Why is Taiwan’s economy so successful?
compared to the previous years. Within the Asia Pacific, Taiwan has ranked 4 th among 40 countries and its overall score is above the world averages. From the report, Taiwan’s economy hit the best performance in the 27 years history of the index and reached closer to the rank of “free” as Taiwan economic freedom is considered “mostly free” this year.
What was the economy like in the 1980s in Taiwan?
Apr 18, 2015 · On what is Taiwan's economy based? the feng shui system large and interlocking conglomerates small and mid-sized family-owned companies a lack of government control oil ANS: small and mid-sized family-owned companies
What was the economic condition of Taiwan after WW2?
One reason given for that circumstance is that Taiwan’s economy is based primarily on small- and medium-sized companies rather than on large conglomerates—as has been the case in Japan and South Korea. Early on, Taiwan adopted a policy of import substitution, imposing high tariffs to protect its budding industries.
How dependent is Taiwan’s economy on external demand?
Taiwan's economy remains export-oriented, thus it depends on an open world trade regime and remains vulnerable to downturns in the world economy. The total value of trade increased over fivefold in the 1960s, nearly tenfold in the 1970s, and doubled again in the 1980s. [60]
What is Taiwan's economy based on?
What is significant about Taiwan's economy?
When did Taiwan's economy grow?
Taiwan’s economic growth beginning in the mid-1960s was so spectacular that it acquired the appellation “economic miracle.”. In the 1990s Taiwan’s economy slowed, but its growth remained good, even during the East Asian financial crisis of 1997.
What is Taiwan known for?
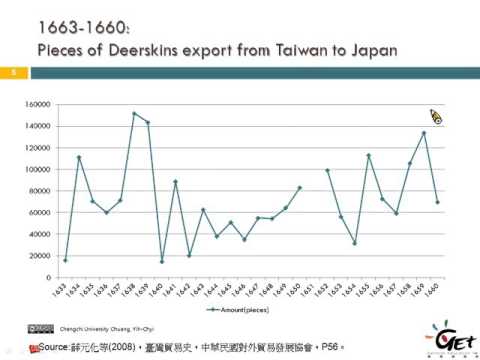
Taiwan has long been known for its productive agriculture, based on its rich volcanic soil, plentiful rainfall, and good climate. In fact, those conditions are what attracted early Chinese migrants. During the Japanese colonial period Taiwan exported large quantities of rice and sugar to Japan.
What happened to Taiwan in the 1990s?
In the 1990s Taiwan’s economy slowed, but its growth remained good, even during the East Asian financial crisis of 1997. In 2001 Taiwan experienced a recession, mainly caused by political paralysis. Its economy again underwent a downturn, beginning in 2008 with the global recession, from which it recovered only slowly.
What was the economic boom of the 1960s?
Taiwan ’s economic boom of the 1960s and for several decades after was preceded by land reform, which generated a marked growth in the agriculture sector. Rural prosperity stimulated industrial development, while more-efficient farming released labour for Taiwan’s industrialization that drove the economy in the 1960s and ’70s.
Is mineral exploitation important in Taiwan?
Mineral exploitation plays almost no role in Taiwan’s economy, although it was once important. In the late 19th century, Taiwan served as a coaling station for steamships, utilizing locally mined coal.
Where is natural gas purchased?
Natural gas is purchased mainly from Qatar, Malaysia, and Indonesia. In the years before the start of its dramatic economic expansion in the 1960s, Taiwan benefited from cheap power generation, including hydroelectric installations and thermal plants burning domestic coal.
Is Taiwan a member of the World Trade Organization?
These developments reflect Taiwan's economic importance and its desire to become further integrated into the global economy. Taiwan is a member of the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC).
Is Taiwan a capitalist country?
The economy of Taiwan is a highly developed capitalist economy with most government firms being privatized. It is the seventh largest in Asia and 20th -largest in the world by purchasing power parity allowing Taiwan to be included in the advanced economies group by the International Monetary Fund and gauged in the high-income economies group by the World Bank. Taiwan is the most technologically advanced computer microchip maker in the world.
Is Taiwan a US country?
Taiwan has transformed itself from a recipient of U.S. aid in the 1950s and early 1960s to an aid donor and major foreign investor, with investments primarily centered in Asia. Private Taiwanese investment in mainland China is estimated to total in excess of US$150 billion, and official tallies cite Taiwan as having invested a comparable amount in Southeast Asia.
Is Taiwan a member of the WTO?
Taiwan, as an independent economy, became a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO) as Separate Customs Territory of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen and Matsu (often shortened to "Chinese Taipei"-both names resulting from PRC interference on the WTO) in January 2002.
What is the semiconductor industry in Taiwan?
The semiconductor industry, including IC manufacturing, design, and packing, forms a major part of Taiwan's IT industry. Due to its strong capabilities in OEM wafer manufacturing and a complete industry supply chain, Taiwan has been able to distinguish itself from its competitors. The sector output reached US$39 billion in 2009, ranking first in global market share in IC manufacturing, packaging, and testing, and second in IC design. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) and United Microelectronics Corporation (UMC) are the two largest contract chipmakers in the world, while MediaTek is the fourth-largest fabless supplier globally. In 1987, TSMC pioneered the fabless foundry model, reshaping the global semiconductor industry. From ITRI 's first 3-inch wafer fabrication plant built in 1977 and the founding of UMC in 1980, the industry has developed into a world leader with 40 fabs in operation by 2002. In 2007, the semiconductor industry overtook that of the United States, second only to Japan. Although the global financial crisis from 2007 to 2010 affected sales and exports, the industry has rebounded with companies posting record profits for 2010. The international industrial forecast of semiconductor manufacturing, which is the flagship industry of the economy of Taiwan that faces immense competition ahead with its American counterparts. Taiwan has the largest share of 300 nm, 90 nm, and 60 nm manufacturing capacities worldwide, and was expected to pass Japan in total IC fab capacity by mid-2011.
What are the main crops in Taiwan?
Taiwan's main crops are rice, sugar cane, fruits (many of them tropical), and vegetables. Although self-sufficient in rice production, Taiwan imports large amounts of wheat, mostly from the United States. Meat production and consumption has risen sharply, reflecting a high standard of living.
What is Taiwan's energy consumption?
Taiwan's energy consumption is dominated by crude oil & petroleum products (48.52%), followed by coal (29.2%), natural gas (12.23%), nuclear power (8.33%), and hydroelectric power (0.28%). The island is also heavily dependent on imported oil, with 72% of its crude oil coming from the Middle East in 2002.
What is the capitalist economy of Taiwan?
Taiwan has a capitalist economy, which means that privately-owned companies decide on production techniques and operate to earn a profit. Banks and industrial companies that were previously owned by the state are now also privately owned. The economy of Taiwan is the 19th largest in the world in terms of purchasing power parity. It is considered an advanced economy by the International Monetary Fund and has the highest Global Entrepreneurship Index in Asia. Additionally, it ranks as the 5th largest economy in the region of Asia.
Is Taiwan a capitalist country?
Taiwan has a capitalist economy , which means that privately-owned companies decide on production techniques and operate to earn a profit. Banks and industrial companies that were previously owned by the state are now also privately owned.
How much did Taiwan export in 2014?
Top Export Goods and Partners Of Taiwan. In 2014, Taiwan exported $318 billion worth of goods. This economy is largely reliant on its export industry, which makes it vulnerable to global market fluctuations.
What is a positive trade balance?
A positive trade balance means this country exports more than it imports. Its major imports include: electronics, machinery, crude petroleum, computers, coal, organic chemicals, and metals. A large portion of its imports come from the following countries: Japan (17.6%), China (16.1%), and the US (9.5%).
What is Taiwan's economy?
Taiwan Economy. Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is the seventh-largest economy in Asia and the 22nd-largest economy in the world. With an export-oriented, dynamic capitalist economy, Taiwan is one of the Four Asian Tigers, along with Hong Kong, Singapore, and South Korea.
What is Taiwan known for?
The country is known for its rapid industrialisation between the 1960s and 1990s. In 1997, Taiwan was one of the few countries that withstood the Asian financial crisis due to its economic policy that restricted capital outflow. In the past three decades, the Taiwanese economy has grown at an average rate of 4.8% year-over-year.
What is the Taiwan Stock Exchange?
TWSE’s primary index is the Taiwan Capitalisation Weighted Stock Index (TAIEX).
What countries does Taiwan trade with?
Top Taiwan trading partners include China, Hong Kong, and the U.S. Nearly 75% of Taiwan exports go to Asian countries. Last year, the country managed to maintain a surplus in its trade balance. The total value of Taiwan’s exports reached $336 billion last year, up 6% from the previous year.
Is Taiwan a tiger?
With an export-oriented, dynamic capitalist economy, Taiwan is one of the Four Asian Tigers, along with Hong Kong, Singapore, and South Korea. The country is known for its rapid industrialisation between the 1960s and 1990s. In 1997, Taiwan was one of the few countries that withstood the Asian financial crisis due to its economic policy ...
Is Taiwan a high income country?
The World Bank categorised Taiwan as a high-income economy. Taiwan’s GDP per capita based on purchasing power parity (PPP) reached over $53,000 in 2018. By 2024, the IMF expects Taiwan’s GDP per capita (PPP) to exceed $68,000. The total population of Taiwan stood at around 23.5 million in 2018.
What is the official currency of Taiwan?
Taiwan’s official currency is the New Taiwan dollar (NT$), which replaced the Old Taiwan dollar in 1949. It is issued by the Central Bank of the Republic of China (Taiwan), located in Taipei.
Why is Taiwan's economy so strong?
A key reason for Taiwan’s strong economic performance is because it “never had to lock down its economy, so manufacturing plants have continued to run as normal ,” said Gareth Leather from Capital Economics. Taiwan’s economy has held up better than most Asian countries, thanks in part to how well it handled the coronavirus outbreak, ...
Does China control Taiwan?
China claims self-ruled Taiwan as part of its territory. The Chinese Communist Party has never governed Taiwan. Still, Beijing’s political claims over Taiwan means that Taiwanese businesses have special access to the mainland that foreign firms do not — since China will try to steer its reliance away from U.S. technology and imports, said Marro.
Is Taiwan better than Asia?
Street Signs Asia. Taiwan’s economy has held up better than most Asian countries, thanks in part to how well it handled the coronavirus outbreak, said an economist from research house Capital Economics.
Overview of The Economy of Taiwan
Leading Industries of Taiwan
- As evidenced by its employment pattern, the services sector is the leading industry in Taiwan. In fact, it contributes 73% of the GDP. Overall, the economy is very diversified with several different industries. Some of the most important of these include communications and information technology, electronics, petroleum refining, chemicals, armaments, chemicals, food processing, …
Top Export Goods and Partners of Taiwan
- In 2014, Taiwan exported $318 billion worth of goods. This economy is largely reliant on its export industry, which makes it vulnerable to global market fluctuations. Its principal exports include electronics, flat panels, ships, petrochemicals, machinery, metals, textiles, plastics, and chemicals. A large percentage of its exports go to the following countries: China (27.1%), Hong Kong (13.2…
Top Import Goods and Partners of Taiwan
- The 2014 imports to Taiwan totaled $277.5 billion, giving this country a positive trade balance of $40.5 billion. A positive trade balance means this country exports more than it imports. Its major imports include: electronics, machinery, crude petroleum, computers, coal, organic chemicals, and metals. A large portion of its imports come from the following countries: Japan (17.6%), China (…
Challenges Faced by The Economy of Taiwan
- Despite the apparent health of this economy, Taiwan does face some significant challenges to continued growth. The economy has recently stagnated. Its exports have been decreasing over the past few years, and work wages have not kept up with the cost of living. Additionally, the GDP only increased by .7% in 2015 which is significantly less than the 3.9% growth the country saw i…
Future Economic Plans of Taiwan
- To combat the previously mentioned challenges, the government of Taiwan has created a plan for the future of its economy. Part of this plan involves transitioning the economy to more technology-related and service-oriented jobs. It is also planning to diversify its export partners to avoid relying on exporting to just a few countries. The government also intends to continue with …
Popular Posts:
- 1. how to view blurred text in course
- 2. how to do a law conversion course
- 3. what is the primary objective of operating system attacks course hero
- 4. what to know before a first aid course
- 5. what does the quote the course of true love never did run smooth mean
- 6. how much is a billion crash course
- 7. where is the green hell obstacle course
- 8. what is ro? how is this value related to our success in eradication specific diseases? course hero
- 9. which is a true statement about any quality improvement process course hero
- 10. how to get a refund from course hero