The Hydrologic Cycle (also called the Water Cycle) is the continuous movement of water in the air on the surface of and below the Earth. This cycle is the exchange of energy which influences climate. When water condenses it releases energy and warms the environment. What is the hydrologic cycle and how does it work?
Full Answer
What is the hydrologic cycle?
The hydrologic cycle involves the continuous circulation of water in the Earth-Atmosphere system. At its core, the water cycle is the motion of the water from the ground to the atmosphere and back again.
What is hydrologic cycle is there a beginning and or end in the cycle Why?
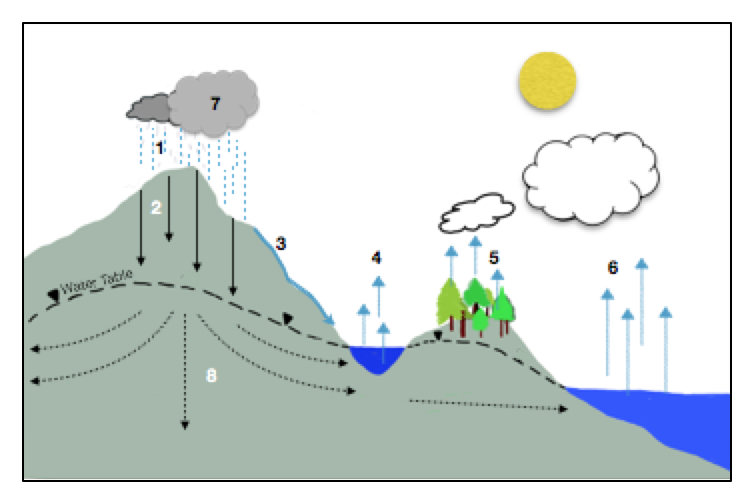
The movement of water around Earth's surface is the hydrologic (water) cycle (figure 3). Figure 3. Because it is a cycle, the water cycle has no beginning and no end.
Is there an end of hydrologic cycle?
The water cycle (also called the hydrologic cycle) is the continuous movement and storage of water across the earth in all forms: liquid, solid (ice) and gas (water vapor). There is no start or end to the water cycle, but for explanation purposes we will start at the sun.
What are the subsystems on the hydrologic cycle?
Precipitation, evaporation, freezing and melting and condensation are all part of the hydrological cycle - a never-ending global process of water circulation from clouds to land, to the ocean, and back to the clouds.
What is the most important benefit of hydrological cycle?
Importance of hydrological cycle: It enables the availability of water for all living organisms and regulates weather patterns on our planet. As water undergoes infiltration, the ground purifies it of pollutants and contaminants. The water cycle continually feeds freshwater to all life on the planet.
What is hydrological cycle explain with the help of a diagram?
The water cycle is defined as a natural process of constantly recycling the water in the atmosphere. It is also known as the hydrological cycle or the hydrologic cycle. During the process of the water cycle between the earth and the atmosphere, water changes into three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas.
What are the 7 steps of the hydrologic cycle?
A fundamental characteristic of the hydrologic cycle is that it has no beginning an it has no end. It can be studied by starting at any of the following processes: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, interception, infiltration, percolation, transpiration, runoff, and storage.
What are the importance of the water cycle?
The water cycle is an extremely important process because it enables the availability of water for all living organisms and regulates weather patterns on our planet. If water didn't naturally recycle itself, we would run out of clean water, which is essential to life.
What is hydrologic cycle PDF?
The hydrological cycle is the system which describes the distribution and movement of water between the earth and its atmosphere. The model involves the continual circulation of water between the oceans, the atmosphere, vegetation and land.
What is the main energy source for the hydrologic cycle?
The sunThe sun provides energy which drives the water cycle on Earth.
How can hydrologic cycle be affected?
Climate change intensifies this cycle because as air temperatures increase, more water evaporates into the air. Warmer air can hold more water vapor, which can lead to more intense rainstorms, causing major problems like extreme flooding in coastal communities around the world.
What is hydrogen cycle and how does it work?
The hydrologic cycle begins with the evaporation of water from the surface of the ocean. As moist air is lifted, it cools and water vapor condenses to form clouds. Moisture is transported around the globe until it returns to the surface as precipitation.
Which hydrologic process should come first in the hydrologic cycle?
evaporation ofThe hydrologic cycle begins with the evaporation of water from the surface of the ocean. As moist air is lifted, it cools and water vapor condenses to form clouds.
What are the 7 steps of the hydrologic cycle?
A fundamental characteristic of the hydrologic cycle is that it has no beginning an it has no end. It can be studied by starting at any of the following processes: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, interception, infiltration, percolation, transpiration, runoff, and storage.
What is the hydrological cycle Class 7?
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the continuous movement of water from the earth's surface to the atmosphere and then back to the ground. It is a continuous process.
What is hydrologic cycle quizlet?
hydrologic cycle (water cycle) The cycle through which water in the hydrosphere moves; includes such processes as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and surface and groundwater runoff and infiltration.
What is the water cycle?
The water cycle describes how water is exchanged (cycled) through Earth's land, ocean, and atmosphere. Water always exists in all three places, and in many forms—as lakes and rivers, glaciers and ice sheets, oceans and seas, underground aquifers, and vapor in the air and clouds.
What are the three major processes of the water cycle?
The water cycle consists of three major processes: evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
What is the process of a gas changing to a liquid?
Condensation is the process of a gas changing to a liquid. In the water cycle, water vapor in the atmosphere condenses and becomes liquid. Condensation can happen high in the atmosphere or at ground level. Clouds form as water vapor condenses, or becomes more concentrated (dense).
How does the water cycle affect the Earth's physical features?
The water cycle also influences the physical geography of the Earth. Glacial melt and erosion caused by water are two of the ways the water cycle helps create Earth's physical features.
What is the process of water evaporation?
The water cycle's evaporation process is driven by the sun. As the sun interacts with liquid water on the surface of the ocean, the water becomes an invisible gas (water vapor). Evaporation is also influenced by wind , temperature, and the density of the body of water.
How were the Great Lakes created?
The Great Lakes were created as an enormous ice sheet melted and retreated , leaving liquid pools. The process of erosion and the movement of runoff also create varied landscapes across the Earth's surface. Erosion is the process by which earth is worn away by liquid water, wind, or ice.
How does the water cycle affect the climate?
Climate is all the weather conditions of an area, evaluated over a period of time. Two weather conditions that contribute to climate include humidity and temperature.
What is the water cycle?
The water, or hydrologic, cycle describes the pilgrimage of water as water molecules make their way from the Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back again, in some cases to below the surface. This gigantic system, powered by energy from the Sun, is a continuous exchange of moisture between the oceans, the atmosphere, and the land.
How do cloud droplets produce precipitation?
Cloud droplets can grow and produce precipitation (including rain, snow, sleet, freezing rain, and hail ), which is the primary mechanism for transporting water from the atmosphere back to the Earth’s surface. When precipitation falls over the land surface, it follows various routes in its subsequent paths. Some of it evaporates, returning ...
What causes the gradual shrinking of snow banks in cases when the temperature remains below freezing?
The gradual shrinking of snow banks in cases when the temperature remains below freezing results from sublimation. Together, evaporation, transpiration, and sublimation , plus volcanic emissions, account for almost all the water vapor in the atmosphere that isn’t inserted through human activities. While evaporation from the oceans is ...
How does water enter the atmosphere?
In addition, a very small portion of water vapor enters the atmosphere through sublimation, the process by which water changes directly from a solid (ice or snow) to a gas.
What happens when precipitation falls over the land surface?
When precipitation falls over the land surface, it follows various routes in its subsequent paths. Some of it evaporates, returning to the atmosphere; some seeps into the ground as soil moisture or groundwater; and some runs off into rivers and streams.
How does water vapor move from the atmosphere to the surface?
After the water enters the lower atmosphere , rising air currents carry it upward, often high into the atmosphere, where the air is cooler. In the cool air, water vapor is more likely to condense from a gas to a liquid to form cloud droplets. Cloud droplets can grow and produce precipitation (including rain, snow, sleet, freezing rain, and hail ), which is the primary mechanism for transporting water from the atmosphere back to the Earth’s surface.
What is the hydrologic cycle?
Definition of the Hydrologic Cycle. The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, defines the movement and storage of water through Earth. Water on Earth is constantly moving and changing states. Water can be found all around the globe and is constantly on the move.
What is the largest movement of water in the water cycle?
The largest movement of water in the water cycle is the evaporation of water from the oceans. Evaporation - occurs as water turns to vapor and enters the atmosphere. Condensation - occurs as gaseous water turns to liquid. Precipitation - more commonly known as rain.
What is the movement of water over the ground?
Runoff - is the movement of surface water over the ground. Infiltration - occurs as water enters the ground to become groundwater. Sublimation - is more commonly known as snow. Melting - occurs as temperatures increase and solid water transforms to liquid. Groundwater flow - is the movement of water below the surface.
What is reservoir water?
A reservoir stores water for a period of time and can include the atmosphere, the oceans, lakes, rivers, soils, glaciers, snowfields, and groundwater. Water travels through the hydrologic cycle in various forms of movement, such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, infiltration, sublimation, melting, and groundwater flow. ...
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
How much water is stored in glaciers?
Only 3% of water is fresh water available for drinking, and of that 3%, almost 69% is trapped in glaciers or underground. A reservoir stores water for a period of time. Not all reservoirs hold water for the same amount of time. Glaciers, for example, can keep water trapped as ice for thousands of years. The atmosphere, on the other hand, keeps ...
What is runoff in water?
Runoff - is the movement of surface water over the ground.
Popular Posts:
- 1. course hero, he release of which chemical mediator causes primary dysmenorrhea?
- 2. course hero which of the following statements are true about the boltzmann factor
- 3. which is the best course at pinehurst
- 4. how lin is a ged course
- 5. what would be the best high school course pathway for accounting undergraduate
- 6. how to get the ap course certification
- 7. where to take emt basic course
- 8. what are reef golf course
- 9. how has entertainment influenced the course of history
- 10. where is bay hill golf course pga