What is 5.14.1 plant mixture?
What is 5.9.1?
What is the job standard mix?
What is Clause 1.3?
How thick is a porous friction course?
What are the unique characteristics of military aircraft?
Does Y.7.1 mean BS EN ISO 9000?
See 2 more
What is porous friction course runway?
An alternative to grooving as a means of facilitating surface water dispersal is the laying of a Porous Friction Course (PFC) which allows water to pass vertically through the surface layer and then move horizontally clear of the runway beneath, but essentially parallel to the surface.
What is Permeable Friction Course?
Permeable Friction Courses (PFC) are open-graded bituminous mixtures placed over an impervious base. The interconnected air voids allow rainwater to drain into the pavement thus providing a safer driving surface in wet weather and a filter for highway runoff.
What is the purpose of a friction course in an asphalt pavement design?
Their macrotexture facilitates drainage of water from the tire/pavement interface, improving tire contact with the pavement and reducing the potential for hydroplaning.
What is porous mix?
Porous asphalt mixtures easily allow the access of water; these mixtures are highly permeable such that water can quickly pass water through them.
What is friction course?
Open graded friction courses (OGFCs) are a type of pavement that have been built across the United States since the 1950's. These asphalt mixes contain only a small portion of fine aggregate, creating a pavement with a relatively large percentage of air voids.
What is gap graded asphalt?
The gap graded asphalt mixtures are the mixtures in which the aggregate particles of certain sizes are partially missing. The gap graded asphalt mixtures will have higher air-voids when compared to dense graded asphalt mixtures.
What is open graded asphalt?
Open Graded Asphalt (OGA) is a porous asphalt material that produces a highly textured surface. It provides a safer wet weather surfacing by reducing the amount of surface water leading to improved visibility and skid resistance. It also generates lower tyre noise compared to other bituminous surfacings.
What is OGFC asphalt?
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) has been used since 1950 in different parts of the United States to improve the surface frictional resistance of asphalt pavements. OGFC improves wet weather driving conditions by allowing the water to drain through its porous structure away from the roadway.
How long does porous asphalt last?
twenty yearsPorous asphalt pavement can last up to twenty years before showing cracks or potholes. It is a very durable product and it retains the ability to handle rainwater for many years. Porous asphalt has been used successfully in parking lots, walkways, playgrounds and high-volume highways that carry heavy trucks.
How are porous roads made?
Porous asphalt pavements are constructed in the form of an underlying, open-graded stone bed that provides drainage for the water. As the water drains through the porous asphalt and into the stone bed, it slowly infiltrates into the soil.
Why is porous asphalt used?
PURPOSE: Porous asphalt used in place of traditional impervious paving materials decreases the total amount of runoff leaving a site, promotes infiltration of runoff into the ground, reduces the amount of pollutants carried to a storm drain or waterway, and aids with reducing peak runoff velocity and volume.
Does asphalt have friction?
Actually the fundamental mechanism of the tire-asphalt pavement friction is very complex [4] and there are many impact factors affecting the friction performance, including the tire type, pavement structure characteristics, pavement material characteristics, aggregate gradation, wet and dry condition, vehicle speed [5] ...
In which circumstances rigid pavement will be recommended over the flexible pavement?
In case of areas where soil subgrade is weak (like clay) and drainage conditions are also difficult to maintain at desired level of performance (like in urban areas or in situations where road passes through habitation), rigid pavement can be a good choice.
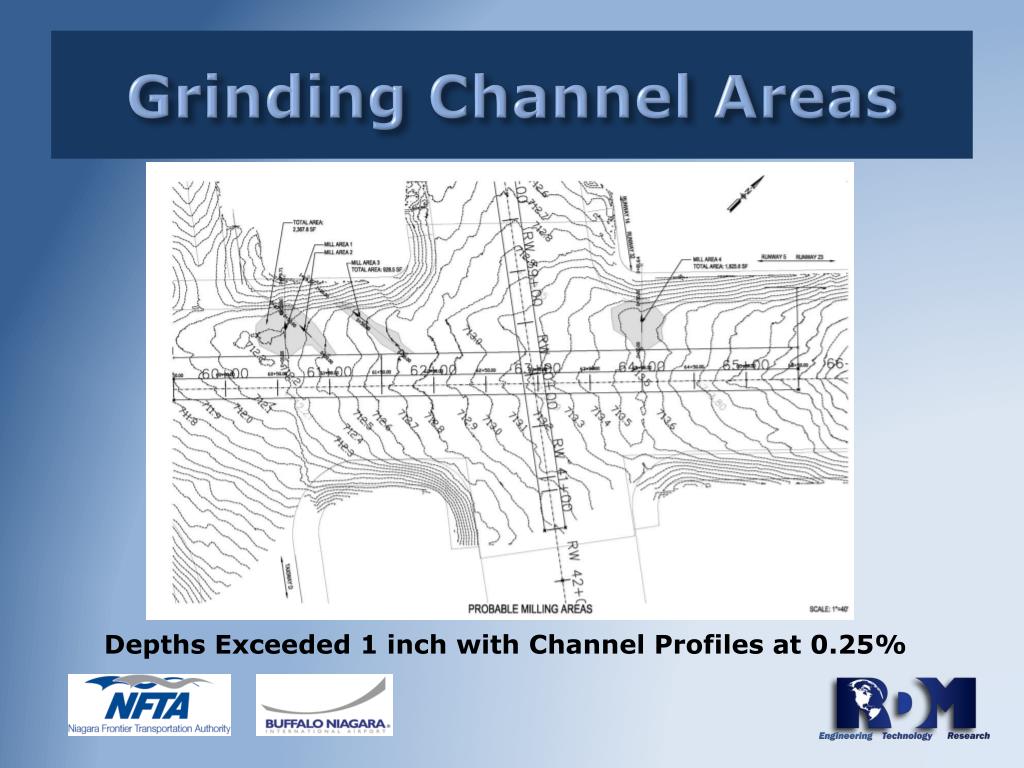
How thick is a porous friction course?
5.16.1 The total compacted thickness of Porous Friction Course at any point shall not be less than the specified course thickness or exceed this thickness by more than +6 mm / - 0 mm.
Is trafficking permitted on freshly laid surfacing?
5.29.1 No trafficking of freshly laid surfacing is permitted until the surfacing has cooled to ambient temperature or has hardened off sufficiently. Traffic allowed on finished cold surfacing shall be restricted to the minimum required for the conveyance of mixed materials for the laying of the surfacing immediately adjacent to the area being laid.
Abstract
Porous friction courses (PFCs) are mainly recommended as surface drainage layers on high-speed road-corridors and runway pavements. Permeability and sound attenuation characteristics are considered to be the indices for performance assessment of PFCs. One of the reasons for the loss of permeability in PFCs is densification under heavy traffic.
1. Introduction
Porous friction courses (PFCs) are typical open-graded asphaltic mixes, composed of relatively uniformly-graded aggregate and asphalt cement or modified binders, and are mainly used to serve as drainage layers, either at the pavement surface or within the pavement structure [1].
2. Specimen preparation and test plan
Straight-run bitumen and crushed stone aggregates are the major constituents of PFC mixes. The straight-run paving grade bitumen used in the present investigation was supplied by Mangalore Refinery and Petrochemicals Limited (MRPL), Mangalore. Crushed granite stone aggregates obtained from local stone-crushing plants were used in this study.
4. Conclusions and recommendations
Laboratory studies were conducted to characterize the PFC mixes for different compaction efforts using the Marshall compaction method. PFC mixes corresponding to four aggregate gradations and two binder contents (4.5% and 5.0% by mass of total mix) were studied for three levels of compaction 35 blows, 50 blows, and 75 blows.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support extended by the Ministry of Science and Technology (Government of India) under FIST–2005 for this research, and the National Institute of Technology Karnataka for having provided the basic infrastructure, manpower, and other timely assistance.
What is the moisture content of PFC?
2004 TxDOT specifications (Item 342) require that the mixture contain no more than 0.2 percent moisture by weight which should ensure better control of mixing temperature and a more homogeneous mixture. Some states only require the use of aggregate in a surface dry condition for PFC production (7). The British Standard establishes 1 percent (by mass of the mixture at the required temperature) as the maximum moisture content for PA mixtures during construction (8).
What is PFC in asphalt?
Porous or permeable friction courses (PFC) are hot mix asphalt mixtures placed at the surface of a pavement structure in a thin layer to produce several benefits for the traveling public in terms of safety, economy, and the environment. It is a sacrificial wearing course consisting of an aggregate with relatively uniform grading and little or no fines and mineral filler and it is designed to have a high air void content compared to dense-graded mixtures.
What should be corrected before putting a PFC in a pavement?
Before placement of PFC, the pavement surface should be corrected to avoid zones that allow water accumulations (e.g., zones with permanent deformation). Lateral and longitudinal drainage of the underlying surface must be provided to guarantee adequate water discharge from the PFC.
What is a PFC?
1. CHAPTER 1.0 INTRODUCTION . Porous or permeable friction courses (PFC) are hot mix asphalt (HMA) mixtures placed at the surface of an asphalt pavement structure in a thin layer to produce several benefits for the traveling public in terms of safety, economy, and the environment.
Can PFC clog mats?
Any edge clearing (Figure 2) should be performed prior to placement of the PFC. These fines on the outside edge of the mat can cause the mixture to clog near the edge.
Is PFC resistant to permanent deformation?
Literature from Spain suggests that PFC mixtures are highly resistant to permanent deformation, and no laboratory tests are required to evaluate the material response for this type of distress1. This is based on more than 20 years of performance data. OVERVIEW OF THE PFC MIXTURE DESIGN PROCEDURE .
What is 5.14.1 plant mixture?
5.14.1 The plant mixtures shall be transported without delay to the laying sites from the mixing plant or from hot storage bins taking care to prevent segregation. The vehicles shall be double sheeted during transit and while waiting to prevent loss of heat, contamination and wetting. All vehicles shall be mechanically sound and roadworthy and shall be suitable for the spreading equipment in use and shall have insulated bodies.
What is 5.9.1?
5.9.1 The proportion of filler shall be measured by weight. Where the Specification for the material being mixed requires a definite proportion of an added filler, extracted dust shall not be automatically fed back into the mixer.
What is the job standard mix?
The ‘Job Standard Mixture’ shall be the ‘Laboratory Standard Mixture’, modified as necessary in accordance with Section 6 of this Specification. It shall be the standard for the routine production of Porous Friction Course for the works subject to the plant tolerances permitted in Clause 4.5.
What is Clause 1.3?
However, having regard to the various design parameters affecting the choice of construction and specifications, including scope of work, aircraft type and frequency of usage, location of pavement on an airfield, design life, timescale constraints and existing pavement constructions, the guidance notes cannot be exhaustive. Further advice on a project/works specific basis can be obtained from the Construction Support Team, DE.
How thick is a porous friction course?
5.16.1 The total compacted thickness of Porous Friction Course at any point shall not be less than the specified course thickness or exceed this thickness by more than +6 mm / - 0 mm.
What are the unique characteristics of military aircraft?
1.1.1 The unique characteristics of military aircraft, in terms of speed, weight, tyre pressures, etc., create specialist requirements in the surfacing of MOD airfields. As such, specialist materials specifications are required to meet these needs.
Does Y.7.1 mean BS EN ISO 9000?
Y.7.1 Whilst the Supplier may have registration to the BS EN ISO 9000 series, it does not necessarily mean that his system is fully focused on the specific requirements of the Contract, nor does any second party scheme run by another purchaser. Monitoring of the system should take place irrespective of whether the Supplier has, or has not, achieved registration.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the term that describes the failure of a kidney to develop in a newborn? course hero
- 2. how do i know if a course is degree applicable
- 3. in coursera what is audit the course
- 4. why align an online course to standards
- 5. what is the main currency that drives life in the cell crash course answers
- 6. 36 of what number is 18 course hero
- 7. how long golf course
- 8. why is course hero so expensive
- 9. what skills do i need to take a wemt course
- 10. where can it take a defensive course in leesburg florida