The key to writing effective learning outcomes is the selection of active, measurable verbs—the tasks you want students to do at the end of your class. Words like know , understand , or appreciate are difficult to measure, and they rarely get at the higher order thinking tasks most of us really want to see in our students.
- Focus on the student--what the student will be able to do by the end of the course or program.
- Describe outcomes, not processes or activities.
- Start each outcome with an action verb.
- Use only one action verb per learning outcome.
- Avoid vague verbs such as know and understand.
What is the difference between course objectives and learning outcomes?
How to write learning outcomes. Writing learning outcomes can be made easier by using the ABCD approach. This strategy identifies four key elements of an effective learning outcome: Audience; Behavior; Condition; Degree
How to write course learning outcomes for your syllabus?
o What Are GOOD Course Learning Outcomes? • Good Course Learning Outcomes use action verbs to specify the demonstrable and measurable knowledge, skills or dispositions possessed by students completing this course. (Instead of using verbs or phrases like, know, understand, appreciate, be aware of, learn comprehend,
How do you evaluate learning outcomes?
The key to writing effective learning outcomes is the selection of active, measurable verbs—the tasks you want students to do at the end of your class. Words like know , understand, or appreciate are difficult to measure, and they rarely get at the higher order thinking tasks most of us really want to see in our students.
What are some examples of learning outcomes?
But learning outcomes are also an important step for an instructor as part of course design, because without clearly defined learning outcomes it is challenging to create a course that has strong and intentional alignment in what the students are learning, practicing, and being assessed on during the quarter.
How do you write a course learning outcome?
Steps for Writing OutcomesBegin with an Action Verb. Begin with an action verb that denotes the level of learning expected. ... Follow with a Statement. Statement – The statement should describe the knowledge and abilities to be demonstrated.
What are the 4 learning outcomes?
Learning outcomes verbsClassify.Demonstrate.Explain.Express.Illustrate.Match.Select.Recognize.More items...•Dec 7, 2021
What are course learning outcomes?
Course Learning Outcomes are statements clearly describing the meaningful, observable and measurable knowledge, skills and/or dispositions students will learn in this course.
What are the 5 learning outcomes?
The five learning outcomesChildren have a strong sense of identity.Children are connected with and contribute to their world.Children have a strong sense of wellbeing.Children are confident and involved learners.Children are effective communicators.
What makes a good student learning outcomes?
More specifically, good learning outcomes: Are very specific, and use active language – and verbs in particular – that make expectations clear. This informs students of the standards by which they will be assessed, and ensures that student and instructor goals in the course are aligned.
How do you write course objectives and learning outcomes?
How do I write Effective Learning Objectives? 1,3Reflect on the course. ... Brainstorm specific things what you want students to know and do by the end of the course. ... Refer to resources that can help you identify action verbs that will be observable and measurable. ... Draft your learning outcomes and prioritize them.More items...•Jan 26, 2022
What are the 10 learning outcomes?
Top 10 Learning Outcomes to Help Children Develop During COVID-191 Develop a Growth or Innovation Mindset. ... 2 Develop Empathy. ... 3 Develop Resourcefulness. ... 4 Develop Creativity. ... 5 Become More Collaborative. ... 6 Strengthen a Sense of Belonging. ... 7 Become a Critical Thinker. ... 8 Develop Resilience and Persistence.More items...
How do I use learning outcomes in teaching?
Learning outcomes describe the measurable skills, abilities, knowledge or values that students should be able to demonstrate as a result of a completing a course. They are student-centered rather than teacher-centered, in that they describe what the students will do, not what the instructor will teach.
What is EYLF learning outcomes?
The EYLF Learning Outcomes are goals which can be achieved by a child during their learning. The outcomes and sub outcomes cover a variety of areas which include identity, community, wellbeing, learning and communication.Jan 7, 2015
Where do we get the learning outcomes?
Learning outcomes are statements that describe the knowledge or skills students should acquire by the end of a particular assignment, class, course, or program, and help students understand why that knowledge and those skills will be useful to them.
What are your own goals for learning?
Examples of Personal Learning GoalsDevelop Communication Skills. ... Negotiation Skills. ... Ethics and Social Responsibility. ... Teamwork and Flexibility. ... Reasoning and Making Good Judgment. ... Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills. ... Analytical Thinking. ... Creative Thinking.More items...
Why are learning outcomes important?
Learning outcomes are usually discussed within the context of program-wide assessment, but they can be valuable components of any class because of the way they sharpen the focus on student learning. Learning outcomes:
What is the key to writing effective learning outcomes?
The key to writing effective learning outcomes is the selection of active, measurable verbs— the tasks you want students to do at the end of your class. Words like know , understand, or appreciate are difficult to measure, and they rarely get at the higher order thinking tasks most of us really want to see in our students.
What is a learning outcome?
A Learning Outcome (LO) is a measurable, observable, and specific statement that clearly indicates what a student should know and be able to do as a result of learning. Well-written learning outcomes involve the following parts: Action verb. Subject content. Level of achievement.
What is the level of achievement?
A level of achievement identifies how proficient students need to be in a task. For example, in a Composition course, you might say “Write a literature critique with no grammatical errors”. This tells students the level of achievement that’s expected of them.
What is a CLO?
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) are central to your course’s curriculum. They articulate to students, faculty, and other stakeholders what students will achieve in each course and how their learning will be measured. A Learning Outcome (LO) is a measurable, observable, and specific statement that clearly indicates what a student should know ...
What is Dee Fink's learning outcomes?
This guide for course design from faculty developer Dee Fink will walk you through a process for developing learning outcomes that address different levels of cognitive thinking (in alignment with Bloom’s) but additionally some more humanistic learning outcomes. In his model, these latter outcomes are what make learning experiences “significant”, meaning that the learning will have a greater impact and persist longer because it includes an element of personalization and application to one’s own life.
What is Bloom's taxonomy?
Bloom’s taxonomy is a framework that provides a language and method for developing learning outcomes that vary across different levels of cognitive development. Skills like simple recall are called “lower order” cognitive skills and more complex skills like analysis and making predictions are “higher order”. The following resource on Bloom’s Taxonomy can help you craft clear learning outcomes across the spectrum as well as evaluate any current learning outcomes you have already developed. This framework can also be used to help you evaluate the type of questions you create for an exam or other assignment.
How to write learning outcomes?
Why Write Learning Outcomes? 1 describe to students what is expected of them 2 plan appropriate teaching strategies, materials and assessments 3 learn from and make changes to curriculum to improve student learning 4 assess how the outcomes of a single course align with larger outcomes for an entire program
Where are learning outcomes used?
Outcomes are used on many scales, from developing curriculum for a program of study to creating lessons for a single class activity. At the highest level, learning outcomes can be established at the university level. You can review the learning outcomes for DePaul graduates at the institutional level or program level.
What is a learning goal?
Learning goals are broad statements written from an instructor's or institution's perspective that give the general content and direction of a learning experience. They generally describe what an instructor or program aims to do; i.e., “The curriculum will introduce students to the major research methods of the discipline.”
What is learning objective?
Learning Objectives. Learning objectives are statements of what you intend to teach or cover in a learning experience. They tend to be. More specific than learning goals. Not necessarily observable nor measurable. Instructor-centered rather than student-centered. Useful in helping you formulate more specific learning outcomes.
What should outcomes be?
Outcomes should specify the skills and knowledge students must demonstrate to prove mastery instead of focusing on the assignment format, such as a quiz or essay. Well-worded outcomes should remain flexible enough to accommodate a variety of formats for a corresponding assessment.
What is the Center for Teaching and Learning?
The Center for Teaching and Learning supports the Assessment Certificate Program —a unique collaboration between DePaul and Loyola universities that provides professional development opportunities for faculty and staff in the field of assessment.
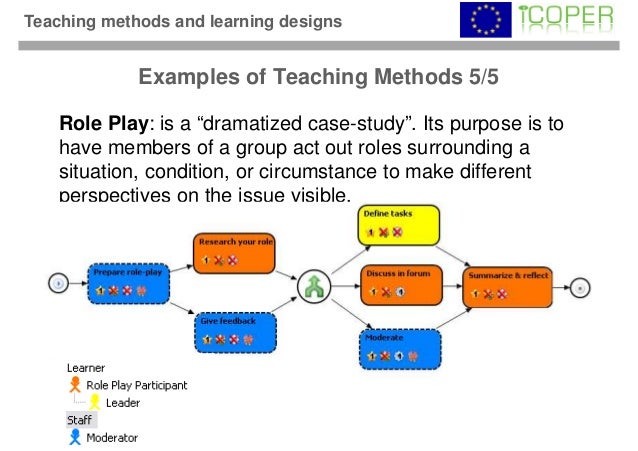
Steps to Writing Course Learning Outcomes For Your Course
- Step 1
Select an action verb using Bloom’s Taxonomy: “Linking iPads and Bloom’s Taxonomy” by Danny Maas See accessible version of this image. This is not an exhaustive list, but it does provide examples of specific verbs that link to different levels of student learning. For a more detailed ov… - Step 2
Next, select the subject content students are performing that task for. For example, in CLO 1 above, “areas of consensus and disagreement among publications on global warming” is the subject content: this is what the students are listing. Similarly, in the CLO “Develop a business pl…
Levels of Achievement
- A level of achievement identifies how proficient students need to be in a task. For example, in a Composition course, you might say “Write a literature critique with no grammatical errors”. This tells students the level of achievement that’s expected of them. Importantly, you don’t need a level of achievement for every CLO. You don’t need to say “effectively”, “accurately”, or “correctly” on a …
Conditions of Performance
- A condition of performance identifies if students are only performing this outcome in a specific context. For example, in a Welding course with a field placement, you might say “Demonstrate oxy-fuel-gas cutting techniques with limited supervision”. This tells students that they will be performing this task, but that they will be supervised while they do so. Again, you don’t need a co…
Tips and Tricks
- CLOs should be SMART outcomes. Use the following chart to see if your outcomes follow SMART principles: CLOs should have only one verb, and only one area of significant subject content. If your CLO includes multiple verbs, select the one that articulates the highest level of learning students will demonstrate in the course. If your CLO includes multiple topics, select the one that …
More Information
- Doran, G. T. (1981). "There's a S.M.A.R.T. Way to Write Management's Goals and Objectives", Management Review, Vol. 70, Issue 11, pp. 35-36. (Available through the library- login required for off-campus access.)
Popular Posts:
- 1. what is mass media course
- 2. how do you take tableau course on udemy if you don't have tableau
- 3. how to find valencia course number
- 4. those who possess the best information and know how to use it win course hero
- 5. what is the link between grade/subject and the nc standard course of study
- 6. what makes a memorable course of study
- 7. what is the purpose of the information literacy course?
- 8. what is the definition of business ethics? course hero
- 9. what language is the second-most common in latin america? course hero
- 10. mcps students who fail a course see the counselor