Participants were asked when they officially withdrew from the course. Slightly more than half (51.5%) indicated that they officially withdrew from class right after they decided to 3 withdraw, while 48.5% indicated they stopped attending and withdrew later.
What is the impact of class withdrawals on college students?
percentage of students who withdrew from all their courses fell from 12-14 percent in the early 2000's to 9-10 percent in recent years, and up to 11 percent in Fall 2021. The number of students enrollments decreased in Fall 2020 and Fall 2021 (during the Covid-19 Shelter-In-Place order in California) and the percentage of students who withdrew from all courses increased during …
What is the percentage of students who withdraw from statistics courses?
Oct 09, 2021 · 55% of college students struggle to find financial support for their studies. Consequently, 51% of college dropouts drop out because of the lack of money. 79% of the students delay their graduations due to financial difficulties.
How do course withdrawals affect graduation and retention rates?
Jun 08, 2020 · A similar number of course withdrawals would result in 1.65 to 3.01 times greater odds of stopping out in our sample. Full results for the other variables in the retention model can be found in Table 6. Table 5. Odds ratio estimates for D ratios of 20%–100% and F and withdrawal ratios of 20%–99% by institution.
What percentage of college students drop a class?
Withdrawal. After the drop period has passed, students taking courses through UMGC are permitted to withdraw from a course until 65 percent of the course has been completed. A withdrawal means that students will receive a "W" grade for the course and will be responsible for all fees and all or a portion of the tuition.
Why do students withdraw from courses?
Dowd and Harris both said the most common reason for withdrawing is failing a course. Dowd said some professors will give WPs even if a student is failing, but that some will just give the student a WF.Oct 16, 2013
Are course withdrawals a useful student success strategy?
In conclusion, results are mixed on why students withdraw from courses, and little is known about the implications of course withdrawal. However, research does indicate that course withdrawal may impact student retention and degree completion.
Is withdrawing from a class normal?
It does not affect the student's GPA (grade point average). Although students may be reluctant to have a “W” on their transcript, sometimes “W” stands for Wisdom. Withdrawing from one class may make success in other classes manageable and allow your student to end the semester with a strong GPA.
What percent of students go away for college?
In the United States, the overall dropout rate for undergraduate college students is 40%. 30% of the dropout rate comes from college freshman dropping out before their sophomore year. In 4-year colleges, 56% of students drop out within 6 years.Nov 22, 2021
Is a withdrawal fail better than a fail?
Failing & Then Re-Taking a Class Croskey notes that dropping a class is better than withdrawing, but withdrawing is better than failing. “A failing grade will lower the student's GPA, which may prevent a student from participating in a particular major that has a GPA requirement,” Croskey says.
Does withdrawal affect financial aid?
The Federal Return of Title IV Funds procedure mandates that students who officially withdraw (drop all classes) or unofficially withdraw (stop attending without dropping all classes) may only keep the financial aid they have "earned" up to the time of withdrawal.
How many W is too many transcripts?
As a general rule of thumb, having one “W” should not be too big of a deal. However, if you continue to get them, medical schools will see this as a red flag in your potential to do well at medical school. Myth 2: You should always take a bad grade over a “W.”
What are the consequences of withdrawing from a course?
Sadly, in academia, there's also the word “Withdraw.” Withdrawing means you drop a class after the allowed add/drop period ends. You won't receive a grade for the class, but a “W” will show up on your transcript, indicating that you were not doing well in the course and essentially quit the class.May 2, 2020
Do withdrawals affect grad school?
If you withdraw from a course during an otherwise "normal" semester, most people judging your transcript from the perspective of graduate school admissions will assume that you were not doing well in the course. If you later complete the course with a good grade (A or B), this won't matter much.May 1, 2019
How many students don't go to college because they can't afford it?
“Nearly 60 percent [of respondents] said they worry about having enough money to pay for school, while half are concerned about paying their monthly expenses. 32 percent of students reported neglecting their studies at least sometimes because of the money they owed.
Are people dropping out of college due to Covid?
Out of the country's 2.6 million students who started college in fall 2019, 26.1 percent, or roughly 679,000, didn't come back the next year, according to the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center.Feb 10, 2022
What degree has the highest dropout rate?
Computer sciencesComputer sciences and business and administrative studies are among the degree subjects with the highest drop-out rates; with around nine per cent of students dropping out by their second year.Jan 20, 2022
What percentage of students withdrew from a course in their first term?
The overall percentage of students who withdrew from at least one course in their first term was approximately 20% . This figure ranged from 15%–25% across the nine universities, suggesting some variability in the number of students withdrawing from courses across institutions. For brevity, the results will focus on relationships that were found to be statistically significant at the alpha = .05 level.
Is course withdrawal bad for GPA?
Even so, these data reveal that course withdrawal is nearly as damaging for first- to second-year retention. It does not appear that course withdrawals are a viable student success strategy in most circumstances. Although course withdrawal may allow students to protect their GPAs, it may result in academic disengagement nearly as damaging as course failure. At best, course withdrawal appears to be most beneficial when a student is certain to fail, or when the student must maintain a certain GPA or full-time enrollment status due to scholarship requirements. Even then, there may be learning gains from persistence in a course and grade substitution policies that might mitigate a low GPA. It is clear that academic advisors and faculty have complicated yet key roles in advising students who navigate this landscape.
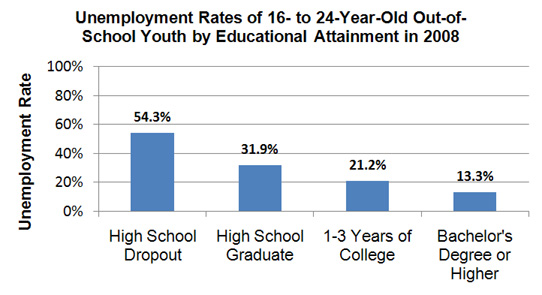
Background
Executive Summary
- To better understand the impact of class withdrawals and other important education-related topics, Zion & Zion conducted a nationwide survey of 1,200 college students in two groups: 1. Current freshmen and sophomores at 4-year colleges and universities 2. Students in their first year at a 2-year community or junior college We explored the prevalence and motives of student…
Prepared For College
- For the most part, students profess to be academically prepared for success prior to starting college (see Figure 2). While 73% of students claim to have been prepared or very prepared for college, there is a disturbingly large chunk—27%—who admit to being only moderately prepared, unprepared or very unprepared. But as Figure 3 demonstrates, there’s little evidence of a relation…
Why Drop A Class?
- Our survey data suggests this is the place to start—understanding whystudents are dropping a class. See Figure 4. The reasons for dropping classes are fairly evenly split between multiple causes. Leading the way at 21% is the generic “I didn’t like the course,” a catch-all statement reflecting multiple causes converging with no single cause dominant. The next most common a…
Putting The Data to Work
- There are several implications of our findings for managing and marketing colleges. First, the reasons for dropping classes are varied. There is no single dominant cause that colleges can focus on to reduce the course drop rates. Second, the push for adapting teaching, testing and course styles to a diverse student body is an important element in combatting the course droppi…
Popular Posts:
- 1. vsu how many course withdrawals before being penalizd
- 2. when computing the rate earned on total common stockholders equity course hero
- 3. how long does aceable defensive course take
- 4. where can i take a course in quick books in miami fl
- 5. how to set up a racing drone course
- 6. how long is the ocean course at kiawah island
- 7. which of the following is true regarding productivity ratios cpa course hero
- 8. how do you increase student success in your online course
- 9. why take a communication course
- 10. how to upload defensive driver course certificate on geico