Endometrial cancer can be detected in the following ways: The doctor manually probes the uterus for lumps or thickening Vaginal ultrasound Dilation and curettage (also known as a D and C) Treatment Endometrial cancer is general treated with hormone therapy, surgery, chemotherapy or a combination of these approaches.
Full Answer
How is endometrial cancer detected and treated?
Cancer can be confirmed only by removing a small sample of tissue or cells (biopsy). When symptoms suggest endometrial cancer, the following tests may be used to detect cancer: Endometrial biopsy: When a small tissue sample is taken from the inner lining of the uterus. A thin tube is inserted through the cervix into the uterus, and a sample is gently scraped off for …
How is endometrial cancer graded?
Apr 21, 2022 · Hormone therapy involves the use of hormones or hormone-blocking drugs to change the body’s hormone levels. This can help slow the growth of endometrial cancer cells.
How can Mayo Clinic help with endometrial cancer?
May 20, 2021 · Chemotherapy may be recommended for treating advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer that has spread beyond the uterus. Hormone therapy. Hormone therapy involves taking medications to lower the hormone levels in the body. In response, cancer cells that rely on hormones to help them grow might die.
What is endometrial cancer and what causes it?
Endometrial biopsy: This procedure uses a small, flexible tube that is put into the uterus to collect an endometrial tissue sample. The sample is examined under a microscope to see if cancer or other abnormal cells are present. An endometrial biopsy procedure is often done in a …
Does stage 1 endometrial cancer require chemo?
What is the treatment for stage 1 endometrial cancer?
Is stage 1 endometrial cancer curable?
When is endometrial cancer considered cured?
Does a hysterectomy cure endometrial cancer?
Does stage 1 endometrial cancer require radiation?
For women with higher grade tumors, radiation will likely be recommended after surgery. Vaginal brachytherapy (VB), pelvic radiation, or both can be used. Some younger women with early endometrial cancer may have their uterus removed without removing the ovaries.Mar 30, 2022
What is the best treatment for endometrial cancer?
Can endometrial cancer come back after hysterectomy?
How often does endometrial cancer come back?
Nine patients (37.5%) recurred within the first year, 13 (54.2%) within the second year, 2 (8.3%) within the third year and 2 (7.7%) after 5 years. Altogether, 24 patients (92.3%) recurred within 3 years.
What were your symptoms of endometrial cancer recurrence?
Is endometrial cancer easy to treat?
Does endometrial cancer spread quickly?
How to test for endometrial cancer?
An endometrial biopsy is the most commonly used test for endometrial cancer and is very accurate in postmenopausal women. It can be done in the doctor's office. A very thin, flexible tube is put into the uterus through the cervix. Then, using suction, a small amount of endometrium is removed through the tube. The suctioning takes about a minute or less. The discomfort is a lot like menstrual cramps and can be helped by taking a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (like ibuprofen) before the procedure. Sometimes a thin needle is used to inject numbing medicine (local anesthetic) into the cervix just before the procedure to help reduce the pain.
What is the lab report for endometrial cancer?
If cancer is found, the lab report will state what type of endometrial cancer it is (like endometrioid or clear cell) and what grade it is.
What are the causes of colon cancer?
If the doctor suspects hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) as an underlying cause of the endometrial cancer, the tumor cells can be tested for protein and gene changes. Examples of HNPCC-related changes include: 1 Having fewer mismatch repair (MMR) proteins 2 Defects in mismatch repair genes (dMMR) 3 DNA changes (high levels of microsatellite instability, or MSI-H) that can happen when one of the genes that causes HNPCC is faulty
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer of the reproductive system?
This is a doctor trained to diagnose and treat diseases of the female reproductive system. Gynecologists can diagnose endometrial cancer, and sometimes treat it. Specialists in treating cancers of the endometrium and other female reproductive organs are called gynecologic oncologists.
How does a hysteroscopy work?
Hysteroscopy. For this procedure, the doctor puts a tiny telescope (about 1 / 6 inch in diameter) into the uterus through the cervix. To get a better view of the inside (lining) of the uterus, the uterus is filled with salt water (saline). This lets the doctor look for and biopsy anything abnormal, such as a cancer or a polyp.
How to find out if you have endometrial changes?
To find out exactly what kind of endometrial change is present, the doctor must take out some tissue so that it can be tested and looked at with a microscope. Endometrial tissue can be removed by endometrial biopsy or by dilation and curettage (D&C) with or without a hysteroscopy. A gynecologist usually does these procedures, which are described below.
What is the procedure called to see if a woman has cancer?
This helps the doctor see the uterine lining more clearly. This procedure is called a saline infusion sonogram or hysterosonogram.
What is the most important factor in determining a treatment plan for endometrial cancer?
However, the staging of endometrial cancer is the most important factor in determining a treatment plan.
How to find out if endometrial cancer has spread?
If endometrial cancer is found after examining uterine tissue samples, further tests may be done to see if the cancer cells have spread within the uterus or to other parts of the body. The process used to find out if and how far the cancer has spread beyond the uterus is called staging. Tests and procedures that may be used in the staging process include removal of the uterus (hysterectomy), and biopsies of other sites, chest x-ray, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), and CT scan.
What is the stage of endometrial cancer?
The stages of endometrial cancer are: Stage I indicates cancer in the uterus lining and/or the muscle layer of the uterus only. In Stage II, the cancer has spread within the uterus to cervical tissue (but not beyond), or to the stroma where the cervix and uterus meet.
What is the procedure to check for cancer in the vagina?
Most appointments to diagnose endometrial cancer begin with a pelvic exam to check for abnormal areas or lumps around your vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and rectum. Exams are generally completed in conjunction with your Pap test, a procedure to collect cells from the surface of the cervix and vagina.
What is endometrial biopsy?
Endometrial biopsy: When a small tissue sample is taken from the inner lining of the uterus. A thin tube is inserted through the cervix into the uterus, and a sample is gently scraped off for examination under a microscope. This is done to see if cancer or other abnormal cells are present.
How to detect cancer in the uterus?
When symptoms suggest endometrial cancer, the following tests may be used to detect cancer: Endometrial biopsy: When a small tissue sample is taken from the inner lining of the uterus. A thin tube is inserted through the cervix into the uterus, ...
What is stage IV cancer?
Stage IV indicates that the cancer has spread beyond the uterine area and pelvic organs into other parts of the body, such as the abdomen, intestine, and/or lymph nodes in the groin. Some cases may include spread into the liver, lungs, or bones.
How to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer?
Some strategies may help you lower your risk of developing endometrial cancer: Manage your weight: If you’re overweight or obese, losing weight and maintaining the weight loss might lower your risk of endometrial cancer. More research is needed to learn how weight loss affects the risk of endometrial cancer.
What are the symptoms of endometrial cancer?
This can include: changes in the length or heaviness of menstrual periods. vaginal bleeding or spotting between menstrual periods. vaginal bleeding after menopause. Other potential symptoms of endometrial cancer include:
What test is used to test for abnormalities in the uterus?
If your doctor detects abnormalities during the ultrasound exam, they may order one or more of the following tests to collect a sample of tissue for testing: Endometrial biopsy: In this test, your doctor inserts a thin flexible tube through your cervix into your uterus.
How much more likely is endometrial cancer in women who are overweight than women who aren't overweight?
According to the American Cancer Society, women who are overweight (BMI 25 to 29.9) are twice as likely to develop endometrial cancer as women who aren’t overweight. Those with obesity (BMI > 30) are more than three times as likely to develop this type of cancer.
How long does uterine cancer last?
More than 80 percent of people with uterine cancer survive for five years or longer after receiving the diagnosis. If you have endometrial cancer, early diagnosis and treatment increases your chances of remission.
What is the name of the lining of the uterus?
Endometrial cancer is a type of uterine cancer that starts in the inner lining of the uterus. This lining is called the endometrium. , approximately 3 in 100 women will be diagnosed with uterine cancer at some point in their lives.
What is it called when a surgeon removes a lymph node?
To learn if the cancer has spread, the surgeon will also remove nearby lymph nodes. This is known as lymph node dissection or lymphadenectomy.
How to reduce endometrial cancer risk?
Hormone therapy carries other risks, so weigh the benefits and risks with your doctor. Consider taking birth control pills . Using oral contraceptives for at least one year may reduce end ometrial cancer risk.
Why is endometrial cancer often detected early?
Endometrial cancer is often detected at an early stage because it frequently produces abnormal vaginal bleeding. If endometrial cancer is discovered early, removing the uterus surgically often cures endometrial cancer.
What causes endometrial cancer?
What's known is that something occurs to create changes (mutations) in the DNA of cells in the endometrium — the lining of the uterus.
What is the hollow, pear-shaped pelvic organ where fetal development occurs?
The uterus is the hollow, pear-shaped pelvic organ where fetal development occurs. Endometrial cancer begins in the layer of cells that form the lining (endometrium) of the uterus. Endometrial cancer is sometimes called uterine cancer. Other types of cancer can form in the uterus, including uterine sarcoma, but they are much less common ...
What are the factors that increase the risk of endometrial cancer?
Factors that increase the risk of endometrial cancer include: Changes in the balance of female hormones in the body. The ovaries make two main female hormones — estrogen and progesterone. Fluctuations in the balance of these hormones cause changes in the endometrium.
Does obesity cause endometrial cancer?
Being obese increases your risk of endometrial cancer. This may occur because excess body fat alters your body's balance of hormones. Hormone therapy for breast cancer. Taking the hormone therapy drug tamoxifen for breast cancer can increase the risk of developing endometrial cancer.
Can hormone replacement therapy help with menopause?
If you're considering hormone replacement therapy to help control menopause symptoms, talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits. Unless you've undergone a hysterectomy, replacing estrogen alone after menopause may increase your risk of endometrial cancer.
What is the treatment for endometrial cancer?
Drug treatments for endometrial cancer include chemotherapy with powerful drugs and hormone therapy to block hormones that cancer cells rely on. Other options might be targeted therapy with drugs that attack specific weaknesses in the cancer cells and immunotherapy to help your immune system fight cancer.
What is the procedure to diagnose endometrial cancer?
Hysteroscopy. During hysteroscopy, your doctor uses a thin, lighted instrument (hysteroscope) to view the inside of your uterus. Tests and procedures used to diagnose endometrial cancer include: Examining the pelvis. During a pelvic exam, your doctor carefully inspects the outer portion of your genitals (vulva), ...
What kind of doctor treats endometrial cancer?
If endometrial cancer is found, you'll likely be referred to a doctor who specializes in treating cancers involving the female reproductive system (gynecologic oncologist).
How to get a sample of cells from inside the uterus?
To get a sample of cells from inside your uterus, you'll likely undergo an endometrial biopsy. This involves removing tissue from your uterine lining for laboratory analysis. Endometrial biopsy may be done in your doctor's office and usually doesn't require anesthesia. Performing surgery to remove tissue for testing.
Why doesn't the immune system fight cancer?
Your body's disease-fighting immune system might not attack cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. For endometrial cancer, immunotherapy might be considered if the cancer is advanced and other treatments haven't helped.
What is hormone therapy?
Hormone therapy involves taking medications to lower the hormone levels in the body. In response, cancer cells that rely on hormones to help them grow might die. Hormone therapy may be an option if you have advanced endometrial cancer that has spread beyond the uterus.
What is the procedure called when you have to remove tissue from a biopsy?
If enough tissue can't be obtained during a biopsy or if the biopsy results are unclear, you'll likely need to undergo a procedure called dilation and curettage (D&C). During D&C, tissue is scraped from the lining of your uterus and examined under a microscope for cancer cells.
How to diagnose endometrial cancer?
While an ultrasound is a helpful tool, the only way to diagnose endometrial cancer is through a biopsy.
What is the gold standard test for endometrial cancer?
Whatever starts the process, it's important to keep in mind that an endometrial biopsy (when a tissue sample is removed from the inner lining of the uterus) is the gold standard test for diagnosing endometrial cancer. That said, other tests like a thorough medical history and blood and imaging tests certainly aid in the diagnostic process.
What is the first test for a woman's reproductive organs?
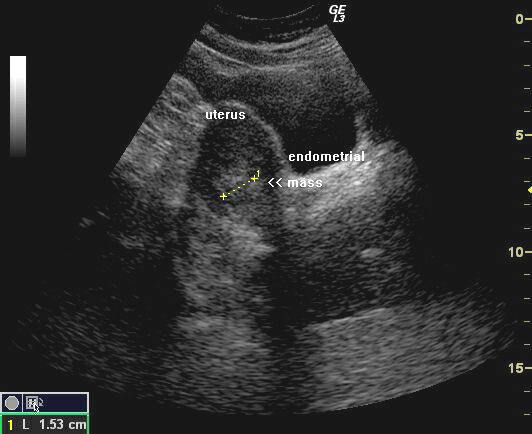
An ultrasound (a machine that uses sound waves to take images of the body) is the first test used to evaluate a woman's reproductive organs, including her uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. 2 Your doctor may start with a pelvic ultrasound , in which the ultrasound probe is placed (along with warm gel) on the lower abdomen or pelvis. Then he will move forward with a transvaginal ultrasound , which is a more optimal test for visualizing the uterus and determining whether or not endometrial cancer is present.
What is the procedure to check if a woman is bleeding from the uterus?
After reviewing a woman's medical history, a gynecologist will perform a physical examination, including a pelvic exam, to confirm that the bleeding is coming from the uterus and not from other organs (for example, the vulva, cervix, anus, or rectum).
What is the surgical staging of endometrial cancer?
Many women with endometrial cancer, especially those with more advanced disease, benefit from surgical staging, which involves surgery to comprehensively evaluate how far disease has spread in the body.
What is the name of the doctor who diagnoses endometrial cancer?
Once endometrial cancer is diagnosed, a specialized cancer doctor (called a gynecologic oncologist) will stage the cancer, which means she will determine if and how far the cancer has spread.
What tests are performed to rule out non-uterine problems?
Labs and Tests. In addition to a medical history and physical examination, various tests may be performed, mostly to rule out non-uterine problems. For instance, since the cervix connects the uterus to the vagina, a pap smear may be performed. During a pap smear, a cell sample is taken from the cervix to screen for cervical cancer.
How is endometrial cancer diagnosed?
Dr. Rossi: Right now endometrial cancer is diagnosed typically with a biopsy of the uterine lining, which usually occurs in a clinical office. A physician will perform the exam, which is very much like having a Pap smear. They will place a very thin tube into the uterine cavity and obtain some cells, which will include uterine lining cells ...
How many women die from endometrial cancer each year?
The National Cancer Institute estimates that about 52,000 new cases of endometrial cancer are diagnosed each year, and about 8,600 women die each year of the disease. Today, we are speaking with Emma Rossi, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Indiana University in Indianapolis, about the diagnosis and treatment ...
What is the number one genetic or inherited risk for endometrial cancer?
The number one genetic or inherited risk for endometrial cancer is a condition called Lynch syndrome. About 10% to 20% of women with endometrial cancer will have this cancer as a result of being born with a predisposition for cancer. This is Lynch syndrome, which is a condition in both men and women that causes an increased risk for colon cancer in ...
What is the number one risk factor for uterine cancer?
The number one risk factor for uterine or endometrial cancer is obesity. And that’s an increasing problem across the United States and the Western world in general. As a result, we are seeing increasing rates of endometrial cancer incidence.
Why do women get cancer at an early stage?
The reason that most women are diagnosed at an early stage is because this type of cancer really does present with symptoms early in its course, and a woman who is clued into these symptoms typically communicates this with her doctor.
Can a Pap smear detect cancer?
Very, very occasionally it is diagnosed in a routine Pap smear, but Pap smears are designed to detect cervical cancer and do not reliably detect uterine or endometrial cancer, although occasionally the shed uterine cancer cells can show up in the Pap smear.
Endometrial Cancer
If you've been following our other lesson on endometrial cancer, then you're all caught up as to what endometrial cancer is. But for those of you who may have missed our other lesson or like to do things out of order, endometrial cancer is a cancer that occurs in the endometrial lining of the uterus.
Diagnosis
But how does a doctor confirm that these symptoms are indeed signs of endometrial cancer? Many problems with the female reproductive tract can also include abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain.
Treatment
And that brings us to Step 3: Treatment options. Once a woman is diagnosed with endometrial cancer, the first step is to determine what stage the cancer is at. Like most other cancers, the stages of endometrial cancer are associated with how far along the disease has progressed.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the course biological sciences
- 2. how to order the h&rblock 2018 tax course book
- 3. how to doo a high rope course your first time
- 4. how much mri course cost
- 5. which course is located on the grounds at the westin mission hills
- 6. how should i design my course captivate
- 7. what causes pneumoconiosis course hero
- 8. what is cert course
- 9. how to beat donkey kong crash course wii u
- 10. which course demand in future