Does a coarse thread hold better than a fine thread?
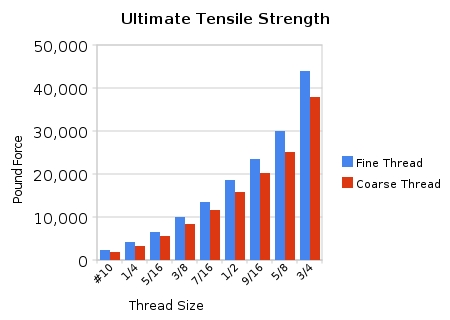
Size for size, a fine thread is stronger than a coarse thread. This is both in tension (because of the larger stress area) and shear (because of their larger minor diameter). Because of the smaller pitch, they allow finer adjustments in applications that need such a feature.
What is stronger fine or coarse thread?
- Fine threads won’t loosen as a result of the smaller thread include and off torque.
- With fine thread bolts, finer adjustments are made possible as a result of the small pitch.
- Fine thread bolts are tapped into hard materials with greater ease.
- Less torque is required to develop equivalent bolt preloads.
How to make a thread wait until another thread finish?
SHARE:
- Introduction In this tutorial, We'll learn how to use Thread.join () method in java. ...
- Thread.join () Syntax below is the syntax from Thread API. join () method is an overloaded method so we should be careful which method should be used. ...
- Thread.join () Example To Wait For Another Thread Execution Completion
Which is stronger coarse or fine thread bolts?
Value for money is important when it comes to buying fasteners and only the best quality will do. In many instances, fine thread bolts are stronger than coarse thread bolts. This can be seen in terms of tension as a result of a larger stress area as well as the shear as a result of the larger minor diameter.
Do fine threads strip easier than coarse threads?
Coarse threads are much less likely to experience thread galling than fine threads. Aerospace applications generally use coarse threads on sized 8–32 and smaller. Coarse threads are used when threaded into aluminum or cast iron because the finer threads tend to strip more easily in these materials.
What are advantages of coarse threads over fine threads?
Coarse threads are more durable and have greater resistance to stripping and cross-threading. The height of each thread is greater than the corresponding fine thread so there is more material between each thread making flank engagement greater.
What is the strongest screw thread?
Metric trapezoid thread, TR-40×7.
What is the advantage of a coarse thread?
Pros of Coarse Threads: Greater resistance to stripping and cross-threading. Faster installation than fine threaded fasteners, partially because they aren't prone to seizing during tightening. This can result in significant time and money savings in high volume assembly applications.
What is difference between fine and coarse thread?
What is the difference between fine and coarse thread fasteners? A. A fastener with a fine thread equates to a fastener with a large number of threads per distance along the fastener. In contrast, a coarse thread fastener equates to a fastener with a low number of threads per distance along the fastener.
What's the difference between coarse and fine?
The main difference between the two is in how large is the increment in each step. With coarse, a small movement results in a large jump, while the opposite is true in fine.
What are fine threads used for?
Fine threading makes tapping a hole much easier due to its narrow, shallow ridges. Fine thread fasteners are perfect to use in applications where vibration is an issue, since the shallow pitch of the thread works to prevent loosening of the fastener under vibration over time.
Which screw thread is stronger than other threads?
4. Which of the following screw thread is stronger than other threads? Explanation: Buttress thread is stronger than other threads because of greater thickness at the base of the thread. The buttress thread has limited use for power transmission.
What are the 3 basic types of threads?
There are three standard thread series in the Unified screw thread system that are highly important for fasteners: UNC (coarse), UNF (fine), and 8-UN (8 thread).
What are the cons and pros of selecting a coarse vs fine thread for a fastener?
Fine threads also possess larger minor diameters, which provide high shear strengths. Coarse threads tap better into brittle materials and are less likely to cross thread. Coarse threading lends itself to thicker coatings and platings before thread adjustments need to be made.
When would you use a coarse screw?
Coarse Threads Vs Fine Threads Fine thread screws are best for applications with smaller, shorter and specific measurements – coarse thread screws are better for comparatively bigger applications. Coarse thread screws are suitable for applications that need to be done with high speed and precision.
Can I use fine thread drywall screws on wood?
Fine thread drywall screws are made specifically for use with steel studs. Fine thread screws can be used when installing drywall on wood studs, but coarse thread drywall screws cannot be used with steel stud framing. Coarse thread screws are better suited for wood stud framing.
Why fine thread bolts over coarse thread?
Let’s take a look at a few more of the benefits of choosing fine thread bolts over coarse thread bolts: Fine threads won’t loosen as a result of the smaller thread include and off torque. With fine thread bolts, finer adjustments are made possible as a result of the small pitch. Fine thread bolts are tapped into hard materials with greater ease.
What is fine thread bolt?
Fine thread bolts are tapped into hard materials with greater ease. Less torque is required to develop equivalent bolt preloads. This doesn’t mean that coarse thread bolts aren’t of value to your applications that need fastening. Let’s take a look at the positives of coarse thread bolts:
When was Marsh Fasteners last updated?
Last Updated on July 1, 2020 by Marsh Fasteners. If you’re working with stainless steel bolts on a regular basis, chances are that you are going to want to invest in the strongest possible option. Value for money is important when it comes to buying fasteners and only the best quality will do.
Is coarse thread better than fine thread?
Coarse thread bolts aren’t prone to seizing during tightening and are therefore more suited to high speed assembly than fine thread bolts.
Why are fine threads used?
Because of the smaller pitch, they allow finer adjustments in applications that need such a feature. Fine threads can be more easily tapped into hard materials and thin-walled tubes. Fine threads require less torque to develop equivalent bolt preloads.
What is the difference between fine and coarse threaded bolts?
Bolts with coarse threads have a larger pitch (fewer threads per axial distance) compared to fine threads. A coarse threaded bolt is specified for most applications unless there is an overriding reason to use a fine threaded bolt (e.g. thorough thread adjustment is crucial for the application). Furthermore, fine thread fasteners are more difficult to obtain.
Which thread is more susceptible to galling?
Fine threads are more susceptible to galling than coarse threads.
Is fine thread stronger than coarse thread?
The potential benefits of fine threads are: Size for size, a fine thread is stronger than a coarse thread. This is both in tension (because of the larger stress area) and shear (because of their larger minor diameter). Because of the smaller pitch, they allow finer adjustments in applications that need such a feature.
Why are fine threads stronger under static loading?
Fine threads are technically stronger under static loading, because they have a larger minor diameter which translates into a larger cross-sectional area A s.
Can fine threads be used for load bearing joints?
In conclusion, fine threads should not be used for load bearing joints unless there is a very specific reason and testing is done to validate the joint. Some exceptions could be hard to tap materials or thin wall materials. For non-load bearing joints that require adjustment, fine threads may be your best option.
Does a fine thread have vibration resistance?
In the past, vibration resistance was thought to be a benefit of fine threads. The smaller helix angle, at least in theory, slows down the loosening process. A tradeoff of this benefit is the slower assembly time of fine threads; the smaller helix angle requires more angle of rotation to advance, slowing down the assembly process. A better solution to vibrational loosening can often be found in some sort of locking mechanism which can be recommended by your fastener source.
Which is better, coarse or fine thread?
Fine Thread. While coarse threading fasteners are better suited for general purpose applications, fine thread applications tend to have many benefits that make them the ideal choice when specifics matter. Fine threading has a higher tensile strength than coarse threading and it can be measured more accurately.
What is fine threading?
Fine threading consists of very shallow peaks and valleys when compared to coarse. As a result, tapping a hole for fine threading can be significantly easier as there is much less material to cut to form the threads. Fine threading also has a very shallow pitch (helical angle).
What is a helical thread?
This helical shaped threading can be either wide set and deep which are considered coarse thread while a more narrow helical shape with shallow ridges is considered to be fine thread.
Why use coarse thread fasteners?
Commonly chosen for construction simply because their threading can be lightly damaged and still work effectively. Coarse threading allows for more material to sit between these threads as they are installed.
What is fine thread fastener?
Fine thread fasteners are ideal for environments where vibration is considered an issue. Now that you know how to compare coarse thread vs. fine thread fasteners, you can make the right choice when deciding on which fasteners you need for a project.
Is it harder to strip or cross thread?
Due to this, it is harder for coarse threaded fasteners to strip or cross thread. Their extra tolerance allows for nicks or marring to occur on the edges of the threading without inhibiting the ability to fasten them. Coarse threading is also much less likely to gall then fine threading.
Does coarse threading gall?
Coarse threading is also much less likely to gall then fine threading. Fine threading requires many more turns per inch which generates more friction. Excess friction dramatically increases the chance of galling in fasteners. Regardless we recommend using an anti-seize solution especially on stainless steel fasteners.
Why are fine threads preferred?
When working with stainless steel, aluminum, titanium and other alloys, fine threads are preferable, particularly because of their strength.
What is coarse thread?
Coarse threads are typically called for in most industrial applications, particularly in aviation and military situations, due to a variety of advantages.
What is the role of threads in fasteners?
When it comes to fasteners, threads are key. Threads determine how well fastener components (like nuts, bolts and screws) hold materials and machines together, and maintain their integrity over time.
Can fine threaded bolts gall?
Fine threaded bolts can also gall (when metallic surfaces slide against one another and friction and adhesion cause material to be pulled from one surface and then adhered to the other) more easily than coarse threads, and they are often harder to obtain.
Which is stronger, coarse or fine thread?
It's a legitimate question, considering that coarse threads are stronger and have an overall greater resistance to cross-threading and stripping, while the fine thread fasteners have a slightly larger tensile stress area. The short answer is that for general industrial applications, coarse thread bolts present several advantages over fine threads.
Why are coarse threads better than fine threads?
The short answer is that for general industrial applications, coarse thread bolts present several advantages over fine threads. Higher resistance to stripping. In applications where the length of the thread engagement is short, coarse threads are preferable due to their higher resistance to stripping. Innately, coarse threads have ...
How fast is a 3/8-16 thread fastener?
They are easier and faster to assemble. A typical coarse thread fastener of 3/8-16 inch can be installed almost 70% faster than its 3/8-24 fine thread counterpart, thus saving you time, money and energy.
Why do stainless steel nut threads gall?
Galling occurs due to abnormal surface friction and the closer the fit between the mating threads, the more welded the nut will be.
Popular Posts:
- 1. where to run on the course in a marathon
- 2. when dies a 5 hour course expire
- 3. how many credits per course at upenn
- 4. how long do teachers accept work after course ends
- 5. how long does hunter education course take
- 6. when is a payee holder in due course
- 7. how large is los altos golf course
- 8. how to find course syllabus on
- 9. who know if the course will transfer to the new school
- 10. how to teach a course at cambridge adult school