What is the course of the radial nerve?
Anatomical Course. The radial nerve then descends down the arm, travelling in a shallow depression within the surface of the humerus, known as the radial groove. As it descends, the radial nerve wraps around the humerus laterally, and supplies a branch to the medial head of the triceps brachii.
What happens to the radial nerve in a fracture?
The radial nerve however is particularly vulnerable, as it runs in the spiral grove, and is therefore tightly adherent to the humerus along the majority of its course in the arm. A fracture is therefore highly likely to disrupt the nerve.
Where does the radial nerve enter the humerus?
In the distal part of the arm, the radial nerve wraps around the distal humerus and courses anterior to the lateral condyle of humerus, where it penetrates the lateral intermuscular septum. Upon crossing the cubital fossa, the radial nerve terminates by dividing into two terminal branches: superficial (sensory) and deep (motor).
What are the symptoms of abnormal radial nerve function?
People who have abnormal radial nerve function will often experience symptoms of numbness or tingling in areas such as the back of the hand. The radial nerve provides information to the muscles of the back of the arm and forearm about when to contract.
What is the course of the radial nerve?
Course. The radial nerve lies posterior to the axillary artery in the axilla and enters the posterior compartment of the arm under teres major muscle via the triangular interval. In the posterior compartment of the arm, it winds its way around the spiral groove of the humerus, accompanying profunda brachii artery.
Where does the radial nerve begin and end?
The radial nerve arises in the axillary region and descends down along the posterior surface of the humerus. It then passes through the cubital fossa and terminates in the posterior compartment of the forearm, by dividing into two terminal branches: superficial (sensory) and deep (motor).
Where does the radial nerve lies?
axillaDescription. The radial nerve is one of the terminal branches of the posterior cord. In the axilla, it lies behind the axillary and upper brachial arteries and passes anterior to the tendons of teres minor, latissimus dorsi and subscapularis.
Which fracture affects radial nerve?
A radial nerve injury associated with a humeral shaft fracture is an important injury pattern among trauma patients. It is the most common peripheral nerve injury associated with this fracture.
Where does the radial nerve cross the humerus?
The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The nerve, along with accompanying vessels, crosses medial to lateral obliquely over the posterior surface of the humerus in the spiral groove.
Where does the radial nerve end?
The Radial Nerve branches off to the Deep Branch after it passes through the cubital fossa and then continues as the Posterior Interosseous Nerve after it passes between the supinator muscle heads.
Where does the radial nerve enter the hand?
The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve, and a superficial branch, which goes on to innervate the dorsum (back) of the hand....Radial nerveInnervatesposterior compartment of the arm, posterior compartment of the forearmIdentifiersLatinnervus radialisMeSHD0118268 more rows
Which main structure does the radial nerve supply quizlet?
The radial nerve supplies the triceps brachii muscle as well as 12 muscles in the forearm.
Which nerves are involved in fracture of humerus?
The radial nerve is most likely to be damaged in humerus fractures that have a lateral displacement of the distal fracture segment, as the nerve is tethered to the bone and cannot withstand the forces applied to it as a result of the displacement.
What nerve is affected in supracondylar fracture?
Complications. Nerve palsies are common with supracondylar fractures, with neuropraxia rates around 10%; however, this rarely results in permanent damage. The anterior interosseous nerve is most commonly affected by the initial injury, however ulnar nerve palsy is the most common post-operative complication.
What type of fracture dislocations are associated with radial nerve injury in the arm?
The radial nerve is most frequently injured in association with humeral fractures. Typically these injuries occur at the junction of the middle and distal thirds (Holstein-Lewis fracture). These are usually spiral fractures where the distal fragment displaces proximally and radially.
Where does the radial nerve innervate?
The radial nerve is one of five main branches of the brachial plexus. It provides motor and sensory innervation to the arm and forearm and sensory innervation to the hand.
What are the symptoms of radial nerve damage?
Symptoms. Symptoms of radial nerve injury may include pain, numbness, and/or paresthesia, especially in the middle finger, index finger, thumb, back of the hand, and/or arm. Wrist drop and finger drop may also be present.
What would happen if the radial nerve was damaged?
Weakness, loss of coordination of the fingers. Problem straightening the arm at the elbow. Problem bending the hand back at the wrist, or holding the hand. Pain, numbness, decreased sensation, tingling, or burning sensation in the areas controlled by the nerve.
What does radial nerve pain feel like?
A radial nerve injury usually causes symptoms in the back of your hand, near your thumb, and in your index and middle fingers. Symptoms may include a sharp or burning pain, as well as unusual sensations in your thumb and fingers. It's common to experience numbness, tingling, and trouble straightening your arm.
Where does the radial nerve originate?
The radial nerve is the largest terminal branch of the brachial plexus. It originates from the posterior cord along with the axillary nerve , carrying fibers from ventral roots of spinal nerves C5-C8 and T1. The radial nerve arises in the axilla, immediately posterior to the axillary artery , between coracobrachialis and teres major muscles.
Which branch of the radial nerve enters the hand from the radial side?
The superficial branch continues the course of the radial nerve and enters the hand from the radial side. This branch is also known as the " sensory branch " because of its primary role to provide sensation to the thenar eminence and dorsal aspect of the radial 3 and a half digits of the hand. Brachial plexus Explore study unit.
What nerve is responsible for the sensory supply of the skin of the arm, forearm and hand?
The branches of the radial nerve provide motor supply for the posterior muscles of the arm and forearm , as well as the sensory supply of the skin of the arm, forearm and hand . Due to its length, the radial nerve is the most commonly injured nerve of the upper extremity. The most known presentation of radial nerve palsy is the "wrist drop".
What nerve is most commonly injured?
The radial nerve is the most commonly injured nerve of the arm. The injuries of this nerve usually occur due to fractures of the humerus. The nerve can also be injured when it is "overused" (e.g. sports-related injuries) or compressed (e.g. improper use of crutches).
What nerve terminates when crossing the cubital fossa?
Upon crossing the cubital fossa, the radial nerv e terminates by dividing into two terminal branches: superficial (sensory) and deep (motor). Learning about the nervous system can be pretty scary. Try out nervous system quizzes and diagrams and soon you will see there’s nothing to be afraid of!
Where is sensory loss located?
For example, if the nerve is injured in the axillary region, the sensory loss will be located at the lateral arm and the posterior aspect of the forearm radiating to the radial aspect of the hand and digits.
Which nerve innervates the cubital region?
Upon entering the cubital region, and before its division, the radial nerve provides one more sensory branch called the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve. This nerve innervates a strip of skin down the middle of the posterior forearm. The deep branch, also known as the “motor branch”, provides motor innervation to the posterior compartment ...
Overview
The radial nerve helps you move your elbow, wrist, hand and fingers. It runs down the back of the arm from the armpit to the hand.
Function
The radial nerve provides motor (movement) and sensory functions to the arm. It:
Anatomy
The radial nerve is one of five terminal nerve branches that make up the brachial plexus. The brachial plexus is a complex bundle of nerves that control movements and sensations in your shoulders, arms, hands and fingers.
Conditions and Disorders
Certain conditions and problems can cause pressure on the radial nerve, causing a pinched nerve and nerve (neuropathic) pain. Conditions that affect the radial nerve include:
Where is the radial nerve located?
Forming in the area of the shoulder joint at the confluence of several branches of the brachial plexus, the radial nerve courses down the arm, past the elbow joint, into the forearm, across the wrist, and all the way to the tips of your fingers.
What is the function of the radial nerve?
There are two major functions of the radial nerve. 1 One of these functions is to provide a sensation that is experienced in the hand, forearm, and arm. The other major function of the radial nerve is to deliver messages to specific muscles about when to contract.
What nerve is responsible for the sensations of the upper extremity?
The radial nerve provides important information to your brain about the sensations experienced in the upper extremity and also delivers information to the muscles of the upper extremity about when to contract. Injury to the radial nerve can cause abnormal function of the nerve leading to unusual sensations and impaired muscle function.
What is the most common type of fracture associated with injury to the radial nerve?
The most common type of fracture associated with injury to the radial nerve are fractures of the humerus bone. 4 The radial nerve wraps very tightly around the humerus bone and can be injured when there is a fracture of the bone. Most radial nerve injuries associated with fractures will heal spontaneously and do not require surgical intervention.
What causes nerve contusion?
Nerve contusions typically occur when there is a blunt force of trauma that causes abnormal function of the nerve. 3 A nerve contusion can occur as a result of a sports injury or a variety of other conditions that cause direct pressure to a nerve.
Which nerve provides information to the muscles of the back of the arm and forearm about when to contract?
The radial nerve provides information to the muscles of the back of the arm and forearm about when to contract. Specifically, the triceps muscle in the back of the arm and the extensor muscles of the back of the forearm are the major muscle groups that are supplied by the radial nerve.
Which nerve travels down the arm, past the elbow joint, into the forearm, and across the wrist all
Branches of the brachial plexus form the major peripheral nerves of the upper extremity. One of these nerves is called the radial nerve ; others include the median nerve and the ulnar nerve. The radial nerve travels down the arm, past the elbow joint, into the forearm, and across the wrist all the way into the fingers.
What nerve is the lower lateral?
Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm ( skin on the lateral surface of arm) Posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm ( skin of the middle of the back of forearm) Motor branches: Nerve to lateral head of triceps. Nerve to medial head of triceps. Nerve to anconeus.
What nerve supplies skin on the back of the arm?
Sensory branch: Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm ( supplies skin on the back of arm) Motor branches: Nerve to long head of triceps. Nerve to medial head of triceps. In the spiral groove: Sensory branches: Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm ( skin on the lateral surface of arm)
Where does the spiral groove end?
At the lower end of the spiral groove it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to enter the anterior compartment of arm. It then enters the cubital fossa and at the level of lateral epicondyle it terminates by dividing into superficial and deep (posterior interosseous ) branches.
Where does the superficial branch of the forearm run?
The superficial branch enters the forearm and runs deep to brachioradialis. In the lower 1/3rd of the forearm it winds around the lateral aspect of radius to reach the anatomical snuff box on the dorsum of hand. It terminates by dividing into digital branches.
Where does the teres major enter the arm?
It enters the posterior compartment of arm at lower border of the teres major through the lower triangular space. It then lies in the spiral groove of humerus along with the profunda brachii vessels between the lateral and medial heads of triceps.
Which branch of the cubital fossa is the sensory branch?
Nerve to extensor carpi radialis longus. In the cubital fossa (Terminal branches): Superficial branch (sensory branch) Innervates the skin over the lateral part of the dorsum of hand and dorsal surface of lateral 3 ½ digits upto the middle phalanx.
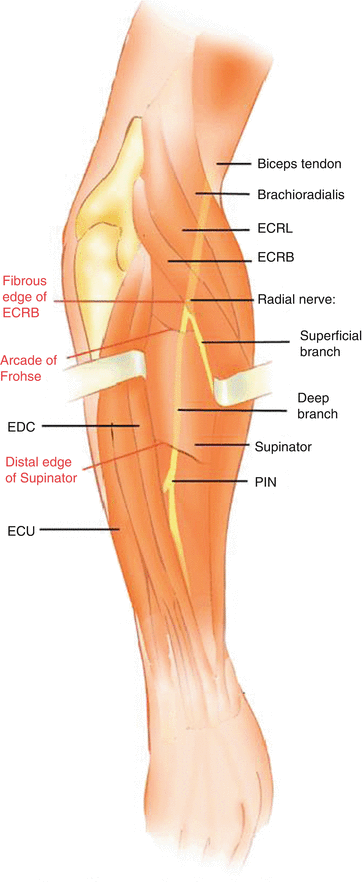
Popular Posts:
- 1. of course money grows on trees why do you think banks have branches aoc
- 2. how long is a boldmethod course
- 3. what is a genetics course about
- 4. what subject is discrete structures course
- 5. course hero do think that terrorism should be considered a hazard? explain, why or why not?
- 6. in what area of italy are siena and florence located course hero
- 7. how many hours home inspector course florida
- 8. what is new york ipirp (keystroke) course
- 9. please asymptomatic paget disease will help what course of treatment
- 10. which of the following statements is true about the microcultures around the world? course hero