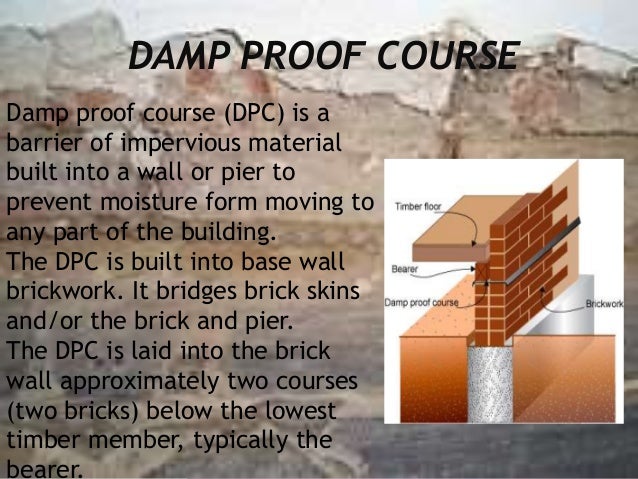
- What is Damp Proof Course? The damp proof course (DPC) is generally applied at basement levels, which restricts the movement of moisture through walls and floors.
- What is the abbreviation of DPC in Construction? The abbreviation of DPC is the Damp Proof Course.
- What are the desirable properties of DPC Material? ...
- What are the types of DPC Materials?
Full Answer
What is a damp proof course and do I need one?
Feb 10, 2022 · The damp proof course is an important layer for any building walls that is installed near the ground to keep the walls from becoming moist. Excess moisture rising from the ground may be a problem in properties that do not have a damp protection layer installed. Excess moisture may wreak havoc on decorations, plaster, and even cause damp rot in uncovered wood.
What is a functioning damp course?
Sep 05, 2019 · A Damp Proof Course is an essential element of a property that is required to protect the property against any moisture rising from the ground. In this, we will be provided with a deeper understanding of what is a damp proof course and its types.
How does a damp-proof course work?
Basically, a damp proof course is a waterproof barrier than prevents rising damp from occurring. The barrier must be installed outside the house to prevent moisture from seeping in. Damp proof courses are made from a variety of water-resistant materials. Which material or materials are used depends on the job.
How do you find a damp course on a wall?
Oct 23, 2019 · A damp proof course is one of the most important elements of a property. The DPC protects the property against moisture rising from the ground. This page will provide a deeper understanding of what is a damp proof course and what the best types of damp proof treatments are. Excess moisture gaining access to your property can result in a range of …
What does a damp course do?
A damp-proof course (DPC) is a barrier through the structure designed to prevent moisture rising by capillary action such as through a phenomenon known as rising damp. Rising damp is the effect of water rising from the ground into property.
How do you fix damp course?
The most common and effective way to treat rising damp is to install a remedial damp proof course by injecting a water repellent damp proof cream into the mortar bed joint of affected walls.
Where is the damp course on a house?
A damp proof course (DPC) is a layer near the bottom of the walls of a house which prevents rising damp. In a property without a DPC, water can rise up from the ground through capillary action and through porous elements in your brickwork.
What happens when you have a damp proof course?
The damp proof course prevents damp from the ground rising up the walls and damaging your property. Properties which have no appropriate damp protection layer or has a damaged damp course may be affected by excess moisture rising from the ground.Oct 23, 2019
What are the signs of rising damp?
Rising Damp SignsDamp Or Wet Patches Appearing On Walls. ... Salts Within The Plaster | One of the Most Frequent Signs of Rising Damp. ... Flaky Or Bubbling Plaster. ... Rotting Skirting Boards And Flooring. ... Damp and Musty Smell. ... Rusting Iron And Steel Fasteners. ... Crumbling Bricks and Mortar Between Bricks.Aug 9, 2019
How do you find a damp proof course?
You can find your DPC by taking a look at the external wall. Look down at ground level and look up about 6 inches or so up the wall. Somewhere around here you will see a thin black line of either slate or plastic running horizontally across the brick work. This is your DPC.Nov 18, 2015
Can you do a damp proof course yourself?
Now you can even obtain your own Product Guarantee Certificate after injecting your own damp proof course. The new generation of UltraCure DPC Creams have appeared and for the first time private individuals and developers, builders and DIY enthusiasts can reliably and cheaply inject their own chemical DPC.
Can you paint over damp proof course?
Can you paint over damp? No. Never paint over damp – it doesn't address the root cause of bubbling paint or peeling wallpaper, and you'll need to paint it again very soon. Fix the source of the damp then let the wall fully dry out before painting it.Jul 23, 2021
Can decking go above damp course?
The damp proof course (dpc) of a dwelling should never be compromised or bridged which is why you often see advice to install decks well below dpc level particularly where DIY installation is involved. However, many people have successfully installed decks above the DPC, for example to be level with patio/French doors.
Is a damp proof course necessary?
The reason why a damp proof course is important is because any excess moisture entering a building can lead to more serious property problems such as timber decay or structural damage. Properties that do not have an effective damp proof course are more prone to suffer from the following: Wet rot. Dry rot.
Do you need a damp proof course?
Why do you need a damp proof course A functioning damp course is an essential part of any property in order to prevent moisture from the earth and soil rising up the walls through capillary action (also known as rising damp) and damaging the property as a result.
How much is damp proofing UK?
How much does damp proofing cost?Damp proofing costsCost + VAT (Range low - high)Average costDamp proofing course£250 - £1,500£850Damp proofing external walls cost£750 - £2,500£1,500Damp proofing cellar / basement cost - tanking£30 - £60 per sqm£45 per sqmInjection damp proofing cost£1,000 - £5,000£3,5003 more rows
Why does a damp proof course fail?
Some of the most common include: subsidence causing the building to move - creating a break in the original DPC, building renovations that raise the ground level above the current damp proof course, and breakdown due to age and deterioration.
What is a damp proof membrane?
The damp proof membrane is positioned underneath a concrete slab with the intention of protecting the concrete from any moisture and therefore making it damp proof.
What is damp proofing cream?
Sometimes called a ‘remedial’ damp proof course, this process involves the injection of a ‘damp proof cream’ made from a silicone-based liquid that reacts with the silica in the masonry to produce a water-repelling layer within the wall.
What happens if you build a house after 1920?
If your property was built after 1920 it is also possible that your current damp proof course has weakened and failed over time to allow water ingress and potential rising damp problems.
What Is Damp Proof Course?
The damp proof course is an important layer for any building walls that is installed near the ground to keep the walls from becoming moist.
Materials for Damp Proof Course (DPC)
The following characteristics should be present in an efficient damp proofing material:
What are the types of DPC Materials?
Bitumen felts (which can be hessian-based or fiber/glass fiber-based), plastic sheeting (polythene sheets), and other flexible materials are examples.
Methods of Damp Proofing
A. Providing D.P.C. course B. Providing cavity walls C. Surface treatment D. Integral treatment E. Guniting and F. Pressure grouting.
What Is DPC In Construction?
DPC means Damp Proof Course which is applied at basement levels, which restricts the movement of moisture through walls and floors of a building. Mostly DPC courses are required in new build properties which are most sensitive to moisture in order to prevent rising dampness subsequently.
What Is Damp Proof Course?
A Damp Proof Course is an essential element of a property that is required to protect the property against any moisture rising from the ground. In this, we will be provided with a deeper understanding of what is a damp proof course and its types.
Types of DPC And Its Thickness
Currently, various remedial damp-proof courses are available which can be installed. However, it is important to select the appropriate damp proof course which will be well suited to the construction of the property.
DPC Level In Construction
Capillary Action in the brickwork causes the moisture to rise up in the building hence the foundation of a building is always intact with the moisture present in the soil. Hence to tackle such phenomenon DPC (Damp Proof Course) is provided at the plinth level of the construction.
Plinth Protection
Plinth protection is provided to prevent water implication into the soil and reach the equal of the plinth wall and floor by capillary action resulting in moisture, acting as a barrier and water in the ground near the plinth wall blocks direct access to.
Methods of Damp Proof Course Installation in Construction
The general procedure to be followed while laying a damp proof course is,
What Is Damp Proofing ?
Damp proofing is a method used to prevent dampness to enter through walls or floors into the interior property of the building.
Why is it important to have a damp proof course?
The damp proof course prevents damp from the ground rising up the walls and damaging your property. Properties which have no appropriate damp protection layer or has a damaged damp course may be affected by excess ...
When was damp proof course required?
A damp-proof course is a standard element which is required when building a property. Damp-Proof Coursing was made compulsory in 1875, however many DPC’s installed in the immediate period after this were laid shoddily and no longer fulfil their purpose. Initially DPCs consisted of slate or lead barriers, fitted into the walls to protect ...
Why does my DPC fail?
A DPC may fail because it was not fitted properly or may fail due to deterioration, localised damage or bridging. If the DPC fails then your property may be suffering from rising damp. Rising damp is moisture which defies gravity and moves upwards through walls as a result of capillary action.
What happens when you have no damp protection?
Properties which have no appropriate damp protection layer or has a damaged damp course may be affected by excess moisture rising from the ground. This excess moisture can affect plaster, decoration and can even result in wet rot, or dry rot affecting unprotected timbers.
How to tell if a wall is damp?
If you suspect that your wall is affected by damp then you should inspect the outside and inside off your property looking for defects that could cause damp to affect your wall. You could then use a moisture meter which will tell you if the wall has a higher moisture content than it normally should be.
What is used to install a small electric charge into the wall?
Copper and titanium wiring are used to install a small electric charge into the wall which reverses the polarity of the capillarity in the wall and pulls the rising damp below the level of the new damp course.
Does misdiagnosis solve damp?
It is crucial that a specialist accurately identifies the source of your damp problem. As misdiagnosis will give the wrong remedial repair work which will not solve the damp problem and will cost you more as the work will need to be done twice.
What is the choice of material to function as an effective damp proof course?
The choice of material to function as an effective damp proof course requires a judicious selection. It depends upon the climate and atmospheric conditions, nature of the structure, and the situation where DPC is to be provided.
What are the properties of damp proofing material?
Properties of Materials for DPC. An effective damp proofing material should have the following properties; It should be impervious. It should be strong and durable and should be capable of withstanding both dead as well as live loads without damage. It should be dimensionally stable.
What is DPC material?
DPC Material for floors, roofs etc. For greater wall thickness or where DPC is to be laid over large areas such as floors, roofs, etc., the choice is limited to flexible materials that provide a lesser number of joints like mastic, asphalt, bitumen felts, plastic sheets, etc.
What should a DPC cover?
The DPC should cover the full thickness of the walls, excluding rendering. The mortar bed upon which the DPC is to be laid should be made level, even and free from projections. Uneven base is likely to cause damage to DPC.
What is a DPC?
What is DPC? The damp proof course (DPC) is generally applied at basement levels, which restricts the movement of moisture through walls and floors. The selection of materials for the damp proof course and its various methods of applications in buildings is discussed.
What are flexible materials?
Flexible Materials: Materials like bitumen felts (which may be hessian based or fiber/glass fiber-based), plastic sheeting (polythene sheets), etc. Semi-rigid Materials: Materials like mastic, asphalt, or a combination of materials or layers.
How to find damp proof course?
You can find it by checking the outside of your house and locating a seal that runs horizontally across the brickwork. It usually sits about 6 inches up from ground level.
What is damp proofing?
Once this is determined, there are three types of damp proof course available on the market: 1 Cream or liquid wall injections: The application requires holes to be drilled into your walls. 2 Mortar injections: The same as above, except, mortar is caulked into the holes. Used in homes with more internal wall rubble and those prone to voids. 3 Electroosmotic course: A non-chemical alternative using copper or titanium wiring to create a small electric charge that stops the water from rising. It uses a scientific method to reverse the polarity of the capillarity, keeping the rising water below the level of the new damp course.
How many types of damp proofing are there?
Type of damp proofing: As previously mentioned, there are three types of damp proofing treatments available. Your damp proofing cost will depend on which treatment you need.
How far up from ground level should a damp seal be?
It usually sits about 6 inches up from ground level. This seal might not exist on homes built before 1875 – before a DPC became a compulsory building regulation. If that’s the case, you will need to invest in a damp course to avoid issues such as: Reduced wall integrity. Aggressive mould stains.
What is mortar injection?
Used in homes with more internal wall rubble and those prone to voids. Electroosmotic course. A non-chemical alternative using copper or titanium wiring to create a small electric charge that stops the water rising.
Can you damp proof exterior walls?
If you’re damp proofing exterior walls, you can expect to spend a bit more as there are more processes to consider. For example, if the rising damp was caused because the exterior ground level rose above the DPC in the wall, you will also need to lower the ground level.
Popular Posts:
- 1. in which meiotic phase do the homologous chromosomes pair up? course hero
- 2. what main course goes well with artichokes
- 3. what does the computer info technology course teach you ?
- 4. how long is usual course of antibiotics for bv
- 5. who is on the course practicing at wells fargo
- 6. how to course on understanding etrade screens
- 7. how has pips character changed over the course of the book when it comes to joe
- 8. of course i talk to myself. sometimes i need expert advice who said it
- 9. "can't repeat the past?... why of course you can!"
- 10. what is considered a college prep course