.
How do positive externalities lead to market failure?
Externalities lead to market failure because a product or service's price equilibrium does not accurately reflect the true costs and benefits of that product or service.
What is an example of a positive and negative externality?
For example, education is a positive externality of school because people learn and develop skills for careers and their lives. In comparison, negative externalities are a cost of production or consumption. For example, pollution is a negative externality that results from both producing and consuming certain products.
What are some examples of externalities?
Some examples of negative consumption externalities are:Passive smoking: Smoking results in negative effects not only on the health of a smoker but on the health of other people.Traffic congestion: The more people that use cars on roads, the heavier the traffic congestion becomes.
Why is the social marginal cost of production less than the private marginal cost of production?
Because there are positive externalities in production, the social marginal cost of production is less than the private marginal cost of production. In a free market, a firm will ignore benefits to third parties and will produce at Q1 (free market outcome)
Why is consumption at Q1 socially inefficient?
In a free market, consumption will be at Q1 because demand = supply (private benefit = private cost ) However, this is socially inefficient because at Q1, social marginal cost < social marginal benefit. Therefore there is under-consumption of the positive externality.
What happens when you consume education?
When you consume education you get a private benefit. But there are also benefits to the rest of society. E.g you are able to educate other people and therefore they benefit as a result of your education. (positive consumption externality) A farmer who grows apple trees provides a benefit to a beekeeper.
Popular Posts:
- 1. 1) how could you use a wiki to collaborate with fellow students to improve this course?
- 2. who did lilly play in ice age: collision course
- 3. apush who does not belong review course hero
- 4. what does course mean in high school
- 5. rocket league how to do obstacle course multiplayer
- 6. how do i reset a course on sololearn?
- 7. how to make course available on canvas
- 8. which of the following limb movements occur during "jumping jacks"? course heor
- 9. what course is app res methods for cont issues in california
- 10. how high to start first course of siding