Medication
The EBV antibody test can help determine whether you have ever been infected with the virus and whether the infection has been recent. EBV antibody testing is usually done when you have symptoms of infectious mononucleosis and a monospot test result is negative.
Procedures
- Introduction. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a herpes virus that commonly causes infectious mononucleosis (IM) and linked to different hematological conditions.
- Case Presentation. A 20-year-old male presented with fever, thrombocytopenia, and splenomegaly. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Conclusion. ...
Self-care
What is the best home remedy for mononucleosis?
- Rest. Your body will fight off the infection, so give it plenty of rest.
- Drink fluids. Water and fruit juices both fight off fever and help relieve a sore throat. ...
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers. ...
- Gargle with saltwater. ...
- Moisturize the air you breathe. ...
Nutrition
What are Possible Complications of Mononucleosis?
- Spleen Enlargement. This happens to be the main and most common complication, as it affects three-quarters of people with mono.
- Liver Complications. ...
- Heart Inflammation. ...
- Nervous System Problems. ...
- Swollen Tonsils. ...
- Anemia and Rashes. ...
- Reye syndrome. ...
- Thrombocytopenia. ...
- Anemia. ...
Which blood test may confirm infectious mononucleosis?
What diseases are followed by infectious mononucleosis?
What is the best treatment for mononucleosis?
What are possible complications of mononucleosis?
What are the phases of mono?
Mono has three stages: a prodrome, an acute stage, and a convelescent (recovery) stage. Because mono has a long incubation period, it can be difficult to determine when the illness actually began. On average, the prodrome phase lasts three to five days, while the acute phase can last up to six weeks.
What are the three stages of mono?
Stages of MonoThe prodrome stage. Mono infection occurs in three stages. ... The acute phase. The acute phase, which can last for 2 to 6 days, is when the symptoms begin to worsen. ... The convalescent stage. The last stage is the convalescent or recovery stage, which can last from 2 to 6 months.
How long does it take for mono to run its course?
Most people get better in two to four weeks; however, some people may feel fatigued for several more weeks. Occasionally, the symptoms of infectious mononucleosis can last for six months or longer.
Does mono have to run its course?
Mono needs to run its course naturally. Symptoms usually last 2 to 4 weeks, and some students feel tired for several weeks longer. If students with mono are absent for a long period of time, try to find ways for them to keep up with assignments so they don't fall behind and feel overwhelmed when they return to school.
What is the last stage of mono?
What is the last stage of mono? The convalescent or recovery period of mono is the third and last stage of mono. Your body will still feel tired, and you may face bouts of weakness, but you will slowly be easing yourself from other symptoms. This stage of mono can last three to six months, if not more.
What is the acute stage of mono?
Mono proceeds in three phases. First, a prodrome lasting 1-2 weeks with few if any symptoms. Second, an acute phase lasting 2 to 6 weeks during which the individual may be very sick with fevers, swollen glands, severe sore throat, and exhaustion.
What causes mono to flare up?
Most people have mono only once. In rare cases, the symptoms can recur due to a reactivation of EBV. If mono returns, the virus is in your saliva, but you probably won't have any symptoms unless you have a weakened immune system. In rare instances, mono can lead to what's called chronic active EBV (CAEBV) disease .
What would happen if mono is left untreated?
But a number of conditions, including liver disease and some cancers, can cause your spleen to become enlarged. Mononucleosis may cause enlargement of the spleen. In extreme cases, your spleen may rupture, causing sharp, sudden pain in the left side of your upper abdomen.
How long is a person contagious with mono?
Once your symptoms do appear, they may last for two to four weeks. You can pass the virus to other people through your saliva for up to three months after your symptoms subside. Some studies have reported that you may still be contagious for up to 18 months.
Can mono symptoms come and go?
It can start with a sore throat and swollen glands. And then it can leave you feeling tired and weak for weeks or months. Mono goes away on its own, but rest and good self-care can help you feel better.
Can you get mono from stress?
Can mono come back with stress? Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, so it's possible that this could be one trigger leading to a bout of recurrent mono.
What does mono fatigue feel like?
You might feel more tired than usual and have a mild fever and sore throat. Your lymph nodes, tissue that normally acts as filters, may swell under your arms and in your neck and groin area. You also may have body aches and pains, swollen tonsils, headache, and even a skin rash.
How common is mono?
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) that causes mono is extremely common. Around 90% of Americans are infected with it by age 35. Not everyone who has the virus develops mono symptoms — some people only carry the virus.
How long does mono last?
Symptoms of mono vary, and they can be mild or severe. They tend to come on gradually. If you get sick with mono, it will probably happen four to six weeks after you come in contact with EBV. These symptoms may last for four weeks or longer: Enlarged spleen or liver. Extreme fatigue.
What is the contagious disease of the body?
Mononucleosis. Mononucleosis (mono) is a contagious infection caused by a herpes virus called Epstein-Barr. Other viruses can also cause mono. The infection is common among teenagers and young adults. People with mono experience extreme fatigue, fever and body aches. Treatments can ease symptoms until the illness goes away on its own.
What is the kissing disease?
Mononucleosis is an illness that commonly affects teenagers and young adults, but can affect children as well. Viruses, most commonly Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), and certain infections cause the illness. Mono is sometimes called “the kissing disease” because it spreads easily through bodily fluids like saliva. For most people, mono isn’t serious, and ...
Why is mono called the kissing disease?
Mono is sometimes called “the kissing disease” because it spreads easily through bodily fluids like saliva. For most people, mono isn’t serious, and it improves without treatment. Still, extreme fatigue, body aches and other symptoms can interfere with school, work and daily life.
Can you get Epstein-Barr after mono?
The Epstein-Barr virus stays in your body in an inactive form even after mono symptoms go away. But most people develop mono only once. If EBV reactivates, it rarely causes symptoms. However, you may unknowingly spread the reactivated virus to others.
Does mono work against other viruses?
Antibiotics to fight bacterial infection and antiviral medications to kill other viruses don’t work against mono. Instead, treatments focus on helping you feel better by relieving symptoms. Your care might include: Rest: Mono makes you very tired. Sleep helps your body fight infection.
How many stages of mono?
Over the course of a mono infection, a person will experience three different stages of the disease. In each stage, the infection will present with different symptoms and health complications. chee gin tan / Getty Images.
What are the symptoms of stage 2 mono?
Symptoms become more pronounced. They consist of fever, inflammation or swelling in the lymph nodes, and sore throat. 2 Severe fatigue is also present at this phase. Other symptoms that could be present in those with a mono infection include: 4.
How long does it take to recover from mono?
The timeline from the initial transmission of mono to a full recovery can differ significantly from person to person. In the first four to six weeks after a person catches the virus, they may not know they have it because of the long incubation period.
What is mono in 2021?
Anju Goel, MD, MPH. Published on May 19, 2021. Mononucleosis, or mono for short, is not simply a viral infection with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). It means someone is infected with EBV or another virus and actually has symptoms.
Can mono cause spleen pain?
This can lead to other more serious symptoms such as jaundice. 5 In extremely rare cases, mono can lead to liver failure. 6 Since the spleen can also become affected by mono, some people may experience abdominal pain. Spleen rupture has been reported.
Is EBV asymptomatic or common?
So the virus is common but the disease is not, since more people are asymptomatic. Almost all mono infections are caused by EBV, but 10% of cases are caused by other viruses such as an adenovirus, which causes cold- or flu-like illnesses, and cytomegalovirus, which can lead to hepatitis. 1.
Can mono be prevented?
Currently, there is no medication or vaccine that can prevent or cure mono. Typically, the illness will need to be fought off by the immune system. Therefore, it's important for someone who has mono to rest and get plenty of fluids to help with their recovery.
What does mononucleosis mean for young people?
For young people, having mononucleosis will mean some missed activities — classes, team practices and parties. Without a doubt, you'll need to take it easy for a while. Students need to let their schools know they are recovering from mononucleosis and may need special considerations to keep up with their work.
How do you know if you have mononucleosis?
Your doctor may suspect mononucleosis based on your signs and symptoms, how long they've lasted, and a physical exam. He or she will look for signs such as swollen lymph nodes, tonsils, liver or spleen, and consider how these signs relate to the symptoms you describe.
How long does it take to recover from mononucleosis?
Wait to return to sports and some other activities. Most signs and symptoms of mononucleosis ease within a few weeks, but it may be two to three months before you feel completely normal. The more rest you get, the sooner you should recover. Returning to your usual schedule too soon can increase the risk of a relapse.
What test is done to check for Epstein-Barr?
Antibody tests. If there's a need for additional confirmation, a monospot test may be done to check your blood for antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus. This screening test gives results within a day. But it may not detect the infection during the first week of the illness.
Can a streptococcal infection go with mononucleosis?
Treating secondary infections and other complications. A streptococcal (strep) infection sometimes goes along with the sore throat of mononucleosis. You may also develop a sinus infection or an infection of your tonsils (tonsillitis). If so, you may need treatment with antibiotics for these accompanying bacterial infections.
Do antibiotics help with mono?
Antibiotics don't work against viral infections such as mono. Treatment mainly involves taking care of yourself, such as getting enough rest, eating a healthy diet and drinking plenty of fluids. You may take over-the-counter pain relievers to treat a fever or sore throat.
Can antibiotics cause mononucleosis?
Severe narrowing of your airway may be treated with corticosteroids. Risk of rash with some medications. Amoxicillin and other antibiotics, including those made from penicillin, aren't recommended for people with mononucleosis.
What is the most common cause of mononucleosis?
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the most common cause of infectious mononucleosis, but other viruses can also cause this disease. It is common among teenagers and young adults, especially college students. At least one out of four teenagers and young adults who get infected with EBV will develop infectious mononucleosis.
How long does it take for mononucleosis to show?
Typical symptoms of infectious mononucleosis usually appear four to six weeks after you get infected with EBV. Symptoms may develop slowly and may not all occur at the same time.
What does EBV show in blood work?
The blood work of patients who have infectious mononucleosis due to EBV infection may show—. more white blood cells (lymphocytes) than normal. unusual looking white blood cells (atypical lymphocytes) fewer than normal neutrophils or platelets. abnormal liver function.
How long does it take for a person to get better from mononucleosis?
For some people, their liver or spleen or both may remain enlarged even after their fatigue ends. Most people get better in two to four weeks; however, some people may feel fatigued for several more weeks. Occasionally, the symptoms of infectious mononucleosis can last for six months or longer.
Is Epstein-Barr a contagious disease?
About Infectious Mononucleosis. Infectious mononucleosis, also called “mono,” is a contagious disease. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the most common cause of infectious mononucleosis, but other viruses can also cause this disease. It is common among teenagers and young adults, especially college students.
Can you take penicillin for mononucleosis?
If you have infectious mononucleosis, you should not take penicillin antibiotics like ampicillin or amoxicillin. Based on the severity of the symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend treatment of specific organ systems affected by infectious mononucleosis.
Can you test for mononucleosis?
Laboratory tests are not usually needed to diagnose infectious mononucleosis. However, specific laboratory tests may be needed to identify the cause of illness in people who do not have a typical case of infectious mononucleosis. The blood work of patients who have infectious mononucleosis due to EBV infection may show—.
Abstract
Adenopathy, fever, and pharyngitis are the common triad of symptoms of infectious mononucleosis. Serologic evidence of past exposure to Epstein-Barr virus, the most common cause of infectious mononucleosis, can be found in almost all adults throughout the world.
Infectious Mononucleosis Caused by Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
CMV, a herpes virus, is the second leading cause of infectious mononucleosis, accounting for eight to 10 percent of recognized cases. It is the leading cause of heterophile-negative infectious mononucleosis.
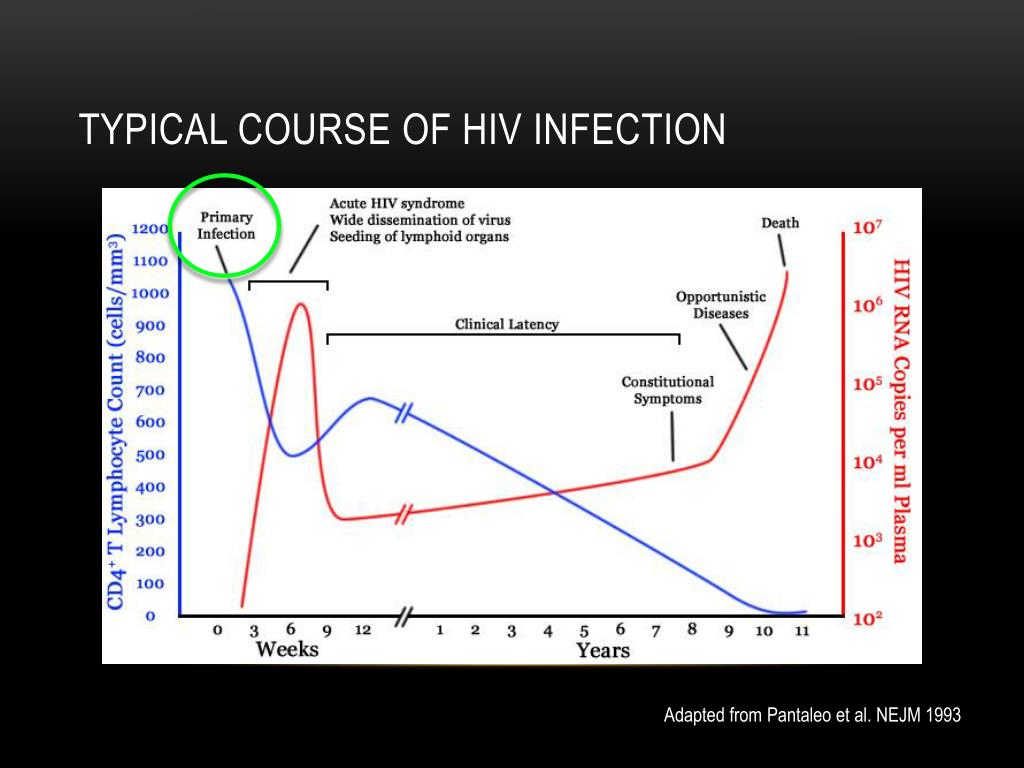
What Are The Stages of Mono?
How Is Mono Treated?
How Quickly Does Mono Progress?
What Are The Long-Term Effects of Mono?
Specialist to consult
Summary
- Signs and symptoms of mononucleosis may include: 1. Fatigue 2. Sore throat, perhaps misdiagnosed as strep throat, that doesn't get better after treatment with antibiotics 3. Fever 4. Swollen lymph nodes in your neck and armpits 5. Swollen tonsils 6. Headache 7. Skin rash 8. Sof…
A Word from Verywell
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Mononucleosis, also known as \"mono,\" is an infectious disease that is usually caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (a herpes virus). Other viruses can also cause mononucleosis. Mononucleosis is not considered a serious illness, but its symptoms may be severe enough to prevent a person from engaging in normal activities for several weeks. The classic ...
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Popular Posts:
- 1. uc application how to list my psychology course
- 2. or the purposes of this course, which of the following is the best working definition of dna?
- 3. which of the following is a type of secondary data: data found in industry articles course hero
- 4. course 5 portal 2 where coop
- 5. what is a pasta course in a formal dinner called
- 6. how to cancel my on demand powerscore course
- 7. what are some strategies to help sharpen sentences and word choice? course hero
- 8. what type of retirement plan is a 401(k) course hero
- 9. how to add coursera course to linked in
- 10. how much is a real estate course in ga