What type of math is math 1?
Math 1 Course Description Math 1 students study linear, exponential, and quadratic functions. They also learn to prove a figure is a specific type of a triangle or quadrilateral through the understanding of parallel and perpendicular lines, midpoint and distance .
What are math 1 subjects?
Mathematics 1Course summary.Algebra foundations.Solving equations & inequalities.Working with units.Linear equations & graphs.Forms of linear equations.Systems of equations.Inequalities (systems & graphs)More items...
What is the course math?
A basic definition of mathematics (or maths, or math, depending where you are in the world) is that it is an education in numeric sciences, using a range of different approaches including algebra, calculus and basic arithmetic.Jan 11, 2022
What is meant by maths 1?
Definitions. Mathematically, 1 is: in arithmetic (algebra) and calculus, the natural number that follows 0 and the multiplicative identity element of the integers, real numbers and complex numbers; more generally, in algebra, the multiplicative identity (also called unity), usually of a group or a ring.
Is it better to take math 1 or 2?
Math 1 is designed for those who've taken two years of algebra and one year of geometry, while Math 2 targets those who've also taken precalculus/trigonometry. Although they cover many of the same topics, Math 1 involves more tricky applications of math concepts since the scope of the exam is narrower.Jun 18, 2021
Are algebra 1 and math 1 the same?
The Algebra I or Mathematics I content standards are the same for all students; however, some students in special education may require accommodations or modifications to instruction.Jun 8, 2021
What is the best course math?
Best Online Math CoursesBecome an Algebra Master by Udemy.Basic Statistics by the University of Amsterdam.Master the Fundamentals of Math by Udemy.Introduction to Mathematical Thinking by Stanford Univesity.Algorithmic Design and Techniques by UC San Diego.Linear Algebra and the Study of Spaces by Udemy.More items...
What math is most useful?
Top 5 Math Classes to Prepare for the FutureStatistics.Trigonometry.Calculus.Advanced Linear Algebra.Game Theory.Sep 5, 2017
What's the first math you take in college?
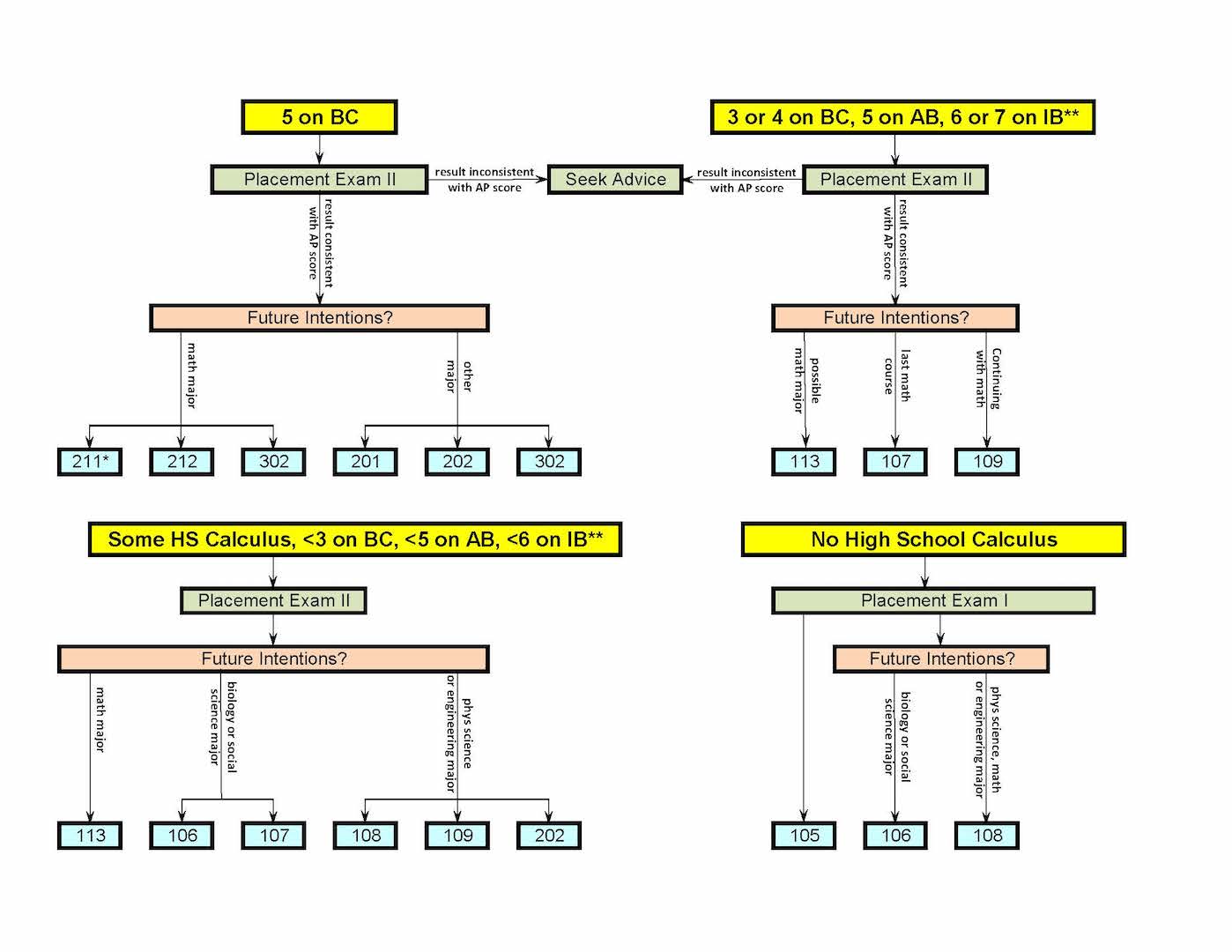
Most first-year students who take a mathematics course will begin in the calculus sequence. Consult the Calculus Placement Decision Chart and visit the Calculus/Statistics Placement page to determine which course to take first. Math 101: Calculus with Problem Solving.Mar 30, 2022
Who invented zero in world?
The first recorded zero appeared in Mesopotamia around 3 B.C. The Mayans invented it independently circa 4 A.D. It was later devised in India in the mid-fifth century, spread to Cambodia near the end of the seventh century, and into China and the Islamic countries at the end of the eighth.Jan 16, 2007
What is special about number1?
ONE is the only number that's the same in binary, base 10 and Roman Numerals. It's the wheels on a unicycle, the rails on a monorail and the players when you go solo. One is the first odd number, the first triangular, square, pentagonal and hexagonal number, and the first tetrahedral, cube and Fibonacci number.
Who invented 1 number?
Hindu-Arabic numerals, set of 10 symbols—1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0—that represent numbers in the decimal number system. They originated in India in the 6th or 7th century and were introduced to Europe through the writings of Middle Eastern mathematicians, especially al-Khwarizmi and al-Kindi, about the 12th century.
About the Program
Development of mathematics as an active science of patterns involving quantity and change, shape and motion, data and chance, and counting and algorithms
Program Components
Digital subscriptions are available for institutions & homeschoolers only.
Additional Details & Resources
This provides a summary of twenty years of research findings for the Core-Plus Mathematics Project (CPMP).
What are the Saxon math courses?
Saxon Math Courses 1, 2, and 3 integrate and distribute traditional units, giving students time to learn and practice skills throughout the year, master content, and develop algebraic thinking for mastery of the Common Core State Standards.
What is a bargain book?
"Bargain Books" are brand new items that have minor physical blemishes due to shipping or handling that do not affect the use of the item. All Bargain Books are sold as is and all sales are final (no returns, exchanges or cancellations).
Why do students like Saxon?
Students like Saxon because they feel successful in math instead of overwhelmed. Because of the format, children are able to work more independently.
What is benchmark test?
Benchmark Tests serve as quarterly exams or to help identify concepts which need additional instruction and practice. The End-of-Course Exam (multiple choice) is a final exam. This Course Assessments Book is expensive and may be necessary if you need to provide tests for an overseeing agency.
Is Saxon Math a good program?
Highly recommended by both Mary Pride and Cathy Duffy, Saxon Math also wins our award for the "Most Requested Text.". Saxon math is a "user-friendly" math program - even for Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus and other usually difficult math topics.
What is the definition of mathematics?
1.1 definition of mathematics: Mathematics is the study of topics such as quantity (numbers), structure, space and change. There is a range of views among mathematicians and philosophers as to the exact scope and definition of mathematics.
Where did the word "math" come from?
The word mathematics comes from the Greek μάθημα (máthēma), which, in the ancient Greek language, means "that which is learnt", "what one gets to know", hence also "study" and "science", and in modern Greek just "lesson". The word máthēma is derived from μανθάνω (manthano), while the modern Greek equivalent is μαθαίνω (mathaino), both of which mean "to learn". In Greece, the word for "mathematics" came to have the narrower and more technical meaning "mathematical study" even in Classical times. Its adjective is μαθηματικός(mathēmatikós), meaning "related to learning" or "studious", which likewise further came to mean "mathematical". In particular, μαθηματικὴ τέχνη (mathēmatikḗ tékhnē), Latin: ars mathematica, meant "the mathematical art". In Latin, and in English until around 1700, the term mathematics more commonly meant "astrology" (or sometimes "astronomy") rather than "mathematics"; the meaning gradually changed to its present one from about 1500 to 1800. This has resulted in several mistranslations: a particularly notorious one is Saint Augustine's warning that Christians should beware of mathematic imeaning astrologers, which is sometimes mistranslated as a condemnation of mathematicians. The apparent plural form in English, like the French plural form les mathématiques (and the less commonly used singular derivative la mathématique), goes back to the Latin neuter pluralmathematica (Cicero), based on the Greek plural τα μαθηματικά (ta mathēmatiká), used by Aristotle (384–322 BC), and meaning roughly "all things mathematical"; although it is plausible that English borrowed only the adjective mathematic(al) and formed the noun mathematics anew, after the pattern of physics and metaphysics, which were inherited from the Greek. In English, the noun mathematics takes singular verb forms. It is often shortened to maths or, in English-speaking North America, math.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what does the mg stand for in golf course maintenance
- 2. why do the cytosol and organelles come only from the mother? course hero
- 3. how long is locating and evaluating information course for colllege
- 4. which topic is most likely to be studied in a microeconomics course? of quizlet
- 5. how to start over a course in duolingo
- 6. how to make a obstacle course for horess
- 7. why are pubic hairs course and curly and regular hair not
- 8. what is the difference between framing and reframing? course hero
- 9. how to take motorcycle course in the army
- 10. what is par on golf course