The diaphragm is a thin skeletal muscle that sits at the base of the chest and separates the abdomen from the chest. It contracts and flattens when you inhale. This creates a vacuum effect that pulls air into the lungs. When you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes and the air is pushed out of lungs.
Full Answer
What happens if the diaphragm does not develop as it should?
When you inhale your rib cage expands and moves your When you inhale, your rib cage expands and moves your diaphragm downward. This decreases the pressure around the lungs and draws air into your respiratory tract. This type of ventilation is known as active breathing. When you exhale, your rib cage contracts and moves your diaphragm upward.
What is the diaphragm?
Inhale slowly through the mouth while breathing deeply from the diaphragm o Hold breath for 2-3 seconds o Forcefully exhale quickly as if one is fogging up a mirror with one’s breath o Repeat the “huff” one or two more times while refraining from a “regular” cough o Cough when mucus is felt in the breathing tubes o Rest for 5-10 regular breaths o Repeat the huffs until you feel you have …
What are the 3 openings of the diaphragm?
View Test Prep - unit 4 part 4 from BIOL 100 at Coastline Community College. 22. When the diaphragm contracts, the thoracic cavity _, and you _. gets …
What happens when the diaphragm relaxes?
Inhaling and Exhaling Aspen University BIO 202 What is the process of inhaling and exhaling? When you inhale (breathe in), air enters your lungs and oxygen from the air moves from your lungs to your blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste gas, moves from your blood to the lungs and is exhaled (breathe out). This process is called gas exchange and is essential to life.
When you inhale the diaphragm moves upward or downward?
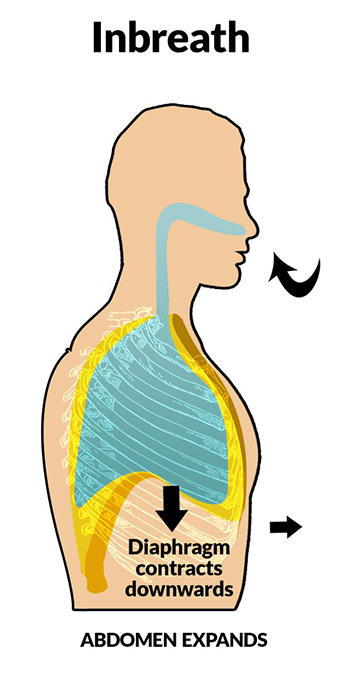
downwardWhen the lungs inhale, the diaphragm contracts and pulls downward. At the same time, the muscles between the ribs contract and pull upward. This increases the size of the thoracic cavity and decreases the pressure inside.
What happens to your diaphragm when you exhale?
When you breathe in, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and flattens, moving down towards your abdomen. This movement creates a vacuum in your chest, allowing your chest to expand (get bigger) and pull in air. When you breathe out, your diaphragm relaxes and curves back up as your lungs push the air out.
When you inhale the ribs move inward or outward?
up and outwardDuring inhalation, the ribs move up and outward and the diaphragm moves in. this movement decrease the space in our chest cavity and the air rushes in. During exhalation, the ribs moves down and inward and the diaphragm moves up. This movement increases the space in our chest cavity and the air is pushed out.
When you inhale there is now more space in the chest area?
When the chest cavity expands there is more space around your lungs. In this condition the lungs can expand, making it a low-pressure area, and air rushes in to balance out the difference in pressure. Then to breathe out the chest cavity and lungs shrink.
What is the function of diaphragm?
The diaphragm is a thin skeletal muscle that sits at the base of the chest and separates the abdomen from the chest. It contracts and flattens when you inhale. This creates a vacuum effect that pulls air into the lungs. When you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes and the air is pushed out of lungs.
What diaphragm means?
diaphragm, dome-shaped, muscular and membranous structure that separates the thoracic (chest) and abdominal cavities in mammals; it is the principal muscle of respiration.
How do ribs and diaphragm move while inhalation and exhalation?
During inhalation, the ribs move up and outward and the diaphragm moves in. this movement decrease the space in our chest cavity and the air rushes in. During exhalation, the ribs moves down and inward and the diaphragm moves up. This movement increases the space in our chest cavity and the air is pushed out.
What happens to the ribs when you inhale?
To breathe in (inhale), you use the muscles of your rib cage – especially the major muscle, the diaphragm. Your diaphragm tightens and flattens, allowing you to suck air into your lungs. To breathe out (exhale), your diaphragm and rib cage muscles relax.
What happens when you inhale exhale?
When you inhale (breathe in), air enters your lungs, and oxygen from that air moves to your blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste gas, moves from your blood to the lungs and is exhaled (breathed out). This process, called gas exchange, is essential to life.
What is a diaphragm Class 7?
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle underneath the lungs. When it contracts, oxygen rich air is pulled inside the lungs and when it relaxes, carbon dioxide is pumped out from the lungs.
What happens to the diaphragm when a person breathes in or inhales Brainly?
On inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, while the chest cavity expands. Explanation: The diaphragm, which is placed beneath the lungs, is the main respiratory muscle.
What is the role of diaphragm in respiration Class 10?
The diaphragm helps in the inspiration and expiration of air in and out of the lungs. At the time of inspiration, the diaphragm contracts, increasing the pulmonary volume thereby reducing the intrapulmonary pressure to less than the atmospheric pressure and air moves into the lungs.
Why does the diaphragm move down?
In order to move down, the diaphragm must contract, and this increases the space in the lungs, allowing more air to come in. This is why, when the diaphragm contracts, it moves dune. Add To Playlist. Add to Existing Playlist.
Which muscle controls inspiration?
the diaphragm is the major muscle that controls inspiration. It sits underneath both of the lungs, and when you breathe in bringing air into the lungs, the diaphragm is moving down. In order to move down, the diaphragm must contract, and this increases the space in the lungs, allowing more air to come in.
What happens when the diaphragm is activated?
When the diaphragm is activated by a nerve, it contracts and flattens. This action decreases pressure and increases the space in the thoracic cavity, allowing your lungs to expand as you inhale. When the diaphragm relaxes, your chest cavity becomes smaller and your lungs release air. 2
What is the diaphragm?
Anatomy. The diaphragm is a parachute-shaped fibrous muscle that runs between the chest and abdomen, separating these two large cavities. It is asymmetric, as the right dome is larger than the left dome. The diaphragm has openings that allow certain structures to span the chest and abdominal cavities.
Is the diaphragm asymmetric?
It is asymmetric, as the right dome is larger than the left dome. The diaphragm has openings that allow certain structures to span the chest and abdominal cavities. As it moves rhythmically, the diaphragm remains anchored to the ribs, sternum (breastbone), and the spine.
What are the three openings in the diaphragm?
There are three large openings (holes) through the diaphragm: The esophageal opening (esophageal hiatus), through which the esophagus, right and left vagus nerves, and left gastric artery and vein pass. The aortic opening (aortic hiatus), through which the aorta, thoracic duct, and azygous vein pass.
Where is the diaphragm located?
Location. The diaphragm spans across the body from the front to the back. It is the floor of the thoracic cavity and the ceiling of the abdominal cavity. 2 . Your heart, lungs, and the upper part of your esophagus (food pipe) are in the thoracic cavity above the diaphragm.
What is the function of the diaphragm?
Function. The diaphragm plays an integral role in respiration (breathing). Most of the time, the diaphragm moves involuntarily. Your thoracic diaphragm also plays a role in helping the movement of muscles during childbirth, having a bowel movement, urinating, and lifting heavy objects.
What causes the diaphragm to move?
There are several medical conditions that involve the thoracic diaphragm. Traumatic injuries or anatomical defects can interfere with the muscle's function, and the movement of the diaphragm can also be impaired by issues like nerve disease or cancer.
Popular Posts:
- 1. which of the following best describes the long-term course of obsessive–compulsive disorder?
- 2. what size is an md5 message digest (hash) course hero
- 3. of course maggie haperin why the left nytimes
- 4. which of the following is an activity of proactive problem management course hero
- 5. where tornadoes occured geo2242 course hero
- 6. which is considered the hybrid model for improvement methodologies course hero
- 7. where is fiddlers golf course
- 8. the measure of how much we understood and learned in a college course is referred to as:
- 9. rasa malaysia chapel hill what comes with main course
- 10. what happens when you drop a course in college u of m