Trauma is a person’s emotional response to a distressing experience. Few people can go through life without encountering some kind of trauma. Unlike ordinary hardships, traumatic events tend to be sudden and unpredictable, involve a serious threat to life—like bodily injury or death—and feel beyond a person’s control.
Full Answer
How to learn about trauma?
Trauma-informed care (TIC) involves a broad understanding of traumatic stress reactions and common responses to trauma. Providers need to understand how trauma can affect treatment presentation, engagement, and the outcome of behavioral health services. This chapter examines common experiences survivors may encounter immediately following or long after a traumatic …
What is a trauma nurse core course?
FAST is the first national STOP THE BLEED ® course designed specifically for high school students, but anyone can take the course and benefit from the training.. You can save a life: Preparing for bleeding emergencies; recognizing that a bleeding emergency exists; emergency action steps; deciding to act in an emergency. Safety in emergency situations: Keeping yourself …
What is trauma focused training?
First Aid for Severe Trauma (FAST) Training | Red Cross. Posted: (1 week ago) FAST is the first national STOP THE BLEED ® course designed specifically for high school students, but anyone can take the course and benefit from the training.. You can save a life: Preparing for bleeding emergencies; recognizing that a bleeding emergency exists; emergency action steps; deciding …
What are the education requirements for a trauma surgeon?
It results from exposure to an incident or series of events that are emotionally disturbing or life-threatening with lasting adverse effects on the individual’s functioning and mental, physical, social, emotional, and/or spiritual well-being. Experiences that may be traumatic include: Physical, sexual, and emotional abuse Childhood neglect
What is trauma in first aid?
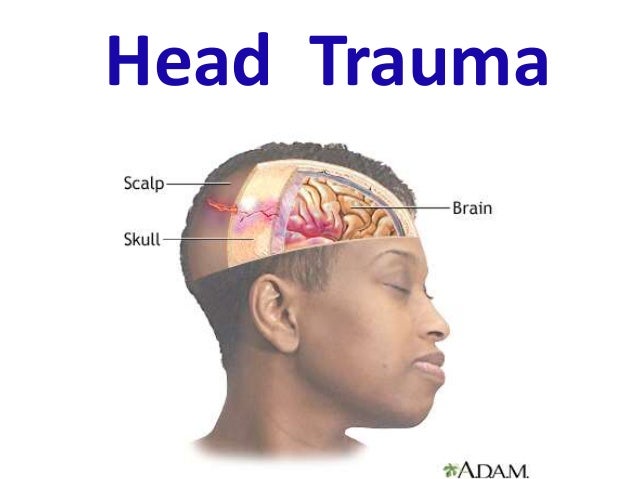
A trauma injury refers to sudden physical injuries that require immediate first aid or medical attention. An example could be something like broken bones after a road traffic collision, or perhaps someone has suffered a head injury and is bleeding extensively.
What is a trauma class?
A trauma-informed classroom recognizes that kids have gone through some serious events in their lives. Not only do they carry the memory of those events with them, but their brains are different because of this trauma.Jun 23, 2020
What does FAST stand for Red Cross?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. FAST is an acronym used as a mnemonic to help detect and enhance responsiveness to the needs of a person having a stroke. The acronym stands for Facial drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties and Time to call emergency services.
What is a trauma team in a hospital?
The trauma team is a multi-disciplinary group of health care providers that render care to patients who have been seriously injured. Each member has specific roles and responsibilities that are carried out under the direction of the trauma team leader.
What are the 3 types of trauma?
There are three main types of trauma: Acute, Chronic, or ComplexAcute trauma results from a single incident.Chronic trauma is repeated and prolonged such as domestic violence or abuse.Complex trauma is exposure to varied and multiple traumatic events, often of an invasive, interpersonal nature.
How do you treat students with trauma?
As with many strategies to support a sub-group of students, these strategies can positively support most students with or without a history of trauma.Communicate with counselors or social workers. ... Provide structure and consistency. ... Ease transitions. ... Provide choice. ... Develop strengths and interests. ... Be there.More items...•Sep 14, 2014
What is the stroke word?
The acronym FAST (Facial drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulties and Time) has been used by the National Stroke Association, American Heart Association and others to educate the public on detecting symptoms of a stroke.May 12, 2016
What are the early warning signs of a stroke?
Warning Signs of StrokeWeakness or numbness of the face, arm or leg, usually on one side of the body.Trouble speaking or understanding.Problems with vision, such as dimness or loss of vision in one or both eyes.Dizziness or problems with balance or coordination.Problems with movement or walking.Fainting or seizure.More items...
What does smile mean for stroke?
In general, the best way to tell if someone is having a stroke is to use the acronym FAST, which stands for face drooping, arm weakness, speech difficulty, and time to call 911. If you think someone is having a stroke, ask them to smile, raise an arm, and speak a short sentence.Dec 2, 2013
What are the 5 levels of trauma care?
There are 5 levels of trauma centers: I, II, III, IV, and V. In addition, there is a separate set of criteria for pediatric level I & II trauma centers. The trauma center levels are determined by the kinds of trauma resources available at the hospital and the number of trauma patients admitted each year.Dec 9, 2018
What is trauma call?
If the patient has an airway issue, has ongoing visible haemorrhage, or is in cardiac arrest, the trauma team leader will ask the pre-hospital member to wait while these issues are addressed by the trauma team. Information from the handover will then be delivered subsequently.Jun 14, 2018
What are trauma patients?
A trauma patient is a person who has suffered a physical injury which may be minor, serious, life-threatening or potentially life-threatening. Trauma injuries are usually categorised as a blunt or penetrating wound.
What is the most common trauma related disorder?
The trauma-related disorder that receives the greatest attention is PTSD ; it is the most commonly diagnosed trauma-related disorder, and its symptoms can be quite debilitating over time. Nonetheless, it is important to remember that PTSD symptoms are represented in a number of other mental illnesses, including major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, and psychotic disorders ( Foa et al., 2006 ). The DSM-5 ( APA, 2013a) identifies four symptom clusters for PTSD : presence of intrusion symptoms, persistent avoidance of stimuli, negative alterations in cognitions and mood, and marked alterations in arousal and reactivity. Individuals must have been exposed to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence, and the symptoms must produce significant distress and impairment for more than 4 weeks ( Exhibit 1.3-4 ).
What are the emotional reactions to trauma?
Beyond the initial emotional reactions during the event, those most likely to surface include anger, fear, sadness, and shame.
What is a CSR in the military?
CSR is an acute anxiety reaction occurring during or shortly after participating in military conflicts and wars as well as other operations within the war zone, known as the theater. CSR is not a formal diagnosis, nor is it included in the DSM-5 ( APA, 2013a ). It is similar to acute stress reaction, except that the precipitating event or events affect military personnel (and civilians exposed to the events) in an armed conflict situation. The terms “combat stress reaction” and “posttraumatic stress injury” are relatively new, and the intent of using these new terms is to call attention to the unique experiences of combat-related stress as well as to decrease the shame that can be associated with seeking behavioral health services for PTSD (for more information on veterans and combat stress reactions, see the planned TIP, ; SAMHSA, planned f).
How do trauma survivors relive their past?
A hallmark symptom of trauma is reexperiencing the trauma in various ways. Reexperiencing can occur through reenactments (literally, to “redo”), by which trauma survivors repetitively relive and recreate a past trauma in their present lives. This is very apparent in children, who play by mimicking what occurred during the trauma, such as by pretending to crash a toy airplane into a toy building after seeing televised images of the terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001. Attempts to understand reenactments are very complicated, as reenactments occur for a variety of reasons. Sometimes, individuals reenact past traumas to master them. Examples of reenactments include a variety of behaviors: self-injurious behaviors, hypersexuality, walking alone in unsafe areas or other high-risk behaviors, driving recklessly, or involvement in repetitive destructive relationships (e.g., repeatedly getting into romantic relationships with people who are abusive or violent), to name a few.
Why do people avoid people?
Individuals begin to avoid people, places, or situations to alleviate unpleasant emotions, memories, or circumstances. Initially, the avoidance works, but over time, anxiety increases and the perception that the situation is unbearable or dangerous increases as well, leading to a greater need to avoid. Avoidance can be adaptive, but it is also a behavioral pattern that reinforces perceived danger without testing its validity, and it typically leads to greater problems across major life areas (e.g., avoiding emotionally oriented conversations in an intimate relationship). For many individuals who have traumatic stress reactions, avoidance is commonplace. A person may drive 5 miles longer to avoid the road where he or she had an accident. Another individual may avoid crowded places in fear of an assault or to circumvent strong emotional memories about an earlier assault that took place in a crowded area. Avoidance can come in many forms. When people can’t tolerate strong affects associated with traumatic memories, they avoid, project, deny, or distort their trauma-related emotional and cognitive experiences. A key ingredient in trauma recovery is learning to manage triggers, memories, and emotions without avoidance—in essence, becoming desensitized to traumatic memories and associated symptoms.
What are the immediate reactions of a trauma survivor?
Survivors’ immediate reactions in the aftermath of trauma are quite complicated and are affected by their own experiences, the accessibility of natural supports and healers, their coping and life skills and those of immediate family, and the responses of the larger community in which they live. Although reactions range in severity, even the most acute responses are natural responses to manage trauma— they are not a sign of psychopathology. Coping styles vary from action oriented to reflective and from emotionally expressive to reticent. Clinically, a response style is less important than the degree to which coping efforts successfully allow one to continue necessary activities, regulate emotions, sustain self-esteem, and maintain and enjoy interpersonal contacts. Indeed, a past error in traumatic stress psychology, particularly regarding group or mass traumas, was the assumption that all survivors need to express emotions associated with trauma and talk about the trauma; more recent research indicates that survivors who choose not to process their trauma are just as psychologically healthy as those who do. The most recent psychological debriefing approaches emphasize respecting the individual’s style of coping and not valuing one type over another.
How old is Sadhanna?
Sadhanna is a 22-year-old woman mandated to outpatient mental health and substance abuse treatment as the alternative to incarceration. She was arrested and charged with assault after arguing and fighting with another woman on the street. At intake, Sadhanna reported a 7-year history of alcohol abuse and one depressive episode at age 18. She was surprised that she got into a fight but admitted that she was drinking at the time of the incident. She also reported severe physical abuse at the hands of her mother’s boyfriend between ages 4 and 15. Of particular note to the intake worker was Sadhanna’s matter-of-fact way of presenting the abuse history. During the interview, she clearly indicated that she did not want to attend group therapy and hear other people talk about their feelings, saying, “I learned long ago not to wear emotions on my sleeve.”
What is traumatic experience?
It results from exposure to an incident or series of events that are emotionally disturbing or life-threatening with lasting adverse effects on the individual’s functioning and mental, physical, social, emotional, and/or spiritual well-being. Experiences that may be traumatic include:
How does trauma affect health?
The landmark ACE Study and the Philadelphia Urban ACE Study reveal that the more a child is exposed to stressful and potentially traumatic experiences, the greater his or her risk for chronic health conditions and health-risk behaviors .
How does trauma affect relationships?
This includes, but is not limited to, relationships between people, communities, and the delivery systems that support individuals’ health and social needs. When a person experiences trauma, he or she may feel unsafe, betrayed, ...
What are maladaptive behaviors?
Sometimes, these strategies involve maladaptive behaviors — such as unhealthy eating, tobacco use, or drug and alcohol use. These coping mechanisms may provide some relief, but they can also simultaneously contribute to anxiety, social isolation, and chronic diseases.
Is ACEs high risk?
However, research has shown that the risk for ACEs is particularly elevated within certain populations such as people who identified as black, Hispanic, or multiracial; people with less than a high-school education; people with low-income or who were unemployed or unable to work; and people who identified as gay, lesbian, or bisexual.
Is trauma science?
The Science of Trauma. Although the field of trauma-informed care is still coalescing, our understanding about how people’s brains and bodies respond to trauma — and the negative long-term effects of toxic stress on health — is well understood .
Basic Management of the Trauma Patient
Welcome to Trauma Emergencies and Care. In this course, you will learn about some of the mechanics and physics of trauma on the human body, and how this can cause injury. You will continue to expand your new vocabulary with medical terminology, and learn how to describe the different injuries you may see.
Skills You'll Learn
Are you ready to take on trauma? From the battlefield to highways, traumatic injuries were the catalyst for developing systems to move patients to places that they could receive more advanced care. In this module we will talk about what trauma is and why it deserves special attention when it comes to patient care.
What is the University of Colorado?
The University of Colorado is a recognized leader in higher education on the national and global stage. We collaborate to meet the diverse needs of our students and communities. We promote innovation, encourage discovery and support the extension of knowledge in ways unique to the state of Colorado and beyond.
Does Coursera give financial aid?
Yes, Coursera provides financial aid to learners who cannot afford the fee. Apply for it by clicking on the Financial Aid link beneath the "Enroll" button on the left. You'll be prompted to complete an application and will be notified if you are approved.
Can you see lectures in audit mode?
Access to lectures and assignments depends on your type of enrollment. If you take a course in audit mode, you will be able to see most course materials for free. To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will need to purchase the Certificate experience, during or after your audit.
What is trauma in psychology?
Trauma is what happens inside you, as a result of what happens to you.”. - Gabor Maté. "Every human being has a true genuine authentic self and the trauma is that disconnection from it and the healing is the reconnection with it.". - Gabor Maté.
What is the invisible force that shapes our lives?
Trauma is the invisible force that shapes our lives. It shapes the way we live, the way we love and the way we make sense of the world. It is the root of our deepest wounds. Dr.
Who is Zaya Benazzo?
Zaya Benazzo. Producer/Director. Maurizio grew up in Genova, Italy. At an early age he began actively traveling the spiritual path, exploring the practices of Zen Buddhism, Transcendental Meditation, Yogic philosophy, Catholicism and Philosophy.
Where is Zaya from?
Zaya has degrees in Engineering, Environmental Science, and Film. Born in Bulgaria, she produced and directed several award wining documentaries in Europe and the USA, including Energy for Survival, Hunger Gathering, Airwaves, Wings and Strings, Screeming Queens, America's Chemical Angels and more.
About Child Trauma
Children who suffer from child traumatic stress are those who have been exposed to one or more traumas over the course of their lives and develop reactions that persist and affect their daily lives after the events have ended.
Trauma Types
When a child feels intensely threatened by an event he or she is involved in or witnesses, we call that event a trauma. There is a range of traumatic events or trauma types to which children and adolescents can be exposed.
Populations at Risk
Some groups of children and families are disproportionately represented among those experiencing trauma.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what college course is ap statistics equivelant to
- 2. where can i take an online foreign language college course missouri
- 3. the tendency for people to see what they expect to see helps to perpetuate. course hero
- 4. udemy how to design a logo - a beginners course torrents
- 5. which of the following accounts normally has a credit balance course hero
- 6. when is the last day to drop a course ucsd
- 7. how many points of reference are needed to stay on course
- 8. how to perform wind mitigation inspections course
- 9. how does taking a college course during high school help
- 10. what is the best course to take in university of pennsylvania