What happens when a river moves from Upper to lower course?
Jun 11, 2013 · Before finding out how a river changes on its course we must first know what a river does. Rivers do three main things: · Erosion (when water hits rocks and makes it wear away into silt) · Transportion (when the current of the water takes the silt with it) · Deposition (when the water leaves the silt behind)
What changes occur as a river flows from its source?
Apr 24, 2014 · In order to achieve this balance rivers erode their banks, change their paths, and transport and deposit sediment along their way. Sections of a River. Rivers have three sections or courses: the upper course, middle course and lower course. The upper course of a river typically sees much erosion of bedrock in order to achieve the equilibrium mentioned above. The upper …
What happens to a river when it approaches the sea?
May 30, 2018 · There are several factors that contribute to the change in courses of the Mississippi River. The main factor is energy. The Mississippi is a very curvy, knowns as meandering, river. As the water flows through each of these meanders, there is a difference in the rate of flow between the inside and the outside of the meander.
Why do rivers become wide towards the lower part of plain?
A river changes shape as it flows from its source to its mouth. A section of the course of a river drawn from source to mouth is known as a long profile. Long profiles Long profile of a river The...
Where does a river change direction?
The Mekong River swells so much that the Tonle Sap River is actually forced to flow backward, northward away from the sea. It's the only river in the world that goes both ways.Feb 2, 2015
What is it called when a river changes course?
Avulsion - A change in channel course that occurs when a stream suddenly breaks through its banks.
What happens when a river changes course?
This change in energy results in an area of erosion and an area of deposition in each meander. Along the outside of the meander, where the water is moving at a higher velocity, the banks of the riverbed are being cut away.May 30, 2018
Why do rivers change?
The shape of rivers and streams changes through time as erosion, deposition, and transport of sediment occurs. Rivers and streams maintain a dynamic equilibrium between discharge, slope, sediment load, and sediment size (Lane 1955).
Why do rivers change direction?
Rivers changing direction is relatively common, according to the scientists, but is usually caused by tectonic forces, landslides or erosion.Apr 18, 2017
What are the effects of changing the course of a river on the environment?
More frequent droughts and shifting precipitation patterns lower water levels in rivers, lakes and streams, leaving less water to dilute pollutants. Higher temperatures cause more frequent algal blooms and reduce dissolved oxygen levels, both of which can cause fish kills and do significant harm to ecosystems.
Who owns the land when a river changes course?
If a river changes course quickly, cutting a new channel, then a landowner with property on just one side of a river suddenly may end up owning property on both sides. The rapid change of the river's location, known as avulsion, does not alter ownership boundaries.
How do rivers change?
Rivers change in kinetic energy, water flow rates, velocity, discharge and more as they go from start to finish. You may notice when looking at the path of a river that it gains width and depth as it gets closer to its endpoint at sea level.
What are some examples of ways in which a river will move around geography it cannot change quickly?
Rivers take the path of least resistance, skirting around tougher rocks or materials that aren’t as easily broken down by the strength of the water. Waterfalls, rapids and the movement of a river around hills or mountains are all examples of ways in which a river will move around geography it cannot change quickly.
What causes erosion in a river?
The river’s kinetic energy (or the energy that comes from the moving of the water as it flows downhill) is what causes the majority of the erosion to the geography of the river. Water moving past and over rocks, dirt, and other materials erodes them and often sweeps them along to be deposited further downstream.
What is the middle course of a river?
Rivers in the upper course erode down vertically which often creates a steep channel profile in what becomes the river valley. The middle course sees a river at a slightly lower altitude than the upper course, but is still maintains a sense of trying to acquire equilibrium in flow and shape.
What are the three sections of a river?
Rivers have three sections or courses: the upper course, middle course and lower course. The upper course of a river typically sees much erosion of bedrock in order to achieve the equilibrium mentioned above. The upper course is also at the highest altitude as this is where the headwaters of the river originate.
Why are rivers important?
Rivers are a unique feature in the geography of the earth. They provide dry inland areas with much needed fresh water and allow climates of every type to support life. Agriculture is supported by rivers and humans benefit from their existence in many ways.
Which path does a river follow?
Rivers typically follow the path of least resistance- from their headwaters to their outlets in the sea they are constantly moving around rocks and eroding valleys, growing and changing as they flow and age. Rivers function to get from their beginnings, or headwaters, to sea level through the most efficient path possible.
What are the factors that contribute to the change in the course of the Mississippi River?
There are several factors that contribute to the change in courses of the Mississippi River. The main factor is energy . The Mississippi is a very curvy, knowns as meandering, river.
When did the Mississippi River change course?
The last major change to the river’s course in the Vicksburg area occurred in 1876. On April 26 of that year, the Mississippi River suddenly changed courses, leaving Vicksburg high and dry.
What are abandoned meanders?
These meanders that became cut off from the rest of the river system create lakes known as abandoned meanders or oxbow lakes. Many of these abandoned meanders provide important marshland wildlife habitat. The last major change to the river’s course in the Vicksburg area occurred in 1876.
What river flows past Fort Hill?
This waterway is not the Mississippi river but rather a passage connected to the Mississippi called the Yazoo River. While the Yazoo River flows past now, in 1863 this was not the case. At that point in time, the Mississippi flowed ...
How long did the Yazoo River Diversion Project take?
The Yazoo River Diversion Project took 25 years to complete, lasting from 1878 until its completion in 1903. This once again gave river traffic access to the town of Vicksburg, which in turn helped bolster the town’s economy which was drying up due to lack of a functional river port.
Why is the flow on the inside of a river bend slower?
Meanwhile, the slower rate of flow on the inside of the river bend allows for the sediments being carried in the water to settle out and be deposited. This allows for the growth of meanders and the change in shape for the river.
Is water on the outside of a meander faster than the inside?
Water on the outside of a meander has a further distance to travel, thus it flows faster than the water on the inside of a meander.
How does the size of a river change as it moves from the source to the mouth?
As the river moves from the source to the mouth – both the depth of the river and the width of the river will both increase. The load of a river will also change as it is transported and eroded along the river's profile. As a result, the size and shape of stones will change as they journey through the river profile.
What is the area of land that it drained by a river and its tributaries?
The drainage basin. A drainage basin is the area of land that it drained by a river and its tributaries. When a droplet of water falls onto the land (as precipitation), gravity will make sure that the water is ‘pulled’ downhill to return to the sea. Part of.
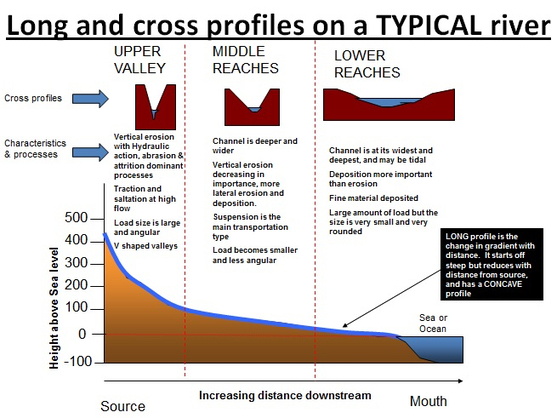
What is the long profile of a river?
Long profile of a river. The source of a river is often, but not always, in an upland area. Near the source, a river flows over steep slopes with uneven surfaces. It often flows over a series of waterfalls and rapids. As a river flows down steep slopes, the water performs vertical erosion.
What is the shape of a cross section through a river channel?
Definitions. Channel shape: this is the shape of a cross section through the river channel itself. It is about the width and depth of the channel. Valley profile: this is the shape of the valley on either side of the river channel. The measure it, we need to be able to measure the length and angle of the slopes perpendicular to the river.
What is sediment carried by a river called?
Sediment carried by the river is called its load. This will vary in size and shape depending on the hardness of the rocks and the time they have been in the river and affected by erosion (attrition). Sediment can be measured with rulers or calipers.
How to measure the depth of a channel?
Take the width of the channel and divide it into 11 equal parts. Measure the depth at the ten points across the channel. Always start from the same side; left or right when looking downstream. Record the measurements on the recording sheet.
How to measure gradient?
To measure gradient take two ranging poles and place them in the channel at a distance of 10 meters apart. Use a clinometers to measure the angle between them.
Why are slopes steep?
Slopes are steep - this can increase the velocity of the river after heavy rainfall, when discharge is high. The river channel is narrow and shallow here. The river's load is large in the upper course, as it hasn't been broken down by erosion yet. When discharge is high vertical erosion erodes the river bed and larger sediments are transported by ...
What is the main process that creates large floodplains and deltas?
The river's load is fine sediment, as erosion has broken down the rocks. The river channel is at its widest and deepest as it flows towards its mouth. Deposition is the main process in this part of the river, which creates large floodplains and deltas.
Why are valleys called V-shaped valleys?
The valley here has steep sides and the valley bottom is narrow. This is why valleys like this are called V-shaped valleys. Upper course - this is where the river starts and is usually an upland area. Slopes are steep - this can increase the velocity of the river after heavy rainfall, when discharge is high.
Why is the channel shallow?
The channel is shallow and narrow because there is not a lot of water in the channel. B – as the river flows into the middle course, there is some vertical erosion but more lateral erosion. The channel is wider and deeper as a result. C - in the lower course there is a lot less erosion, with only some lateral erosion.
What is a long profile?
A long profile is a line representing the river from its source (where it starts) to its mouth (where it meets the sea). A river changes with increasing distance downstream from its source towards its mouth. It moves through its upper course, to its mid-course and finally into its lower course. curriculum-key-fact.
What happened after the river Don burst?
After the River Don burst its banks in places, multiple roads in urban centres such as Rotherham flooded. DnG Photography/Shutterstock. Rivers respond to changes in climate as well. During drier periods, less water flows through river systems. This means that there is often less energy to move the sediments at their beds, ...
Why do floods occur?
This is true, but only part of the explanation. Floods also occur when the amount of water running off the land exceeds the capacity of rivers to carry that flow – as was the case when the River Don breached flood defences in the Sheffield area recently. So, floods are partly caused by the amount ...
When will floods happen in England?
Rivers are changing all the time, and it affects their capacity to contain floods. November 11, 2019 12.03pm EST. The rainfall that has inundated the North of England is the latest in a long line of flood events that are becoming the country’s new normal. Indeed, across the world, flooding is expected to become more frequent and more extreme as ...
Which river is the most densely populated in the world?
For example, the Ganges-Brahmaputra river in India and Bangladesh falls under this category. Its capacity is already changing, and its floodplains are some of most densely populated in the world.
Is flooding more frequent?
Indeed, across the world, flooding is expected to become more frequent and more extreme as the planet heats up. Building robust flood defences and modelling vulnerable areas is crucial if we are to avoid loss of life and livelihoods from these devastating weather events. But our new research reveals that the capacity of rivers to keep water flowing ...
Is a river channel a fixed feature?
Uncertain risk. Unfortunately, such changes are typically ignored by flood engineers and modellers, who generally treat the channel as a fixed feature. If rivers actually change their capacity in space and time, then estimates of flood probability may be incorrect, putting people and property at risk.
Does river capacity increase flood risk?
However, in river systems that carry high volumes of sediment, or in parts of the world where rainfall varies considerably during the year, sudden reductions in river capacity may dramatically increase flood risk for nearby settlements. For example, the Ganges-Brahmaputra river in India and Bangladesh falls under this category.
Popular Posts:
- 1. which of the following statements about smartart graphics is not true? course hero
- 2. how to prepare a 7 course dinner
- 3. makemkv which ice age collision course blu ray title to rip
- 4. how often can you take a driver improvement course
- 5. how to unregister for a course ubc
- 6. ut how to read course number
- 7. what is the cost of the aarp classroom driver safety course
- 8. 1. what argument does the course syllabus make (use your own words)?
- 9. of course i'm right i'm bob quote what about bob
- 10. what does non accredited course mean