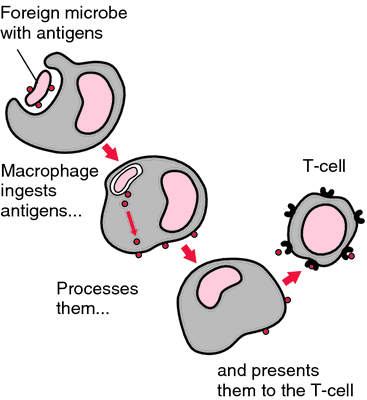
Macrophages and neutrophils work to keep the body clean of debris and invaders, but they also call for backup when an infection is too big for the two of them to handle alone. Other immune system cells, like the T-Cells and B-Cells in our story, are alerted that their help is needed by chemicals the macrophages release.
Full Answer
What does a macrophage do?
A macrophage has the ability to locate and 'eat' particles, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Macrophages are born from white blood cells called monocytes, which are produced by stem cells in our bone marrow.
How do macrophages and neutrophils work together?
Macrophages and neutrophils work to keep the body clean of debris and invaders, but they also call for backup when an infection is too big for the two of them to handle alone. Other immune system cells, like the T-Cells and B-Cells in our story, are alerted that their help is needed by chemicals the macrophages release.
What are the two types of macrophages?
There are two types of macrophages: those that roam and those that stay in a fixed spot. Roaming macrophages can be found mainly in our interstitial fluid, or the fluid between cells. They are constantly on patrol, moving through the tiny channels between our cells on the lookout for unwanted intruders or dead cell debris.
How do macrophages EAT cells?
Macrophages don’t eat cells the same way you might eat your food. Instead, the eating machines engulf viruses and bacteria. This is called phagocytosis. First, the macrophage surrounds the unwanted particle and sucks it in. Then, the macrophage breaks it down by mixing it with enzymes stored in special sacs called lysosomes.
What is the job of a macrophage?
The word 'macrophage' literally means 'big eater.'. It's an amoeba-like organism, and its job is to clean our body of microscopic debris and invaders. A macrophage has the ability to locate and 'eat' particles, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Macrophages are born from white blood cells called monocytes, ...
What is the role of macrophages in the immune system?
The macrophage is a large white blood cell that is an integral part of our immune system. Its job is to locate microscopic foreign bodies and 'eat' them. Macrophages use the process of phagocytosis to engulf particles and then digest them. Some macrophages roam the body and some stay in one particular area.
What is the process of destroying unwanted particles in the body called?
Phagocytosis. A macrophage uses a process called phagocytosis to destroy and get rid of unwanted particles in the body. Phagocytosis literally means 'eat cell.'. The process works like this: as the macrophage engulfs the particle, a pocket called a phagosome is formed around it.
What is the fluid between cells that macrophages roam through called?
The fluid between cells that some macrophages roam through is called interstitial fluid. Learning Outcomes.
How long do monocytes live?
Monocytes move through the bloodstream and when they leave the blood, they mature into macrophages. They live for months, patrolling our cells and organs and keeping them clean. paywall_macrophages-definition-function-types. 6:07.
Where are macrophages found?
These fixed macrophages are found in our brain, bones, liver, kidneys, and lungs, as well as other important internal organs.
Do macrophages destroy cancer cells?
An army of fighter cells is then sent out to destroy the viruses before they can do more damage. Macrophages even attack some cancer cells. Additionally, as previously mentioned, macrophages also clean up dead cell debris and other 'garbage' that may be lying around.
What is the function of a macrophage?
Macrophage Function. A macrophage is a type of phagocyte, which is a cell responsible for detecting, engulfing and destroying pathogens and apoptotic cells. Macrophages are produced through the differentiation of monocytes, which turn into macrophages when they leave the blood. Macrophages also play a role in alerting the immune system to ...
How are macrophages produced?
Macrophages are produced through the differentiation of monocytes, which turn into macrophages when they leave the blood. Macrophages also play a role in alerting the immune system to the presence of invaders.
What is the term for the engulfing and destroying of defective or microbial cells?
Phagocytosis is the term used to describe the engulfing and destroying of defective or microbial cells. When inflammation occurs, monocytes undergo a series of changes to become macrophages and target cells that need eliminating. Once engulfed, cellular enzymes inside the macrophage destroy the ingested particle.
What does the T helper cell do?
On identifying an antigen, the T helper cell activates other cells of the immune system such as cytotoxic T cells to attack the infected cell. T helper cells also stimulate the B cells of the immune system to secrete antibodies. Each antigen has specific antibodies that are produced against it in large amounts.
What is the term for the ability to develop adaptive immunity?
This developed immunity is termed adaptive or acquired immunity.
What are macrophages linked to?
Macrophages are also linked to the presence of other types of cells like basophils and eosinophils, which are most often involved in allergic reactions. These cells also help control the inflammation of tissues. Big eaters. Think of macrophages as cell-eating machines. Their name actually means “big eater” in Greek.
What do neutrophils and macrophages do?
Macrophages and neutrophils work to keep the body clean of debris and invaders, but they also call for backup when an infection is too big for the two of them to handle alone. Other immune system cells, like the T-Cells and B-Cells in our story, are alerted that their help is needed by chemicals the macrophages release.
What happens when a macrophage engulfs a virus?
Phagocytosis: Once a macrophage engulfs a virus (1-3), it's broken down with enzymes from the lysosomes (4,5) then released from the cell as harmless waste material (6) . Macrophages in action. Phagocytosis from Ask A Biologist on Vimeo. Play.
What cells fight infections?
There are red blood cells that bring oxygen to every part of your body and white blood cells that fight infections. Getting to the scene. Infected or damaged cells, like the epithelial cells in our story, call for help by releasing chemicals that attract macrophages already in nearby blood vessels.
How does a macrophage break down waste?
Then, the macrophage breaks it down by mixing it with enzymes stored in special sacs called lysosomes. The leftover material is then pushed out of the cell as waste.
How big are macrophages?
Macrophages are the biggest type of white blood cells - about 21 micrometers - or 0.00083 inches. Still too small to see with your eyes, but big enough to do the important job of cleaning up unwanted viruses, bacteria, and parts of dead cells. Macrophages don’t eat cells the same way you might eat your food.
What type of cells are involved in infection?
Macrophages, a kind of white blood cell, are one of the first types of cells at the infection (along with neutrophils). They get to the infection from your blood. Your blood looks like it is just a red fluid, but it has lots of other kinds of cells, too. There are red blood cells that bring oxygen to every part of your body ...
What is Course Hero?
And Course Hero is one of the most popular websites when it comes to homework help. With their repository of real assignment questions from real and tangible courses from top colleges and schools, the chances of you stumbling into the exact question you were looking for are pretty high.
How much is Course Hero?
You can get a Course Hero subscription for $39.95/month for a month, $19.95/month for a 3-month subscription (one up-front payment of $59.85), or $9.95/month for a yearly subscription (an up-front payment of $119.40). If you plan on using Course Hero often, a subscription might be the way you want to go. You can also pool some money ...
How often can you unblur 30 Course Hero?
With these 30 unlocks you get every month, you can unblur 30 Course Hero documents. These unlocks refresh every month. And if you have any unused ones, they won’t carry over to the next month. It also saves you from having to spend time uploading any of your documents.
How many unlocks does Course Hero give?
When the Course Hero team approves your documents, you’d get free unlocks in an email. For every 10 successfully approved documents, you get 5 unlocks. You can use 1 unlock to unblur one Course Hero document. It’s good practice to upload extra documents, just in case, as only the ones that’ll get accepted will count towards the number ...
Can you use Course Hero for free?
The official way to use Course Hero for free is pretty easy. All you need are copies of original notes or documents. The content should be original, i.e., either you own the copyright or have permission from the person who owns the copyright to upload them, and it should not be plagiarized either. How this works is that after creating ...
Can you make a quiz on Course Hero?
You can make a quiz and submit it for any document on Course Hero, but this requires you to have an unblurred document initially. So, this method can be thought of as a way of getting additional unlocks as it isn’t particularly useful in the beginning when you don’t have any unlocks to unblur a document.
What do macrophages do?
FULL STORY. The term "macrophage" conjures images of a hungry white blood cell gobbling invading bacteria. However, macrophages do much more than that: Not only do they act as antimicrobial warriors, they also play critical roles in immune regulation and wound-healing. They can respond to a variety of cellular signals and change their physiology in ...
What is the role of macrophages in the body?
However, macrophages do much more than that: Not only do they act as antimicrobial warriors, they also play critical roles in immune regulation and wound-healing.
What is the function of macrophages in the immune system?
Immune-regulating macrophages produce high levels of the cytokine interleukin-10, which helps suppress the body's immune response. Suppressing an immune response may seem counter-intuitive, but in the later stages of immunity it comes in handy because it limits inflammation.
How do macrophages differentiate?
The type of macrophage that results from monocyte differentiation depends on the type (s) of cytokines that these cells encounter. Cytokines are proteins produced by immune cells that can influence cell behavior and affect interactions between cells. For example, macrophages that battle microbial invaders arise in response to interferon-γ, a cytokine that is produced during a cellular immune response involving helper T-cells and the factors they produce. These macrophages are considered to be "classically activated."
What is a macrophage that fights microbial invaders?
For example, macrophages that battle microbial invaders arise in response to interferon-γ, a cytokine that is produced during a cellular immune response involving helper T-cells and the factors they produce. These macrophages are considered to be "classically activated.".
What cells are needed to grow muscle tissue?
Oct. 1, 2018 — The immune system's macrophage cells are critical to growing muscle tissues in a lab, say the biomedical engineers who earlier reported the world's first self-healing lab-grown muscles. The discovery ...
What is the role of immune-regulating macrophages in autoimmune disease?
According to Dr. Mosser, immune-regulating macrophages may hold the key to developing treatments for autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis. The focus of new research is on reprogramming the macrophages to assume a regulatory phenotype and prevent autoimmunity, he said.
Popular Posts:
- 1. how much can you make twaching extention course pcc
- 2. what is history 1120 course
- 3. what does an adanced open water course get me
- 4. how to extend kaplan course mcat past fall
- 5. of course sometimes she goes down when there's a
- 6. how i can purchased new physical therapy course manual version 6.0
- 7. what do you put in an electric footbath (besides feet of course)
- 8. how often must a pilot change course
- 9. when to register for course ccp
- 10. how to write a request letter to repeat a course