Treatment Which treatments are most likely to help you depends on your particular situation, including the location of your cancer, its stage and your other health concerns. Treatment for colon cancer usually involves surgery to remove the cancer. Other treatments, such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy, might also be recommended.
What is the treatment for colon cancer?
Treatment for colon cancer is based largely on the stage (extent) of the cancer, but other factors can also be important. People with colon cancers that have not spread to distant sites usually have surgery as the main or first treatment. Chemotherapy may also be used after surgery (called adjuvant treatment). Most adjuvant treatment is given for about 6 months.
What is the best treatment for Stage 4 colon cancer?
Feb 22, 2022 · There are different types of treatment for patients with colon cancer. Seven types of standard treatment are used: Surgery; Radiofrequency ablation; Cryosurgery; Chemotherapy; Radiation therapy; Targeted therapy; Immunotherapy; New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials. Treatment for colon cancer may cause side effects.
What is colorectal cancer?
Based on your treatment options, you might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. These doctors could include: A gastroenterologist: a doctor who treats disorders of the gastrointestinal (GI or digestive) tract A surgical oncologist (oncologic surgeon): a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer A colorectal surgeon: a doctor who uses surgery to treat diseases …
How do you treat Stage 0 colon cancer?
What are the treatment options for Stage 4 colon cancer? Chemotherapy – At this stage, chemotherapy is almost always the first step. Typically, chemotherapy is given before any surgeries if there are too many masses. If the cancer has spread too far to make surgery a viable option, chemo is the main treatment.
What is the course of colon cancer?
In general, colon cancer begins when healthy cells in the colon develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains a set of instructions that tell a cell what to do. Healthy cells grow and divide in an orderly way to keep your body functioning normally.Jun 11, 2021
Which type of treatment is most common for colorectal cancer?
Surgery. Surgery is the removal of the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue during an operation. It is often called surgical resection. This is the most common treatment for colorectal cancer.
At what stage of colon cancer is chemotherapy used?
In stage I colon cancer, surgery to remove the tumor is the only treatment needed. Stage III tumors, which are tumors that have spread to the lymph nodes, are treated with surgery followed by chemotherapy (called adjuvant chemotherapy; it is given after surgery to reduce the risk of a recurrence of the cancer).Aug 11, 2021
How long does it take to treat colorectal cancer?
People with colon cancers that have not spread to distant sites usually have surgery as the main or first treatment. Chemotherapy may also be used after surgery (called adjuvant treatment). Most adjuvant treatment is given for about 6 months.Jun 29, 2020
Can colon cancer be treated with medicine?
Colorectal cancer can also be treated using drugs, which can be given by mouth or directly into the bloodstream. These are called systemic treatments because they can reach cancer cells throughout almost all the body.
Is colon cancer curable at Stage 3?
A stage III colon cancer has about a 40 percent chance of cure and a patient with a stage IV tumor has only a 10 percent chance of a cure. Chemotherapy is used after surgery in many colon cancers which are stage II, III, and IV as it has been shown that it increases the survival rates.
How long does a course of chemo last?
A course of chemotherapy usually takes between 3 to 6 months, although it can be more or less than that. The treatment will include one or more chemotherapy drugs. You may have the chemotherapy into a vein (intravenous drugs), or as tablets or capsules.
Can colon cancer Stage 1 be cured?
Stage I colon cancer is confined to the lining of the colon, does not penetrate the wall of the colon into the abdominal cavity, and has not spread to any adjacent organs or local lymph nodes. Approximately 90% of patients are cured with surgery alone and will not experience a cancer recurrence. 3.
Can colon cancer be cured if caught early?
“Overall, colorectal cancer is highly preventable, and if detected early, it's also one of the most curable types of cancer,” Dr. Lipman notes. Up to 85% of colorectal cancers could be prevented or successfully treated if everyone who is eligible for a colonoscopy got screened.Aug 18, 2021
Where does colon cancer spread first?
While colon cancer can travel throughout the body, there are specific areas where it is more likely to spread. The most common include the liver and lungs, as well as the brain, distant lymph nodes and peritoneum (membrane that lines the abdominal cavity).
Does colon cancer return after surgery?
For most people, colorectal cancer doesn't come back, or “recur.” But in about 35% to 40% of people who get surgery with or without chemotherapy, the cancer may come back within 3 to 5 years of treatment. If this happens, it could be in the colon or rectum, or in another part of the body, such as the liver and lungs.Jan 20, 2021
Can colon cancer come back after 5 years?
ANSWER: The rate of colorectal cancer survival five years after initial diagnosis has been on the rise. But with survival comes a new risk — that of recurrence. Colorectal cancer recurrence within five years after treatment ends is in the range of 7 to 42 percent, depending on the stage of the cancer.Mar 12, 2019
Treating Stage 0 Colon Cancer
Since stage 0 colon cancers have not grown beyond the inner lining of the colon, surgery to take out the cancer is often the only treatment needed....
Treating Stage I Colon Cancer
Stage I colon cancers have grown deeper into the layers of the colon wall, but they have not spread outside the colon wall itself or into the nearb...
Treating Stage II Colon Cancer
Many stage II colon cancers have grown through the wall of the colon, and maybe into nearby tissue, but they have not spread to the lymph nodes.Sur...
Treating Stage III Colon Cancer
Stage III colon cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but they have not yet spread to other parts of the body.Surgery to remove the section of...
Treating Stage IV Colon Cancer
Stage IV colon cancers have spread from the colon to distant organs and tissues. Colon cancer most often spreads to the liver, but it can also spre...
Treating Recurrent Colon Cancer
Recurrent cancer means that the cancer has come back after treatment. The recurrence may be local (near the area of the initial tumor), or it may b...
What tests are needed for colon cancer?
Staging helps determine what treatments are most appropriate for you. Staging tests may include imaging procedures such as abdominal, pelvic and chest CT scans.
How does chemotherapy help with colon cancer?
Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy for colon cancer is usually given after surgery if the cancer is larger or has spread to the lymph nodes. In this way, chemotherapy may kill any cancer cells that remain in the body and help reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
What is the procedure to check for colon cancer?
Colonoscopy. During a colonoscopy , the doctor inserts a colonoscope into your rectum to check for abnormalities in your entire colon. If your signs and symptoms indicate that you could have colon cancer, your doctor may recommend one or more tests and procedures, including:
What is a colonoscopy tube?
Colonoscopy uses a long, flexible and slender tube attached to a video camera and monitor to view your entire colon and rectum. If any suspicious areas are found, your doctor can pass surgical tools through the tube to take tissue samples (biopsies) for analysis and remove polyps. Blood tests.
Is a stoma permanent?
A stoma is usually temporary, but is sometimes permanent. If the cancer has grown into or through your colon, your surgeon may recommend: Partial colectomy. During this procedure, the surgeon removes the part of your colon that contains the cancer, along with a margin of normal tissue on either side of the cancer.
What is the earliest stage of colon cancer?
At its earliest stage (stage 0), colon cancer is limited to the inner lining of your colon. As colon cancer progresses, it can grow through your colon and extend to nearby structures. The most advanced stage of colon cancer (stage IV) indicates cancer has spread to other areas of the body, such as the liver or lungs.
Can colon cancer be treated with surgery?
If your cancer is very advanced or your overall health very poor, your surgeon may recommend an operation to relieve a blockage of your colon or other conditions in order to improve your symptoms. This surgery isn't done to cure cancer, but instead to relieve signs and symptoms, such as a blockage, bleeding or pain.
What is colon cancer?
Key Points. Colon cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the colon. Health history affects the risk of developing colon cancer. Signs of colon cancer include blood in the stool or a change in bowel habits. Tests that examine the colon and rectum are used to diagnose colon cancer.
What are the risk factors for colon cancer?
Risk factors for colorectal cancer include the following: Having a family history of colon or rectal cancer in a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child). Having a personal history of cancer of the colon, rectum, or ovary.
Why do we do clinical trials?
Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
How do you know if you have colon cancer?
Signs of colon cancer include blood in the stool or a change in bowel habits. These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by colon cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following: A change in bowel habits. Blood (either bright red or very dark) in the stool.
Where does cancer go in the body?
The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor ( metastatic tumor) in another part of the body. Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor ( metastatic tumor) in another part of the body .
How many lymph nodes does cancer spread to?
Cancer has spread to one to three nearby lymph nodes or cancer cells have formed in tissue near the lymph nodes; or. through the mucosa (innermost layer) of the colon wall to the submucosa (layer of tissue next to the mucosa). Cancer has spread to four to six nearby lymph nodes. Enlarge.
Where are abnormal cells found in the colon?
Abnormal cells are shown in the mucosa of the colon wall. In stage 0, abnormal cells are found in the mucosa (innermost layer) of the colon wall. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
How is colorectal cancer treated?
Colorectal cancer can also be treated using drugs, which can be given by mouth or directly into the bloodstream. These are called systemic treatments because they can reach cancer cells throughout almost all the body. Depending on the type of colorectal cancer, different types of drugs might be used, such as: Chemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer.
What kind of doctor treats colorectal cancer?
These doctors could include: A gastroenterologist: a doctor who treats disorders of the gastrointestinal (GI or digestive) tract. A surgical oncologist (oncologic surgeon): a doctor who uses surgery to treat cancer.
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with radiation therapy. A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with medicines such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, psychologists, ...
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone. If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, ...
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
How long does it take to get rid of colon cancer?
But usually, Stage 2 colon cancer takes anywhere from three to nine months to treat. And again, more frequent colon cancer screenings may be recommended in the future.
Why is colon cancer staging important?
Colon cancer staging is crucial because it gives cancer care teams – which include surgeons, oncologists, pathologists, radiologists and others – an agreed upon way to talk about the condition. By staging the cancer, care teams can more easily understand diagnoses and collaborate on treatment plans.
What is CT scan for colon cancer?
If cancer is detected, a CT scan is ordered to look for any distant metastasis and local invasion to the other organs. With the initial pathology reports from your colonoscopy and the CT scan results in hand, staging begins –and it’s time to meet with a colorectal surgeon.
How long do people with cancer live?
For instance, if the cancer has a five-year relative survival rate of 71%, people who have the same cancer type and stage are about 71% as likely to live at least five years after diagnosis as people who don’t have that cancer.
Where does colon cancer spread?
But it can also spread to your lungs, brain, the lining of the abdominal cavity, or other distant lymph nodes. Similar to other stages, Stage 4 colon cancer has three classification types: Stage 4A – The cancer has spread to one distant organ or a distant set of lymph nodes.
What does grade mean in cancer?
In some cases, doctors also use “Grade” (G) to describe how the cancer cells compare to healthy cells. The lower the grade, the more the cancer cells look like healthy cells.
Can you have chemotherapy after surgery?
While chemotherapy is often used after surgery, it might be needed prior to surgery based on the characteristics of your cancer, its location and your overall health status. Radiation – Radiation is used very rarely for colon cancer, but may be recommended in combination with chemotherapy or if surgery isn’t an option.
How to reduce the risk of colon cancer?
Take steps to: Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Fruits, vegetables and whole grains contain vitamins, minerals, fiber and antioxidants, which may play a role in cancer prevention.
How to prevent colon cancer?
You can take steps to reduce your risk of colon cancer by making changes in your everyday life. Take steps to: 1 Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Fruits, vegetables and whole grains contain vitamins, minerals, fiber and antioxidants, which may play a role in cancer prevention. Choose a variety of fruits and vegetables so that you get an array of vitamins and nutrients. 2 Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all. If you choose to drink alcohol, limit the amount of alcohol you drink to no more than one drink a day for women and two for men. 3 Stop smoking. Talk to your doctor about ways to quit that may work for you. 4 Exercise most days of the week. Try to get at least 30 minutes of exercise on most days. If you've been inactive, start slowly and build up gradually to 30 minutes. Also, talk to your doctor before starting any exercise program. 5 Maintain a healthy weight. If you are at a healthy weight, work to maintain your weight by combining a healthy diet with daily exercise. If you need to lose weight, ask your doctor about healthy ways to achieve your goal. Aim to lose weight slowly by increasing the amount of exercise you get and reducing the number of calories you eat.
What is the final part of the digestive tract?
The colon is the final part of the digestive tract. Colon cancer typically affects older adults, though it can happen at any age. It usually begins as small, noncancerous (benign) clumps of cells called polyps that form on the inside of the colon. Over time some of these polyps can become colon cancers.
What does it feel like to have colon cancer?
A feeling that your bowel doesn't empty completely. Weakness or fatigue. Unexplained weight loss. Many people with colon cancer experience no symptoms in the early stages of the disease. When symptoms appear, they'll likely vary, depending on the cancer's size and location in your large intestine.
Can colon polyps turn into cancer?
Over time some of these polyps can become colon cancers. Polyps may be small and produce few, if any, symptoms. For this reason, doctors recommend regular screening tests to help prevent colon cancer by identifying and removing polyps before they turn into cancer.
What are the risk factors for colon cancer?
Risk factors. Factors that may increase your risk of colon cancer include: Older age. Colon cancer can be diagnosed at any age, but a majority of people with colon cancer are older than 50. The rates of colon cancer in people younger than 50 have been increasing, but doctors aren't sure why. African-American race.
Do African Americans have colon cancer?
African-American race. African-Americans have a greater risk of colon cancer than do people of other races. A personal history of colorectal cancer or polyps. If you've already had colon cancer or noncancerous colon polyps, you have a greater risk of colon cancer in the future.
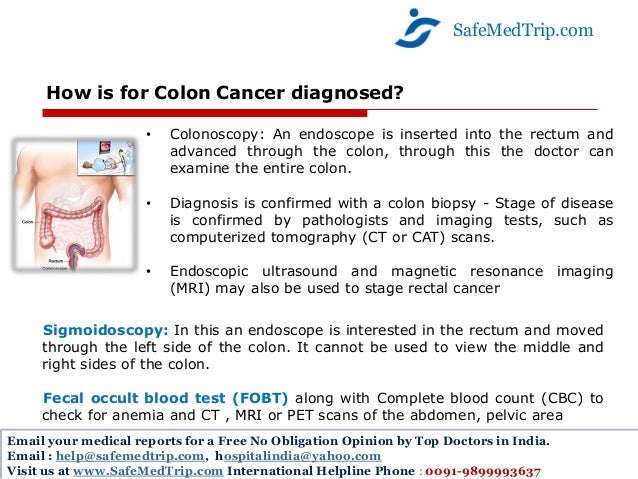
Diagnosis
- Screening for colon cancer
Doctors recommend certain screening tests for healthy people with no signs or symptoms in order to look for signs of colon cancer or noncancerous colon polyps. Finding colon cancer at its earliest stage provides the greatest chance for a cure. Screening has been shown to reduce you… - Diagnosing colon cancer
If your signs and symptoms indicate that you could have colon cancer, your doctor may recommend one or more tests and procedures, including: 1. Using a scope to examine the inside of your colon (colonoscopy).Colonoscopy uses a long, flexible and slender tube attached to a vi…
Treatment
- Which treatments are most likely to help you depends on your particular situation, including the location of your cancer, its stage and your other health concerns. Treatment for colon cancer usually involves surgery to remove the cancer. Other treatments, such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy, might also be recommended.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- A cancer diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. In time, people learn to cope in their own unique ways. Until you find what works for you, you might try to: 1. Learn enough about your cancer to feel comfortable making treatment decisions.Ask your doctor to tell you the type and stage of your cancer, as well as your treatment options and their side effects. The more you kno…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If your doctor suspects you may have colon cancer, you'll likely be referred to specialists who treat colon cancer. You may meet with a number of specialists, including a: 1. Doctor who treats digestive diseases (gastroenterologist) 2. Doctor who uses medications to treat cancer (oncologist) 3. Doctor who removes colon cancer using surgery (surgeon) 4. Doctor who uses ra…
Popular Posts:
- 1. where to take the approved dc fair housing course
- 2. how many days has trump been at a golf course since he became president?
- 3. concerning the armenian genicide, which statement is true course hero
- 4. how to drop an online course valencia
- 5. what to write type of course is high school
- 6. on course what makes a succesful studne
- 7. what is a capstone course in criminal justice
- 8. where does "hope is not a course of action" come from
- 9. how to speak spanish online course
- 10. what skills have you developed during eng225 course,and how might