How do you find the acute angle from the course angle?
Dec 07, 2016 · A course line that crosses all meridians at a constant angle is known as a: A. Rhumb line course. B. Loxodrome. C. Straight line on a Mercator Map. D. All the above. 10. Which choice of navigational chart would be most INAPPROPRIATE for use at the South Pole? A.
What meridians does the rhumb line cut?
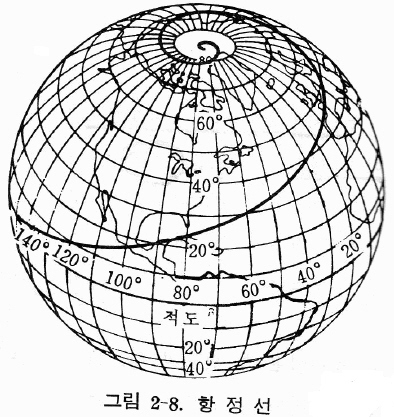
a line on a sphere or other surface of rotation that cuts across all meridians at a constant angle K (see Figure 1). The rhumb line and orthodrome (great circle) on a sphere were introduced and studied in 1624 by W. Snell. On a sphere and oblate ellipsoid of rotation where K = 0° and K = 180°, a rhumb line coincides with a meridian; where K = ±90°, it coincides with a geographic parallel. …
Which two points on a great circle have the same latitude?
(Navigation) A line which crosses successive meridians at a constant angle; -- called also rhumb line, and loxodromic curve. See Loxodromic.
How do you find the distance between course angles?
Such a line on the Earth’s surface is called a rhumb line. When the rhumb line cuts all meridians at 90 o, it will coincide with either a parallel of latitude or with the Equator. When the angle is 0 o, the rhumb line will be along a meridian of longitude. A vessel’s course will always be a rhumb line; thus the course to be steered to travel from one place to another will refer to the angle between …
What is the right angled triangle?
A series of right-angled triangles have been constructed along the rhumb line AZ and in each triangle, one short side lies along a meridian of longitude, one lies along a parallel of latitude and the hypotenuse lies along the rhumb line. It can be seen from the diagram that the east-west distance between two points along the rhumb line is ...
What is the approximate formula for mean latitude?
In most cases, the arithmetic mean of the two latitudes can be used as the middle latitude without appreciable error, so the approximate formula dep.= d.long cos ( mean lat) may be used.
How far is short distance sailing?
Short distance sailing is a term which is applied to sailing along a rhumb-line for distances less than 600 nautical miles. From the formulae derived in this chapter, the following are used extensively in short distance sailing:
rhumb line
A line on the surface of the earth making the same oblique angle with all meridians. Also known as loxodrome.
Rhumb Line
a line on a sphere or other surface of rotation that cuts across all meridians at a constant angle K (see Figure 1). The rhumb line and orthodrome (great circle) on a sphere were introduced and studied in 1624 by W. Snell.
What is composite sailing?
Composite sailing is a modification of great circle sailing to limit the maximum latitude, generally to avoid ice or severe weather near the poles. 2403. Terms and Definitions In solutions of the sailings, the following quantities are used: 1. Latitude (L).
What is the length of arc 1-2?
The length of arc 1-2 is the great circle distance between 1 and 2. Arcs 1- 2, P1, and P2 form a spherical triangle. The angle at 1 is the initial great circle course from 1 to 2, that at 2 the supplement of the final great circle course (or the initial course from 2 to 1), and that at P the DLo between 1 and 2.
What is traverse sailing?
Traverse sailing is the finding of a single equivalent course and distance.
How is speed measured?
Speed is measured in Knots ( kt). 1 knot is one nautical mile per hour. Always measure distances on the chart on the Latitude scale (North - South), at the side, opposite the distance required. (A minute of Longitude varies from approx 1 mile at the Equator to zero at the Poles, so cannot be used for measurements).
How does the Mercator projection work?
The Mercator Projection transforms the spherical earth onto a cylindrical flat sheet of paper. It distorts the latitude and longitude scales towards the Poles, so land masses near the poles are grossly exaggerated in area. But it has the great advantage that lines of a constant compass bearing are straight on the chart, so a navigator can plot a course once and maintain that heading over a long distance. This is called a Rhumb Line, and it crosses all meridians of longitude at a constant angle. It is not the shortest course.
What time zone is France in?
Local tide tables will usually be in local standard time. The sun rises one hour earlier in France, so in the almanac France is in Time Zone -0100, that is 1 hour BEFORE UT (ie you ADD 1 hour to UT to convert to French time). French Standard Time = British Summer Time = UT + 1 hour.
Popular Posts:
- 1. how much charge for the course hero
- 2. how to write the insert into for art course database
- 3. which of the following statements about global course hero
- 4. what strategies do you think you will need to be successful in an online math course
- 5. how to post to wgu course chatter
- 6. who owns muirfield village golf course in dublin ohio
- 7. mira costa how to find course id
- 8. what are good course ratings for undergraduate adjunct professors
- 9. how do you say prepares for the course in french
- 10. kirby air ride how to unlock last course