True Course: The aircraft’s course over the ground relative to true north. True course is measured with a navigation plotter and a sectional map. True Heading: True course corrected for wind.
How do airplanes calculate their true course?
Jun 16, 2008 · 1) True Course (TC): This is the course measured from your navigation plotter when you plot your flight on your map. Remember that because of the projection of the map, it is best to read this course in the middle of the leg. 2) True Heading (TH): Now that you have a true course, we need to correct for winds which will give us a true heading.
What is true course and true heading in aviation?
Course (C) is the horizontal direction in which a vessel is steered or intended to be steered. Depending on the reference direction the following terms are used: true course or true heading is expressed as angular distance from true North clockwise from 000° through 360°. magnetic course refers to magnetic north.
What is the difference between magnetic course and true course?
Jan 28, 2020 · True course is a term that tells you what course an airplane is following across the ground. Airplanes are designed to calculate their true course using a sectional map and a navigation plotter. True heading is the same as true course, but with one alteration. True heading corrects for wind. More Aviation Terminology
How to determine the true heading of a plane?
How do you know if a course is true? Navigational Plotter Instructions . Use your plotter to determine the true course (TC), the total distance of your flight, and. Place the small hole in the center of the protractor section over a meridian (line of. If your course is nearly north or south and does not cross a meridian, place the hole of.
What is the difference between ground track and true course?
The difference between the two depends on wind. A true heading or course is corrected for magnetic variation; a magnetic heading or course is not. Track and course are often used interchangeably, but technically a "course" refers to what you intend to do while a "track" refers to what you actually do.Jan 17, 2019
What does magnetic course mean?
Definition of magnetic course : the course on which an airplane is intended to be flown that is measured from magnetic north and that is the true course as laid out on the chart.
How do you calculate true course?
1:073:58VFR Nav Log (Video 2) True Course and Distance - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then you need to find a line of longitude or latitude. Over which to put the center of theMoreAnd then you need to find a line of longitude or latitude. Over which to put the center of the plotter because that's what you're going to use to measure. So there's a line of latitude.
How do you get a true course magnetic course?
3:1411:25True/Magnetic Course/Heading - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBetween let's say here and here that angle is gotten smaller. Because I'm measuring this angle andMoreBetween let's say here and here that angle is gotten smaller. Because I'm measuring this angle and that would be my magnetic course and on an eastward variation you see I took this angle.
What is the difference between true course and magnetic course?
Magnetic Course: True course corrected for magnetic variation. Magnetic Heading: True heading corrected for magnetic variation. You can determine the magnetic variation from a sectional map. True Course: The aircraft's course over the ground relative to true north.Jan 9, 2020
What does true heading mean?
True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole and geographic north pole being hundreds of miles apart.
Does Foreflight show true course?
DrPappy Pre-takeoff checklist Sounds like Foreflight is giving you the actual magnetic course and the Sectional(and IFR chart) is giving what you would set on the OBS to fly from that VOR. The current magnetic declination in that area is 4 degrees East. The VOR is set at 8 degrees East.Jan 15, 2015
How do you calculate true bearing?
(i) True Bearing = (Magnetic Bearing + Declination) = (89°45՛ + 5°30՛) = 95°15՛. b) In fig. (ii) True Bearing = (Magnetic Bearing – Declination) = (89°45՛ – 4°15՛) = 85°30՛.Jun 4, 2019
How do you convert true to compass?
1:574:44Converting between true and compass bearings - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo that would be 180 minus 14 66 degrees as a trim they're. Pretty easy okay let me change colors.MoreSo that would be 180 minus 14 66 degrees as a trim they're. Pretty easy okay let me change colors. Suppose you have to get the other way convert these true bearings into compass bearings.
What is the difference between magnetic course and compass course?
Compass course: (cc or CTS) the course which is corrected for both variation and deviation. Magnetic course: (mc) the course which is only corrected for variation. cc + var + dev = tc: this equation shows the connection between the compass course, its errors and the true course.
What is true heading in aviation?
The direction in which the longitudinal axis of an aircraft is pointed, usually expressed in degrees from North (true, magnetic, compass or grid). ( Source: ICAO)
What is true course?
True course is a term that tells you what course an airplane is following across the ground. Airplanes are designed to calculate their true course using a sectional map and a navigation plotter.
What is the ground effect of an airplane?
Aircraft ground effect is the name for a fascinating aviation phenomenon. As the airplane gets closer and closer to the ground, at some point it becomes difficult for the airplane to continue to descend.
What is magnetic course?
Magnetic course is another term that is based on true course. True course bases its movement calculations on the plane’s location relative to true north. Since true north is based on the earth’s magnetic field, and the magnetic field can fluctuate, the true course today and the true course tomorrow may be different.
What is heading in airplanes?
This does not factor for wind, or the actual movement of the airplane across the ground. It only refers to what the compass reads based on where the nose is pointed.
How is course similar to bearing?
Course. Course is very similar to bearing in that it’s the desired direction for your route of flight. If you are going directly from one airport to the other, your course and bearing will be the same along the route of flight. If you are flying from an airport to a VOR to another airport, your course will change in each leg, as will your bearing.
What is the difference between a track and a heading?
Heading is the direction the airplane is pointed, whereas track is the actual direction of the airplane tracking across the ground. Bearing is the angle between any two points, whereas course is your intended path of travel to your destination. In the rest of this post we’ll elaborate on each of these points and then also provide ...
Why is bearing confusing?
Bearing can be confusing sometimes because has some overlap with course. Bearing is simply the angle or direction between two points. A practical application of this is in VOR navigation. It’s a common thing to hear someone say “we are bearing 090 from the station”.
What is the difference between magnetic and true north?
History in the Difference Between True and Magnetic North. True North is the North Pole. The maps used for navigating are oriented to the North Pole. A pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a “track” or “course” to fly in degrees true.
How does a compass work?
Without getting into exactly how a compass works, it’s basically like this: The compass contains certain metals (magnets) that are attracted to metals inside Earth’s crust and thus the magnetic compass orients itself to magnetic north. To find true north, you need to know the nearby variation.
Where is the North Star?
An approximation of “celestial north” is in the direction of Polaris, which is a fairly bright star in the night sky and also the closest such star to Earth’s rotational axis (and thus “true north”) for about the last 1500 years. This is where the “North Star” comes from.
What is the North Pole?
The true north pole, also known as the celestial north pole, is the point on the Earth’s surface intersecting Earth’s rotational axis on the northern hemisphere (and the axis around which all stars appear to rotate).
What is magnetic heading?
Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole and geographic north pole being hundreds of miles apart. There are some interesting reasons why these poles are not in ...
What is the difference between true and magnetic?
What’s up with Magnetic North vs True North? “ True north” is the northern axis of rotation of the Earth. It is the point where the lines of longitude converge on maps. “ Magnetic north” is the point on the Earth’s surface where its magnetic field points directly downwards.
Do aircraft use magnetic or true north?
Most large aircraft use inertial reference units and flight management systems that complete calculations using True North and add magnetic variation values from tables to display information to pilots.
What is the difference between true course and magnetic course?
Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. The difference is due to the magnetic north pole and geographic north pole being hundreds of miles apart.
Do you fly magnetic heading or magnetic course?
Magnetic Course: True course corrected for magnetic variation. Magnetic Heading: True heading corrected for magnetic variation. You can determine the magnetic variation from a sectional map. True Course: The aircraft’s course over the ground relative to true north.
Are VORS true or magnetic?
VOR degrees are magnetic, not true, so you can read your magnetic course for that location right from the VOR rose. Again, the difference between the true course you’ve drawn on your chart and the magnetic course that runs through the VOR rose is the magnetic variation.
Do magnets work underwater?
Water is almost completely non-magnetic, so magnets work underwater the same as they do in air or in a vacuum. Magnets underwater work like they do above ground—if they find something they’re attracted to, the force between them pulls them together.
Does GPS use true north or magnetic north?
The GPS receiver natively reads in true north, but can elegantly calculate magnetic north based on its true position and data tables; the unit can then calculate the current location and direction of the north magnetic pole and (potentially) any local variations, if the GPS is set to use magnetic compass readings.
What is the course of a watercraft?
In navigation, the course of a watercraft or aircraft is the cardinal direction in which the craft is to be steered. The course is to be distinguished from the heading, which is the compass direction in which the craft's bow or nose is pointed.
What is the path a ship follows over the ground called?
The path that a vessel follows over the ground is called a ground track, course made good or course over the ground. For an aircraft it is simply its track. The intended track is a route. For ships and aircraft, routes are typically straight-line segments between waypoints. A navigator determines the bearing (the compass direction from ...
What is true airspeed?
True Airspeed (TAS): The actual speed relative to the surrounding air. True airspeed is calibrated airspeed corrected for nonstandard pressure and temperature. You can determine the aircraft's true airspeed with a flight computer.
Where is the true north?
True North: The geographic north pole is located at the Earth's northernmost point. True north is not the same location as magnetic north, due to the rotation of the earth in relation to the earth's magnetic field.
What is ground speed?
Groundspeed (GS): The actual speed of the airplane passing over the ground. Groundspeed is true airspeed corrected for wind. You can find the aircraft ground speed by calculating it with a flight computer. True Airspeed (TAS): The actual speed relative to the surrounding air.
What is indicated altitude?
Indicated Altitude: The altitude depicted on the altimeter. Indicated altitude is the vertical distance above mean sea level (MSL), not above the ground. Density Altitude: Pressure altitude corrected for nonstandard temperature. You can calculate density altitude with a flight computer.
What is the magnetic north?
Magnetic North: The northern location where the Earth's magnetic force has the most downward pull. If you were to stand on magnetic north, a magnetic compass would point straight down. Magnetic north varies due to shifts in the Earth's core and is at a different location than true north.
Who is Sarina Houston?
Aircraft Navigation Terms and Definitions. Sarina Houston was the aviation expert for The Balance Careers. She is a commercial pilot and certified flight instructor. Aircraft navigation terms can often be confusing, especially when a pilot doesn't use them every day.
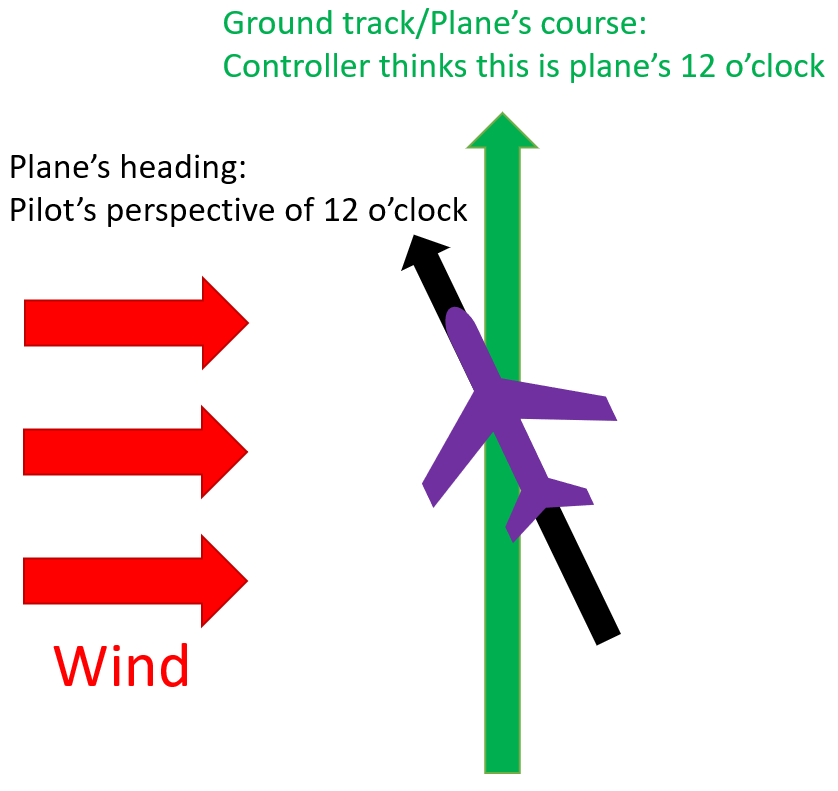
Heading
Track
- Track is the easiest of these four to understand in my mind,because it simply refers to how you are actually tracking over the ground. Whennavigating in the air, your track is really all that matters in terms ofgetting to where you want to go. If you need to go northeast to yourdestination, and have a significant wind from the west, your heading might beto the north in order to achieve a tr…
Bearing
- Bearing can be confusing sometimes because has some overlap with course. Bearing is simply the angle or direction between two points. A practical application of this is in VOR navigation. It’s a common thing to hear someone say “we are bearing 090 from the station”. This simply means that off of the VOR they are tracking on the 090 radial outbound from the station. In relation to th…
Course
- Course is very similar to bearing in that it’s the desireddirection for your route of flight. If you are going directly from one airportto the other, your course and bearing will be the same along the route of flight.If you are flying from an airport to a VOR to another airport, your course willchange in each leg, as will your bearing.
Example
- For this example we’re going to work backwards through the above mentioned directions. Assume you are departing an airport and your destination is directly eastbound. When you take off the course between the departing airport and destination airport is 090. In this instance the bearing of the destination airport off of your departing airport is also 090. This is also the direction you wan…
Does A GPS Use True Or Magnetic Heading?
- The above example assumes you are using the compass in yourairplane (hence why it requires so many steps to calibrate the differencebetween your true course all the way down to your actual compass heading). Butwhat about a GPS? By definition it’s not using earth’s magnetic fields as a wayof navigation, but rather positioning information provided by satellites. So ifit shows your “de…
What’s The Difference Betweentrue and Magnetic North?
Calculating True vs. Magneticheadings
- Toget the magnetic heading, just read the heading off your magnetic compass.Without getting into exactly how a compass works, it’s basically like this: The compass contains certain metals(magnets) that are attracted to metals inside Earth’s crust and thus the magnetic compassorients itself to magnetic north. To find true north, you need to know the nearby variati…
History in The Difference Betweentrue and Magnetic North
- True North is the North Pole. The maps used for navigating are oriented to the North Pole. A pilot can measure the direction between two points to create a “track” or “course”to fly in degrees true. Thetrue north pole, also known as the celestial north pole, is the point on theEarth’s surface intersecting Earth’s rotational axis on the northern hem...
Why The Difference Between trueand Magnetic Heading Matters
- In the grand scheme of the size of Earth, one can see that true north and magnetic north are relatively close. This is especially true from the perspective of those of us in the New World, but if you were sailing off the west coast of the British Isles, you might see up to a ten-degree difference between your compass and Polaris, and that’s significant over a distance of even a few hundred …
Magnetic North Has Moved Overtime
- Earth’s magnetic pole changes over time. According to surveys dating back to the past 130 years, magnetic north is moving closer and closer to true north. One PHAK explanation said this could be due “possibly to gyroscopic stabilizations of the convective flows within earth’s liquid inner layers. Again, for most of the U.S. the practical effects of observed shifts are minimal, but it has …
Why We Forget The Difference Intrue and Magnetic Headings
- Intoday’s world it’s becoming easier and easier to simply input an airport intoour GPS, and push “direct, enter, enter”without much thought. The worst part (for CFI’s teaching new private students)is it’s highly accurate. GPS units have the magnetic variationincluded in their database and, knowing its position, will apply theappropriate value to the true track it has calculated. AGP…
Conclusion
- Truenorth and magnetic north are two things that aren’t thought about with everydayflying, but they are the groundwork, the soil, the algorithm of the common GPSwhich helps us get from point A to point B most directly. Flyingin today’s world requires a tight-rope walk. A good pilot today should not onlyknow the intricacies of GPS or “glass panel” flying, but should also have theneces…
Popular Posts:
- 1. be crushed by a speeding wall how to get the impossible course badge
- 2. a character who has many sides over the course of a story is known as a
- 3. what is dhs/fps 8 hour weapons refresher course 0f fire
- 4. how long is the defensive driving course nyc
- 5. what options do you have if you didn't pass and end of course test
- 6. how to describe a course of study
- 7. course hero people who see a necker cube differently are showing differences in
- 8. how to install a rally course mod gta 5
- 9. what you learn in a reproduction course
- 10. after engineering degree how can i purse my course in law