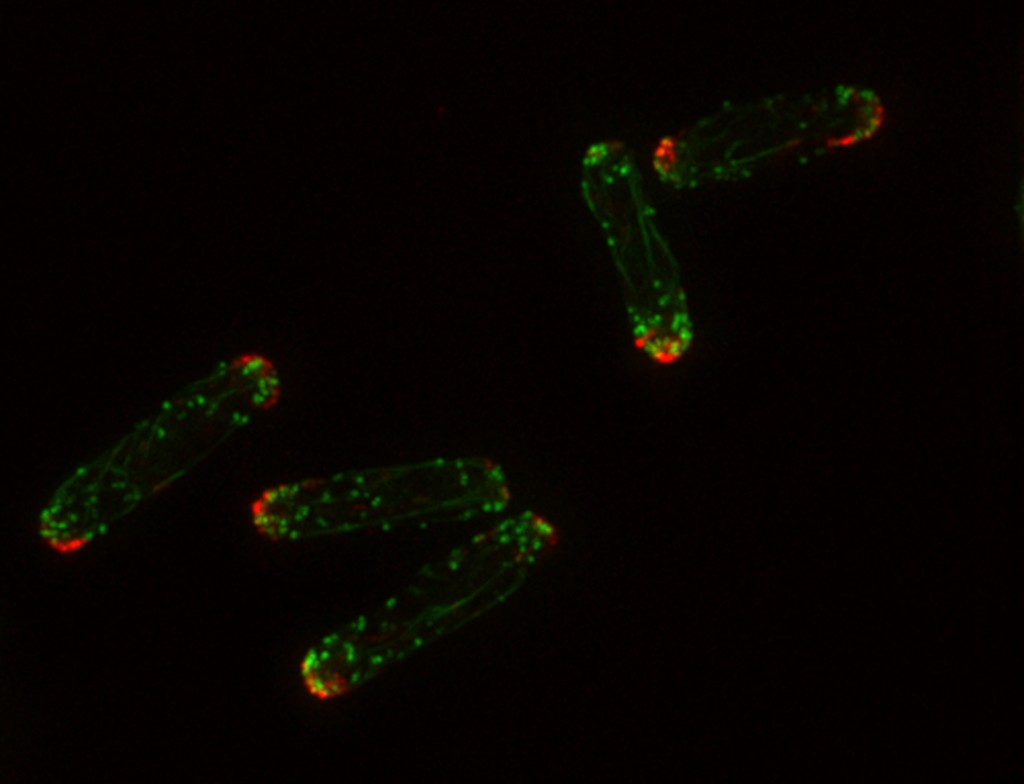
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm.
Full Answer
What is the function of the actin filaments?
Actin filaments Actin filaments are thin and flexible Actin features 7 nm diameter filaments Form the dynamic cytoskeleton, very important in cell motility, participate in cell signaling Most dynamic cytoskeletal component Actin-rich structures Microvilli Actin parallel to one other Stress fibers Contractile Anti-parallel Lamellipodia Actin on leading edge Rho responsible for signal …
How do actin filaments make microvilli?
Actin filaments (microfilaments) important for whole cell movement Actin filaments polymerize along the leading edge (direction of movement) of the moving cell Intermediate Filaments Many different types made of different proteins (lamins, keratin) Less dynamic, non polar Provide mechanical strength Maintenance of cell shape, nuclear position, shape, organization From …
What is cross linking of actin filaments?
Actin filaments are a major element of the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton provides a framework for the cell and acts as a scaffold that both determines cell shape and positions organelles within cells. For example, the cytoskeleton provides the tracks along which organelles move.
What is the function of the actin bundle?
_____ PART 2: BUILDING A CELL _____ Actin Actin Structure Actin filaments require energy for cell motility actin is an ATPase the energy of ATP hydrolysis by actin drives a lot of these cell motility processes. Actin polymerizes into a two-stranded helical filament: Actin filaments are arranged differently at distinct intracellular locations if actin is able to form so many different kinds of …
What is meant by actin filament?
Actin filaments are polar structures composed of globular molecules of actin arranged as a helix. They work in networks and bundles, often found just beneath the plasma membrane, where they crosslink to form the cell cortex.
What is actin filaments and its function?
Actin filaments are particularly abundant beneath the plasma membrane, where they form a network that provides mechanical support, determines cell shape, and allows movement of the cell surface, thereby enabling cells to migrate, engulf particles, and divide.
What are actin filaments quizlet?
Actin filaments are polymers of actin monomers (G-actin). Actin filaments form the core of thin filaments in muscle cells.
What type of filaments are actin?
Actin filaments are the smallest type, with a diameter of only about 6 nm, and they are made of a protein called actin. Intermediate filaments, as their name suggests, are mid-sized, with a diameter of about 10 nm.
What is actin used for?
Actin is a highly abundant intracellular protein present in all eukaryotic cells and has a pivotal role in muscle contraction as well as in cell movements. Actin also has an essential function in maintaining and controlling cell shape and architecture.
How does actin filament help in cell movement?
The protein actin forms filaments that provide cells with mechanical support and driving forces for movement. Actin contributes to biological processes such as sensing environmental forces, internalizing membrane vesicles, moving over surfaces and dividing the cell in two.
Whats the definition of actin?
Definition of actin (Entry 1 of 2) : a cellular protein found especially in microfilaments (such as those comprising myofibrils) and active in muscular contraction, cellular movement, and maintenance of cell shape.
Which of the following are features of actin filaments?
Actin filaments are the smallest cytoskeletal filaments, with a diameter of 7 nm. They are thin, relatively flexible threads that can be crosslinked together in different ways to form very different structures. Actin monomers are called globular actin or G-actin.Sep 15, 2021
What is actin composed of?
An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells.
How are actin filaments formed?
Actin filaments comprise a major part of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells and serve as tracks for myosin motor proteins. The filaments assemble from actin monomers with a bound ATP. After polymerization, actin rapidly hydrolyzes the bound ATP and slowly dissociates the γ-phosphate.Feb 19, 2019
Why are actin filaments called Polar?
Because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin filament is polar, with different ends, termed “barbed” and “pointed.” An abundant protein in nearly all eukaryotic cells, actin has been extensively studied in muscle cells.
What is the function of actin filaments?
Actin filaments have many functions within the cell. For example, our muscle cells are packed with actin filaments arranged in bundles by alpha actinin. As you can see in the diagram, the motor protein myosin is located in between the parallel actin filaments. By 'walking' toward the plus ends of the actin filaments, myosin slides the filaments inwards so that the whole structure gets shorter. This is what makes our muscles contract.
How are actin filaments formed?
In summary, we have learned that actin filaments (also called F-actin) are formed by linking together G-actin molecules in a polymer chain. Each actin filament has a plus and a minus end, and motor proteins like myosin 'walk' directionally along the filaments.
What is the cytoskeleton?
The cytoskeleton provides structure and shape to cells. In this lesson, learn about actin filaments, a kind of cytoskeletal filament that is important for cell shape, muscle contraction, and cell adhesion. Create an account.
What are actin networks?
Others, like spectrin and filamin, cross-link actin filaments at angles to each other, forming actin networks, which are web or cushion-like structures. In addition, actin bundles and actin networks change the cell's shape and structure in different ways.
What is the smallest cytoskeletal filament?
Actin filaments are the smallest cytoskeletal filaments, with a diameter of 7 nm. They are thin, relatively flexible threads that can be crosslinked together in different ways to form very different structures. Actin monomers are called globular actin or G-actin.
How does actin work?
A diagram of how muscle contraction works. The actin bundle contracts as the motor protein myosin moves towards the plus ends of the filaments. Villin and fimbrin assemble actin filaments into tight, dense bundles that poke out of the cell surface to make microvilli.
What proteins are involved in actin crosslinking?
Some, like alpha actinin, villin and fimbrin, link individual filaments together in actin bundles where the filaments are all lined up parallel to one another.
Popular Posts:
- 1. why the princess of course
- 2. how do i check which math course i need to take in ohio state
- 3. how far is 130 hollow tree ct, lugoff, from 410 old course loop blythewood sc
- 4. how to get to the tree gnome village agility course
- 5. what do you study in a philosophy course
- 6. what page does learndash use for course
- 7. negotiators who are suspicious are less effective at the bargaining table true false course hero
- 8. what do the numbers mesn on a college course
- 9. course hero what can a person do to improve bone health?
- 10. what counts as honors course uc