What is the lower course of a river called?
Lower course features In the lower course, the river has a high volume and a large discharge. The river channel is now deep and wide and the landscape around it is flat.
What happens in the lower course of a river?
Oct 13, 2019 · The Lower Course is where the river flows gently because of its gentle slope, and also it looks like a lake habitat. This winding lowland parts of a river contain muddy, slightly warmer water, which flows more slowly. Plants grow in the bed of the river and at its edges. It also contains a deposition.
What are the characteristics of an upper course river?
What is the middle course of a river?
What is upper course and lower course of a river?
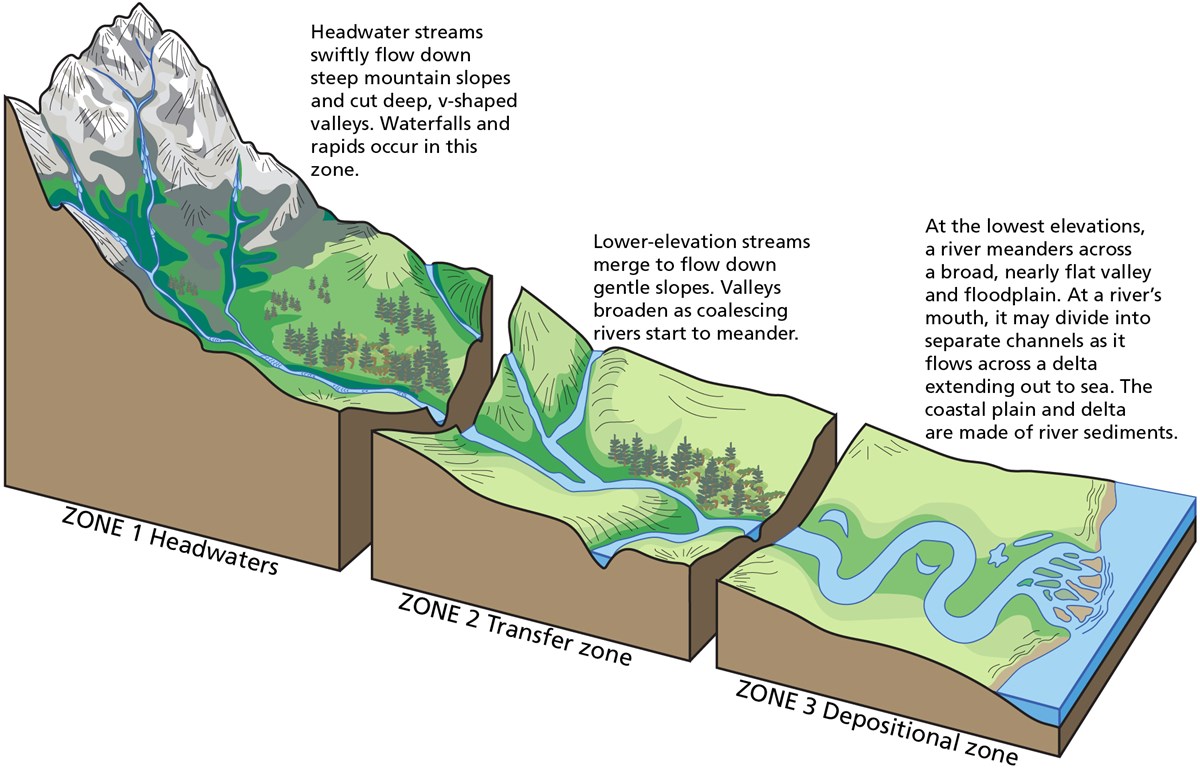
If we look into the whole length of a river we will notice that it has three definite courses: 1. The Upper or Mountain Course 2. The Middle or Plain Course 3. The Lower or Deltaic Course.
What is the course of a river?
Upper course river features include steep-sided V-shaped valleys, interlocking spurs, rapids, waterfalls and gorges. Middle course river features include wider, shallower valleys, meanders, and oxbow lakes. Lower course river features include wide flat-bottomed valleys, floodplains and deltas.
What is the lower course of a river ks2?
The lower course is the furthest from the source. The source of a river is in the mountains or tops of hills, when rain and or snow collects in valleys and flows down the sides of the 'v' shaped hills. Upper Course Features: Deep 'v' shaped valleys, waterfalls, interlocking spurs.Jun 26, 2021
Is the upper course of a river shallow?
Upper course - this is where the river starts and is usually an upland area. Slopes are steep - this can increase the velocity of the river after heavy rainfall, when discharge is high. The river channel is narrow and shallow here.
Why is the volume of water in a river at its greatest in the lower course?
The volume of water in a river is at its greatest in the lower course. This is due to the contribution of water from tributaries. The river channel is deep and wide and the land around the river is flat. Energy in the river is at its lowest and deposition occurs.
What is the area over which rivers flood?
Rivers flood on a regular basis. The area over which they flood is known as the floodplain, and this often coincides with regions where meanders form. Meanders support the formation of floodplains through lateral (sideways) erosion. When rivers flood the velocity of water slows.
When a river floods more substantial material and the majority of deposition occurs next to the river channel?
When a river floods more substantial material and the majority of deposition occurs next to the river channel as the result of increased friction (with the flood plain ). The velocity of the river slows and therefore rapidly reduce its ability to transport material. This leaves a ridge of higher material next to the river channel on both banks of the river known as a levee.
What is the estuary of a river?
An estuary is a wide, sheltered body of water found at a river’s mouth where it broadens into the sea. It is a combination of salt water from the sea and fresh water from a river. As the river meets the sea at high tide, it slows the flow of water leading to deposition. Mudflats and saltmarsh form in these areas. The mudflats can be seen at low tide but are covered by water at high tide. Over time, the mud flats can become colonised with vegetation forming salt marshes.
Where are deltas found?
Deltas are often found at the mouth of large rivers. An example is the Nile Delta. Deltas are formed when a river deposits material faster than the sea can erode it.
Popular Posts:
- 1. over most of the twentieth century, which of the following was greater?course hero
- 2. what is historical studies course
- 3. where to study course rbt hialeah
- 4. how send out an email to everyone in your canvas course
- 5. what road in nicholl noll golf course on
- 6. where can i get the course file for a tywin gw1 golf trainer?
- 7. which of the following best exemplifies the difference between a profit and revenue? course hero
- 8. where is summit golf course
- 9. why wont penn foster let me start my next course
- 10. which of the following are concepts taught in a managerial accounting course?