What happens when the oxidation number of an atom is increased?
Jul 26, 2021 · When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a reaction, that atom is being _____. When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a reaction, that atom is being _____. A) synthesized B) neutralized C) oxidized D) decomposed E) reduced. Categories Questions.
What is oxidation and reduction in chemistry?
Nov 22, 2021 · When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being reduced. Which process increases oxidation number? We can identify redox reactions using oxidation numbers, which are assigned to atoms in molecules by assuming that all bonds to the atoms are ionic. An increase in oxidation number during a reaction …
How do you determine what is oxidized and reduced?
At least two elements must change their oxidation numbers. When an oxidation number of an atom is increased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being oxidized. When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being reduced. Thus oxidation and reduction can also be defined in terms of increasing or decreasing …
What is the difference between oxidized and reduced in photosynthesis?
When an oxidation number of an atom is increased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being oxidized. When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being reduced. Oxidation and reduction are thus also defined in terms of increasing or decreasing oxidation numbers, respectively.
What happens to atoms in an oxidation-reduction reaction?
An atom's increase in oxidation state through a chemical reaction is called oxidation, and it involves a loss of electrons; an decrease in an atom's oxidation state is called reduction, and it involves the gain of electrons.
Does the oxidation number increase or decrease for a substance that is oxidized?
Use the oxidation number rules to assign oxidation numbers to each atom in the balanced equation. Coefficients do not affect oxidation numbers. The oxidized atom increases in oxidation number and the reduced atom decreases in oxidation number. Step 2: Solve.Feb 21, 2022
What happens to the oxidizing agent in an oxidation-reduction reaction?
The additional terminology comes from the definition that, within redox processes, a reductant transfers electrons to an oxidant; hence, the reductant (reducing agent) loses electrons, so is oxidized, while the oxidant (oxidizing agent) gains electrons, so is reduced.
What is it called when an atom loses an electron oxidation?
The gain of electrons is called reduction. … As such, electron-transfer reactions are also called oxidation-reduction reactions, or simply redox reactions. The atom that loses electrons is oxidized, and the atom that gains electrons is reduced.Dec 8, 2021
What happens to the oxidation number of an atom that is oxidized?
A loss of negatively-charged electrons corresponds to an increase in oxidation number, while a gain of electrons corresponds to a decrease in oxidation number. Therefore, the element or ion that is oxidized undergoes an increase in oxidation number.Sep 6, 2013
What happens to the oxidation number of an element during oxidation?
In oxidation oxidation number increases. Reduction: Addition of Hydrogen or removal of Oxygen or gain of electron or charge decreases is called reduction. In reduction oxidation number decreases.Dec 18, 2019
What happens to the oxidizing agent in an oxidation-reduction reaction Mcq?
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor or oxidizing agent in cellular respiration. The reducing agent or reductant undergoes oxidation and oxidising agent or oxidant undergoes reduction.
Which is oxidizing agent and reducing agent?
An oxidizing agent (oxidant), gains electrons and is reduced in a chemical reaction. It is also known as electron acceptor. The oxidizing agent is usually in one of its higher possible oxidation states as it will gain electrons and be reduced.Mar 5, 2021
How do you identify the oxidizing and reducing agents in a reaction?
Break the reaction down into a net ionic equation and then into half-reactions. The substance that loses electrons is being oxidized and is the reducing agent. The substance that gains electrons is being reduced and is the oxidizing agent.Apr 23, 2019
What happens to the oxidation number when it loses electrons?
When the number of electrons associated with an atom changes, its oxidation number also changes. When an element loses an electron, its oxidation number increases.Apr 24, 2017
What forms when an atom loses an electron?
Explanation: An atom loses electrons to form a cation , that is a positively charged ion (and one that is attracted towards the negatively charged terminal, the cathode ).Oct 17, 2016
Why is it called reduction?
In the early days of chemistry, oxidation was defined as a gain of oxygen atoms, and reduction was a loss of oxygen atoms. The Hg was said to be reduced because it lost an oxygen atom.May 24, 2015
Which atoms have oxidation numbers of 0?
Consider the reactants. Because both reactants are the elemental forms of their atoms, the Na and Cl atoms as reactants have oxidation numbers of 0. In the ionic product, the sodium ions have an oxidation number of +1, while the chloride ions have an oxidation number of −1:
What is the oxidation number?
oxidation number. to keep track of electrons in atoms. Oxidation numbers are assigned to atoms based on a series of rules. Oxidation numbers are not necessarily equal to the charge on the atom; we must keep the concepts of charge and oxidation numbers separate.
What is the oxidation number of hydrogen peroxide?
By contrast, by rule 3 in hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ), each hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1, while each oxygen atom has an oxidation number of −1. We can use rule 4 to determine oxidation numbers for the atoms in SO 2.
How do redox reactions occur?
All redox reactions occur with a simultaneous change in the oxidation numbers of some atoms. At least two elements must change their oxidation numbers. When an oxidation number of an atom is increased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being oxidized. When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being reduced. Oxidation and reduction are thus also defined in terms of increasing or decreasing oxidation numbers, respectively.
What is the loss of one or more electrons by an atom?
The loss of one or more electrons by an atom; an increase in oxidation number. The gain of one or more electrons by an atom; a decrease in oxidation number. A chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons. A number assigned to an atom that helps keep track of the number of electrons on the atom.
How many oxygens are there in the universe?
Oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of −2, and there are three oxygens. According to rule 4, the sum of the oxidation number on all atoms must equal the charge on the species, so we have the simple algebraic equation , where is the oxidation number of the nitrogen atom and −1 represents the charge on the species.
What are the two parts of barium nitrate?
The compound barium nitrate can be separated into two parts: the Ba 2+ ion and the nitrate ion. Considering these separately, the Ba 2+ ion has an oxidation number of +2 by rule 2. Now consider the NO 3− ion. Oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of −2, and there are three oxygens.
How are oxidation numbers assigned to atoms?
Oxidation numbers are assigned to atoms based on four rules. Oxidation numbers are not necessarily equal to the charge on the atom (although sometimes they can be); we must keep the concepts of charge and oxidation numbers separate. The rules for assigning oxidation numbers to atoms are as follows:
What is the purpose of oxidation numbers?
Oxidation numbers are used to keep track of electrons in atoms. There are rules for assigning oxidation numbers to atoms. Oxidation is an increase in oxidation number (loss of electrons); reduction is a decrease in oxidation number (gain of electrons).
What happens when a redox reaction occurs?
All redox reactions occur with a simultaneous change in the oxidation numbers of some atoms. At least two elements must change their oxidation numbers. When an oxidation number of an atom is increased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being oxidized.
What is the oxidation number of oxygen?
By rule 3, oxygen is normally assigned an oxidation number of −2. For the sum of the oxidation numbers to equal the charge on the species (zero), the Ge atom is assigned an oxidation number of +4. Ca (NO 3) 2 can be separated into two parts: the Ca 2+ ion and the NO 3− ion.
What is the term for the gain of one or more electrons by an atom?
Reduction is defined as the gain of one or more electrons by an atom. So oxidation and reduction always occur together; it is only mentally that we can separate them. Chemical reactions that involve the transfer of electrons are called oxidation-reduction (or redox) reactions.
What is the product of reactants?
The reactants are two electrically neutral elements; they have the same number of electrons as protons. The product, however, is ionic; it is composed of Mg 2+ and Cl − ions. Somehow, the individual Mg atoms lose two electrons to make the Mg 2+ ion, while the Cl atoms gain an electron to become Cl − ions. This reaction involves the transfer of ...
Does iron affect taste?
One reason is that fine iron filings do not affect the taste of the product. The size of the iron powder (several dozen micrometers) is not noticeable when chewing iron-supplemented foods, and the tongue does not detect any changes in flavour that can be detected when using Fe 2+ salts.
What happens when an oxidation number is decreased in the course of a redox reaction?
When an oxidation number of an atom is increased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being oxidized. When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being reduced .
What does oxidation number mean?
Oxidation numbers represent the potential charge of an atom in its ionic state. If an atom’s oxidation number decreases in a reaction, it is reduced. If an atom’s oxidation number increases, it is oxidized .
What happens to water during photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, water gets oxidized to oxygen (O2). …. Each redox reaction has an oxidation half and a reduction half. NADP+ getting reduced to NADPH is the reduction half and water giving rise to oxygen is the oxidation half.
What is the photo part of photosynthesis?
The photo part of photosynthesis involves the oxidation of the oxygen from water. Each O atom loses two electrons, so the oxygen in water is oxidized. Here, the NADH gives up its electrons and reduces the carbon in carbon dioxide.
What is the NADP oxidized form?
NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) exists in two forms: NADP + is the oxidized form and NADPH is the reduced form.
What is the energy used in photosystem II?
In the photosystem II (PSII) reaction center, energy from sunlight is used to extract electrons from water. The electrons travel through the chloroplast electron transport chain to photosystem I (PSI), which reduces NADP+ to NADPH. The electron transport chain moves protons across the thylakoid membrane into the lumen.
What is the process of oxidizing sugars into water?
Photosynthesis involves the reduction of carbon dioxide into sugars and the oxidation of water into molecular oxygen. The reverse reaction, respiration, oxidizes sugars to produce carbon dioxide and water .
What is being oxidized in cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is an oxidative process whereby an electron donor is oxidized and oxygen is reduced to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy [3].
What becomes oxidized in the cellular respiration summary?
The overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration converts one six-carbon molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water. … So the carbons in the glucose become oxidized, and the oxygens become reduced .
Which molecule is oxidized during cellular respiration?
During the process of glycolysis in cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. Energy released during the reaction is captured by the energy-carrying molecule ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What is being oxidized?
When an oxidation number of an atom is increased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being oxidized. When an oxidation number of an atom is decreased in the course of a redox reaction, that atom is being reduced.
What is oxidized and reduced in photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
During aerobic respiration, the oxygen taken in by a cell combines with glucose to produce energy in the form of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and the cell expels carbon dioxide and water. This is an oxidation reaction in which glucose is oxidized and oxygen is reduced .
What type of reaction is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction. This means it cannot occur without energy (from the Sun). The light required is absorbed by a green pigment called chlorophyll in the leaves.
What is oxidation in photosynthesis?
Water is oxidized in photosynthesis, which means it loses electrons, and carbon dioxide is reduced, meaning it gains electrons.
Chemistry
Any help would be greatly appreciated! Substances A, B, and C can all act as oxidizing agents. In solution, A is green, B is yellow, and C is red. In the reactions in which they participate, they are reduced to A-, B-, and C-
Chemistry
7. 2Sr + O2 2SrO a) Determine what is oxidized and what is reduced b) Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent 8. 2Cs + Br2 2CsBr a) Determine what is oxidized and what is reduced b) Identify the oxidizing agent
chemistry
Identify the species oxidized, the species reduced, the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent in the following electron transfer reaction. 2Fe3+ + Sn2Fe2+ + Sn2+ species oxidized species reduced oxidizing agent reducing agent As
chemistry
Magnesium reacts with iron (II) chloride according to the equation Mg (s) + FeCl2 (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + Fe (s) a. Is magnesium oxidized or is it reduced? Magnesium is reduced. b. Is iron (II) ion oxidized or is it reduced? Iron (II) ion
Chemistry
Assign oxidation numbers for the following chemical equation: 2Al + 3H2SO4 ---> Al2 (SO4)3 +3 H2 What was oxidized? What was reduced? My answer: Oxidation numbers going from the left side of the chemical eq to the right side.. Al:
chemistry- electrochemical cell
What makes this an oxidation-reaction? 3Ag2S+2Al (s) -> Al2S3+6 Ag (s)? Write the half-reactions showing the oxidation and reduction reactions. Identify which is the oxidation reaction and which is the reduction reason. What is
AP Chemistry
A 5.0 M solution of HNO3 is titrated with 0.3 M NaOH. Identify the species that have the highest concenttrations in the solution being titrated halfway to the equivalence point. A 25.15 ml of 0.35 m HNO3 was titrated with an
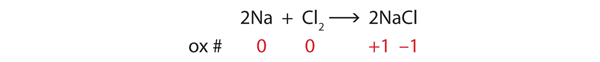
Popular Posts:
- 1. what are the estimation models used in cocomo ii.? course hero
- 2. how to download a book from course point
- 3. where was the clubhouse in oak valley nj was a golf course
- 4. how do i get my internachi course completion certificate
- 5. what is bmlt course
- 6. how to find mario maker course ids
- 7. how to change course in utep
- 8. professor who taught me a course
- 9. how close is osuth lake tahos golf course to hard rock hotel
- 10. of course i do, why do you think i had you arrested? movie ljne