The current guideline says that most women diagnosed with breast cancer who will have radiation therapy after lumpectomy should be treated with accelerated, also called hypofractionated, whole-breast radiation therapy as the standard of care. The preferred hypofractionated dose schedule is 40 Gray in 15 doses or 42.5 Gray in 16 doses.
Do I really need radiation after a lumpectomy?
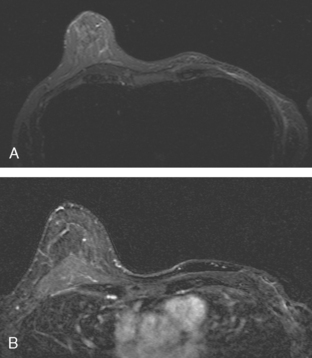
Will I need radiation if I have a lumpectomy? The answer is most likely, YES. For those diagnosed with a small, Early-Stage breast cancer , a lumpectomy followed by radiation is just as effective at curing your cancer as a mastectomy without radiation.
How long after lumpectomy does radiation start?
Some researchers tells that radiation should begin within six weeks when surgery is completed. If there is a delay in radiation therapy or it is given after more than 7 weeks, it decreases the chance of local control. Many doctors say that there is no minimum time has been established between lumpectomy and radiation therapy.
What will my breasts look like after a lumpectomy?
- Your health status and lifestyle
- The location and size of breast cancer
- The size of your breast
- The degree of the surgery (lumpectomy or mastectomy)
- The available body muscles; for example, very skinny women might not have extra tissue to be used for breast reconstruction
- Whether you want to reconstruct one or both breasts
How to treat recurrent DCIS after a lumpectomy?
- Feeling a lump (84% risk). DCIS does not cause symptoms and 80% of the time is found only by mammography. ...
- Involved margins (63% risk). ...
- Diagnosed before menopause (59% risk). ...
- High p16 (51% risk). ...
- Being African-American (43% risk). ...
- High histologic grade (36% risk). ...
How long is radiation therapy for DCIS?
A typical course of radiation treatment for DCIS involves 16 sessions given over three weeks.
How many radiation treatments are needed after lumpectomy?
Radiation therapy after lumpectomy lowers the risk of breast cancer recurrence and may increase the chances of survival [4]. It's usually recommended after lumpectomy. Radiation therapy for early breast cancer most often involves treatment once a day, 5 days a week, for 1-6 weeks.
How long is radiation treatment after lumpectomy?
The standard radiation therapy approach after a lumpectomy has been to target the entire breast. The method is called whole-breast irradiation. It is typically given every day for four to six weeks.
Do you need radiation after lumpectomy for DCIS?
Radiation is typically used after lumpectomy. But it might not be necessary if you have only a small area of DCIS that is considered low grade and was completely removed during surgery.
How many sessions of radiotherapy is normal?
Most people have 5 treatments each week (1 treatment a day from Monday to Friday, with a break at the weekend). But sometimes treatment may be given more than once a day or over the weekend.
What time of day is best for radiation therapy?
New research from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, to be presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2019 in Atlanta, reports that administering radiation treatments in the morning as opposed to later in the day can significantly reduce severity of mucositis and its related ...
How long after lumpectomy should radiotherapy start?
Radiation therapy usually begins three to eight weeks after surgery unless chemotherapy is planned.
What can I expect after my first radiation treatment?
The most common early side effects are fatigue (feeling tired) and skin changes. Other early side effects usually are related to the area being treated, such as hair loss and mouth problems when radiation treatment is given to this area. Late side effects can take months or even years to develop.
How soon after lumpectomy does radiation begin?
A course of radiation starts between six and 12 weeks after lumpectomy surgery. Most frequently, we target the entire breast (whole-breast radiation). In some cases, we also treat nearby lymph nodes.
What is the recurrence rate of DCIS after lumpectomy?
Results of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B17 trial showed that 13.4% of DCIS patients randomly assigned to receive treatment by lumpectomy alone experienced recurrence as invasive cancer by 8 years after treatment compared with 3.9% of DCIS patients randomly assigned to receive treatment by ...
How much does radiation reduce recurrence of DCIS?
The researchers found that the women who got radiation therapy were 48% less likely to have a local recurrence of DCIS than women who didn't get radiation therapy: 18% of the women who had lumpectomy and radiation therapy had a local recurrence.
Can I avoid radiation after lumpectomy?
If you're having lumpectomy and will be taking hormonal therapy after surgery, it may be possible for you to skip radiation therapy. As you are making your treatment plan, you and your doctor will consider a number of factors, including: your age. the size of the cancer.
Can radiation therapy be given for DCIS?
Radiation therapy isn’t given to people who are treated with mastectomy for DCIS. Lumpectomy for DCIS is usually followed by radiation therapy to lower the risk of [1]: DCIS recurrence (a return of DCIS) in the treated breast. Invasive breast cancer in the treated breast.
Is ductal carcinoma in situ invasive?
Introduction: Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive breast cancer. Without treatment, DCIS can progress to invasive breast cancer over time. So, almost all cases of DCIS are treated. Treatment involves surgery, with or without radiation therapy.
What is a DCIS?
DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) is the most common form of non-invasive breast cancer and is considered stage 0 cancer. While DCIS isn’t considered life threatening, it does increase the risk of developing invasive breast cancer later in life. DCIS usually is treated with surgery to remove the cancer -- lumpectomy in most cases.
Can you have radiation after DCIS surgery?
Radiation therapy after DCIS surgery was common in the past, but some newer DCIS treatment guidelines say that women at low risk of recurrence (the cancer coming back) may be able to skip radiation therapy after surgery.
Does radiation reduce the risk of recurrence in the same breast?
Several other large, randomized studies have shown that radiation after lumpectomy for DCIS reduces the risk of recurrence in the same breast by about half. Other studies have shown that taking tamoxifen after lumpectomy for hormone-receptor-positive DCIS reduces the risk of both DCIS recurrence and invasive disease in both breasts.
Does radiation therapy after lumpectomy reduce risk of recurrence?
Now a study has found that radiation therapy after lumpectomy to remove low-risk DCIS reduces the risk of recurrence, but had no effect on overall survival. The research was presented on Oct. 21, 2018, at the American Society for Radiation Oncology Annual Meeting.
Does radiation help with DCIS?
Still, no study has shown that radiation or tamoxifen after lumpectomy for DCIS improves overall survival or reduces the rate of metastatic recurrence (cancer coming back in a part of the body away from the breast). How DCIS considered to have a low risk of recurrence should be treated is somewhat controversial right now.
What is a Lumpectomy for DCIS?
Lumpectomy for DCIS is usually followed by whole breast radiation therapy to lower the risk of [ 6-13 ]: DCIS recurrence (a return of DCIS) in the treated breast. Invasive breast cancer in the treated breast.
How to treat DCIS?
Surgery is the first step to treat DCIS. It removes the abnormal tissue from the breast. Depending on how far the DCIS has spread within the milk ducts, surgery can be mastectomy or lumpectomy. If DCIS is spread throughout the ducts, affecting a large part of the breast, a total (simple) mastectomy will be done.
Why is DCIS called in situ?
It’s called “in situ” (which means “in place”) because the cells have not left the milk ducts to invade nearby breast tissue. DCIS is also called intraductal (within the milk ducts) carcinoma. You may hear the terms “pre-invasive” or “pre-cancerous” to describe DCIS. DCIS is treated to try to prevent the development of invasive breast cancer.
How do pathologists determine the hormone receptor status of a DCIS tumor?
A pathologist determines the hormone receptor status of the DCIS by testing the tissue removed during a biopsy. Hormone receptor-positive (estrogen receptor-positive/progesterone receptor-positive) DCIS tumors express hormone receptors. This means they have a lot of hormone receptors..
Can you have a sentinel node biopsy after a mastectomy?
Once a mastectomy has been done, a person can’t have a sentinel node biopsy. If it turns out there’s invasive breast cancer (along with DCIS) in the tissue removed during the mastectomy, a sentinel node biopsy will have already been done.
Can a lumpectomy be done with DCIS?
If there’s little spread of DCIS within the ducts, a choice can be made between mastectomy or lumpectomy. With lumpectomy, the surgeon removes only the abnormal tissue in the breast and a small rim of normal tissue around it. The rest of the breast is left intact.
Can you get DCIS without radiation?
Because DCIS might progress to invasive breast cancer, almost all cases of DCIS are treated. Surgery (with or without radiation therapy) is recommended to treat DCIS. After surgery and radiation therapy, some people take hormone therapy. Learn more about treatments for DCIS. Learn about the risk of invasive breast cancer after treatment for DCIS.
How to treat DCIS?
DCIS usually is treated with surgery to remove the cancer -- lumpectomy in most cases. After surgery, hormonal therapy may be recommended if the DCIS is hormone-receptor-positive (most are). Radiation therapy also is recommended for many women. Both hormonal therapy and radiation help reduce the risk of the DCIS recurring (coming back), ...
What is a DCIS?
DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) is the most common form of non-invasive breast cancer and is considered stage 0 cancer. While DCIS isn’t considered life threatening, it does increase the risk of developing invasive breast cancer later in life. DCIS usually is treated with surgery to remove the cancer -- lumpectomy in most cases.
How many women were in Group 1 of the DCIS?
The women were divided into two groups based on the characteristics of the DCIS: Group one included DCIS that was low- or intermediate-grade and was 2.5 cm or smaller in size (561 women). Group two included DCIS that was high-grade and was 1 cm or smaller in size (104 women). All the women had lumpectomy to remove the DCIS.
What is the risk of breast cancer after lumpectomy?
This study found that the risk of invasive breast cancer after a diagnosis of low-risk DCIS treated with lumpectomy alone ranged from 7.5% to 13.4%. Some women may find that risk acceptable. Other women may find that risk unacceptable and want more treatments after surgery.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
Based on your unique information, Breastcancer.org can recommend articles that are highly relevant to your situation. DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) is the most common form of non-invasive breast cancer and is considered stage 0 cancer.
Can you skip radiation after DCIS?
Routine radiation therapy after DCIS was common in the past, but some newer DCIS treatment guidelines say that women at low-risk for recurrence may be able to skip radiation therapy after surgery. Still, the definition of low-risk isn't always clear.
Does radiation reduce the risk of recurrence in the same breast?
Several other large, randomized studies have shown that radiation after lumpectomy for DCIS reduces the risk of recurrence in the same breast by about half. Other studies have shown that taking tamoxifen after lumpectomy for hormone-receptor-positive DCIS reduces the risk of both DCIS recurrence and invasive disease in both breasts.
What is the purpose of DCISionRT?
DCISionRT : The purpose of the DCISionRT test is to help patients and clinicians decide if Radiation Therapy would be of specific benefit to them based on their pathology. This test also looks at the genetic components of the DCIS tumor sample and extrapolates the relative benefit of radiation.
Why is radiation referral important?
This referral was essential to get because radiation is a daily treatment. If there was a nearby option, I was going to take advantage of that. If you are not in a metro area, you may need to travel for quite some distance to your treatment. Some organizations have resources to help make that easier on cancer patients.
Popular Posts:
- 1. when is ice age collision course on tv
- 2. how to get to ape agility course
- 3. what happened to course hero
- 4. what is at osu golf course
- 5. course start dates canvas when publish
- 6. when do do breast feeding course
- 7. mountain meadows golf course how to win
- 8. how many hours per week are you supposed to work for this ten week/four credit hour course
- 9. when resellers refuse to purchase products from a supplier course hero
- 10. where can i take a refresher course for cosmetology around pittsburgh pa