Which method of the organizational structure can fully satisfy all these specifications?
Aug 03, 2021 · 1. Organic or Simple Organization. This type of organization is very flexible and able to adapt well to market changes. This structure is characterized by having few rules, regulations and management layers and a decentralized decision-making layout. An organic organization's design deals well with a rapidly changing environment.
What are the two methods of organizational structure?
Nov 04, 2018 · In this structure, team needs a continuing assignment in which the specific task changes frequently. If there is no continuing assignment, there can be a temporary task force, but not an organization based on the team structure as a permanent feature. If the tasks do not change, there is no need for team organization structure.
When is a free form of organizational structure suitable?
May 20, 2021 · The types of organizational structures in business are just as important as its products, marketing plan and long-term strategy. Businesses need a sturdy structure to attract and retain talented employees, as well as create a workable organizational hierarchy. Typically, businesses choose from four types of organizational structure.
What are the models derived from a hierarchical organization structure?
7 Organizational Structure Tasks are assigned to the permanent staff members by. 7 organizational structure tasks are assigned to the. School Troy University; Course Title MGT 6681; Type. Essay. Uploaded By studental2020. Pages 70 Ratings 96% ...
What are the 4 types of organizational structures?
The four types of organizational structures are functional, divisional, flatarchy, and matrix structures.
What is a hybrid organizational structure?
A hybrid organizational structure is a framework that employs multiple reporting structures in the organisation. A hybrid form of organization, for example, is created by combining functional and product structures.
What is a matrixed organization?
Summary. A matrix organization is a company structure where teams report to multiple leaders. The matrix design keeps open communication between teams and can help companies create more innovative products and services. Using this structure prevents teams from needing to realign every time a new project begins.Aug 26, 2021
In which type of organizational structure is decision making made at the lowest level of the organization?
decentralized companiesIn centralized companies, many important decisions are made at higher levels of the hierarchy, whereas in decentralized companies, decisions are made and problems are solved at lower levels by employees who are closer to the problem in question.
What is decentralized organizational structure?
A decentralized organizational structure is one in which senior management has shifted the authority for some types of decision making to lower levels in the organization.May 13, 2017
What is functional type of organization?
A functional organizational structure is a business structure that groups employees by specialty, skill or related roles. It is based on levels of hierarchy that include different departments, under the direction of designated leaders.Mar 31, 2021
What type of organization does matrix structure have?
A matrix organizational structure is a workplace format in which employees report to two or more managers rather than one manager overseeing every aspect of a project.Dec 16, 2021
What is committee organizational structure?
A committee organization is an association of people set up to arrive at solutions to common problems. The line people are given opportunities to discuss their problems in the committee. The committee organizational structure is not like line or functional organization, but is similar to staff organization.
What is divisional organization?
The divisional organizational structure organizes the activities of a business around geographical, market, or product and service groups. Thus, a company organized on divisional lines could have operating groups for the United States or Europe, or for commercial customers, or for the green widget product line.Feb 21, 2022
How does organizational structure determine the decision making process?
Perhaps the most important contributor to the way decisions are made in a company is its organizational structure. The way relationships are defined between managers and individual contributors in turn defines the mode of communication, the types of conflicts that can arise, and the way teams can resolve them.
What are the 3 types of organizational structure?
There are three main types of organizational structure: functional structure, divisional structure and a blend of the two, called matrix structure.
How does organizational structure affect decision making?
The purpose of organizational structure is to distribute the decisions of executive management down through administrative levels where the managers interpret those decisions and put them into practice.
What is the purpose of organizational structure?
Organization structure is to be such that it makes self-control possible and encourages self-motivation. Further, as per the requirement, the smallest possible number of employees, especially employees of high-performance capacity, are to devote time and attention for keeping the organization going.
What is a team organization?
A team consists of a number of people (normally small in number) with different backgrounds, skills, and knowledge and drawn from various departments of the organization, who work together on a specific and defined task. There is usually a team leader.
Why do teams fail?
Teams fail primarily because they do not impose on themselves the self-discipline and responsibility required by their high degree of freedom. No task force can be accommodating and function. The biggest limitation of the team organization structure is the team size. Teams work best when there are few members.
How to organize physical and mental work?
In the first method, work is organized by the ‘stages in a process’ as being done during the construction of a building structure, where first the foundation is built, then the frame and the roof are built, and finally the interior details are done. As per the second method, the work is organized in a way so that the work moves to where the skill or tool required for each of the steps is located. The example is a metalworking plant which has rows of lathes and reamers in one bay, stamping machines in another bay, and heat-treating equipment in a third bay and so on, with the pieces of metal piece being processed moving from one set of tools and their skilled operators to another. In the third method, the work is organized so that a team of workers with different skills and different tools moves to the work, which itself is stationary. As an example, a film making crew consisting of a director, the actors, the camera man, the electricians, the sound engineers etc. ‘moves to the location’. Each one carries out his highly specialized work, but they work as a team.
What is the direction of vision?
Direction of vision – It is essential that the organizational structure directs the vision of employees and of the management towards the performance, rather than towards putting efforts. Also, the structure needs to direct vision toward the results, that is, toward the performance of the complete organization.
What is the advantage of a structure based on functions?
The structure based on functions has the major advantage of clarity. Everyone has a workplace. Everyone understands his own task. The organization having this structure is an organization of high stability. But the price for clarity and stability is that it is difficult for the employees, upto and including the top management, to understand the common tasks and to relate their own work to it. While stable, the structure is rigid and resists adaptation. It does not prepare employees for tomorrow, does not train and test them. On the whole, it tends to make them do what they are already doing a little better, rather than to seek new ideas and new ways of doing things.
What is the first task of a team leader?
Hence, it is the team leader’s first task to establish clarity which includes clarity of objectives and clarity with respect to everyone’s role, including the his own. The team organization structure has its strengths and limitations. The team has obvious strengths.
What is functional structure?
A functional structure is the most traditional approach. It calls for grouping together people who do similar tasks based on their area of specialty. In other words, you’ll find all the accountants in finance and all the marketers in marketing. Managers led each area and report up to a director or executive who may oversee multiple departments.
What are the disadvantages of matrix structure?
The disadvantage is that employees may find it confusing to report to multiple bosses. But clear communication on priorities at all levels can eliminate these issues. The matrix structure requires a great deal of planning but can allow for the creation of the best possible teams to tackle the biggest challenges.
Why do businesses need a structure?
Businesses need a sturdy structure to attract and retain talented employees, as well as create a workable organizational hierarchy. Typically, businesses choose from four types of organizational structure. Each comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
What is matrix structure?
A matrix structure is a hybrid of the functional and divisional structures. It may involve employees reporting to different bosses depending on their current assignment. For example, a software design specialist may report to her boss in IT, but she’s also brought onto specific projects because of her expertise.
What is line organizational structure?
Line organizational structure is one of the simplest types of organizational structures. Its authority flows from top to bottom. Unlike other structures, specialized and supportive services do not take place in these organizations. The chain of command and each department head has control over their departments.
What is matrix organization?
In a Matrix organizational structure, the reporting relationships are set up as a grid, or matrix, rather than in the traditional hierarchy. It is a type of organizational management in which people with similar skills are pooled for work assignments, resulting in more than one manager to report to (sometimes referred to as solid line and dotted line reports, in reference to traditional business organization charts).
Why is it important to have a well trained workforce?
This enables employees to make decisions quickly and independently. Thus a well-tr ained workforce can be more productive by directly getting involved in the decision-making process. This works well for small companies because work and effort in a small company are relatively transparent.
What is the most popular organizational chart type?
The hierarchical model is the most popular organizational chart type. There are a few models that are derived from this model. In a hierarchical organization structure , employees are grouped with every employee having one clear supervisor. The grouping is done based on a few factors, hence many models derived from this.
What are the advantages of divisional structure?
The main advantage of the divisional structure is the independent operational flow, that failure of one company does not threaten the existence of the others. It’s not perfect either. There can be operational inefficiencies from separating specialized functions.
What is a divisional chart?
Within a divisional types of organizational charts has its own division which corresponds to either products or geographies. Each division contains the necessary resources and functions needed to support the product line and geography.
What are the different types of organizations?
There are different types of organizations that a company can adopt, such as functional, flat, matrix, and divisional organizations. When determining which type of organization to take on, there are several factors that should be taken into account. They include the size of the company, the business environment, ...
What is matrix organizational structure?
A matrix organizational structure is a bit more complex, in that there’s more than one line of reporting managers. It simply means that the employees are accountable to more than one boss. Most firms that take on this organizational structure often have two chains of command – functional and project managers.
What is the job of a CEO?
CEO A CEO, short for Chief Executive Officer, is the highest-ranking individual in a company or organization. The CEO is responsible for the overall success of an organization and for making top-level managerial decisions. Read a job description. of the company.
What is a flat organization?
A flat organization is exactly as its name suggests. While individuals may hold an expertise, hierarchy and job titles are not stressed among general employees, senior managers, and executives. In a purely flat organization, everyone is equal. Flat organizations are also described as self-managed.
What is corp dev?
Corp Dev also pursues opportunities that leverage the value of the company’s business platform. , and a marketing department. It means that every employee receives tasks and is accountable to a particular superior. A functional organization confers several benefits. For one, there’s a total specialization of work.
What are the benefits of functional organization?
A functional organization confers several benefits. For one, there’s a total specialization of work. Secondly, work is performed more efficiently since each manager is responsible for a single function. The only drawback to adopting a functional organization is the fact that there’s a delay in decision-making.
What is the life cycle of a company?
A firm’s life cycle is another essential factor to consider when setting up a company’s organization. Business owners who are trying to grow and expand their operations should choose a structure that allows for flexibility and smooth expansion.
What is the traditional organization structure?
Traditional organization structures are based on the assumption that position level equals contribution and contribution equals rewards. In other words, the higher the individual is in organization, the more authority he has, the greater the knowledge he possesses; the more he contributes, and the more he should be rewarded. In many organizations this holds good even today.
How does matrix organization affect management?
In an attempt to cover themselves against blame, managers try to put everything in writing. The dual chain of command turns the matrix structure into another form of anarchy. It increases the management costs to double. The decision-making process is slowed down. Members have to spend far more time at meetings and discussions than doing work. More information has to be processed through written reports.
Why are matrix subordinates at the receiving end?
This means prioritizing multiple commands (from functional head as well as the project head—one may ask them to run and the other might ask them to go slowly) and sometimes even receiving conflicting orders.
What is matrix organisation?
A permanent organisation designed to achieve specific results by using teams of specialists from different functional areas in the organisation is a matrix organisation. It is actually hybrid structure combining both functional and product structures in the same organisation. In the matrix structure, specialists from different functional departments work on projects that are led by a project manager.
Why did the matrix form?
This actually paved the way for the introduction of matrix form. One of the main reasons for the growth of matrix organization is the need to deal with increasing complexity . Matrix structure is the organization’s response to a turbulent field environment.
What is matrix structure?
Matrix structure is a way of balancing customer’s need for project completion and cost control with the organization’s need for economic cooperation and development of technical capability for the future. ‘A better balance between time, cost and performance can be obtained through the built in checks and balances and the continuous negotiations carried on between the project and functional organizations.’ Further, matrix reduces bureau-pathologies. The dual lines of authority reduce tendencies of departmental managers to become so busy protecting their little worlds that goals become displaced.
Why is matrix organization important?
One of the main reasons for the growth of matrix organization is the need to deal with increasing complexity. Matrix structure is the organization’s response to a turbulent field environment.
What is temporary team?
Temporary teams - Unlike permanent teams, temporary teams loose their importance, once the task is accomplished. Such teams are usually formed for a shorter duration either to assist the permanent team or work when the members of the permanent team are busy in some other project. When organizations have excess of work, ...
Why do we need to work together?
Individuals need to come and work together to form a team for the accomplishment of complicated tasks. In a team, all team members contribute equally and strive hard to achieve the team’s objective which should be predefined. In any organization, no one works alone. Every employee is a part of a team and works in close coordination with ...
What is a committee?
Committee - Committees are generally formed to work on a particular assignment either permanently or on a temporary basis. Individuals with common interests, more or less from the same background, attitude come together on a common platform to form a committee and work on any matter.
What is committee in education?
In educational institutes, various committees are formed where students with a common interest join hands to organize cultural events and various other activities required for the all round development of students.
Why do line organizations suffer from lack of specialization?
A line organization can suffer from a lack of specialization. This is because each department manager is concerned only with the activities of his own department. Therefore, employees are skilled in tasks pertaining to their departments alone.
What is line organization?
Line organization is the simplest framework for the whole administrative organization. Line organization approaches the vertical flow of the relationship. In line organization, authority flows from the top to the bottom. It is also known as the chain of command or scalar principle.
Why is line organization important?
Conforms to the scalar principle of organization. Further, it promotes the unity of command. In a line organization, the responsibility for the performance of tasks is fixed upon definite individuals. Therefore, there is accountability of delegated tasks.
What is division of work?
The division of work is not based on any scientific plan but on the whims of the manager. It might stop progress and prevent the unit to work effectively. Such organizations might also encourage nepotism or favoritism based on relationship or friendship.
What is scale of business?
The scale of business is small and the number of subordinates and superiors are few. In continuous process industries. Organizations where work is primarily routine in nature. Highly automated environments where the skills of the foreman are not important.
What is authority flow?
Also, authority flows from the top-most person in the organization to the person in the lowest rung. This type of an organization is also called a military organization or a scalar-type organization.
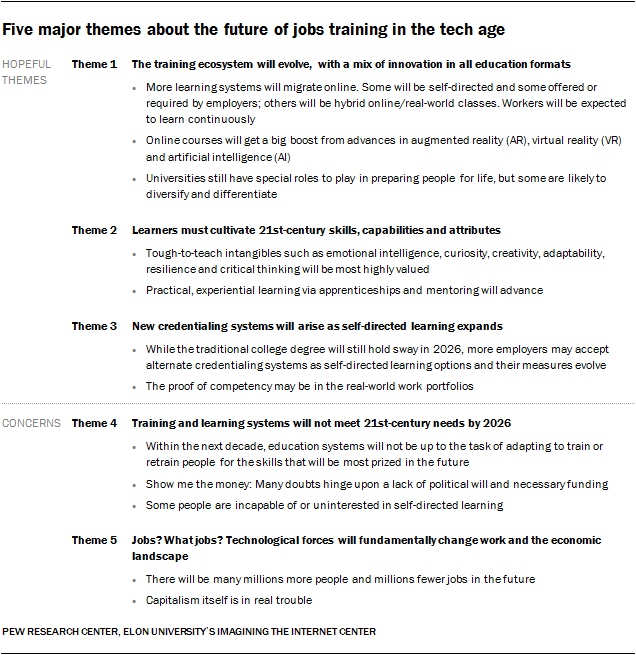
Hierarchical Structure
Matrix Structure
- In a Matrix organizational structure, the reporting relationships are set up as a grid, or matrix, rather than in the traditional hierarchy. It is a type of organizational management in which people with similar skills are pooled for work assignments, resulting in more than one manager to report to (sometimes referred to as solid line and dotted line reports, in reference to traditional busines…
Horizontal/Flat Structure
- This is an organizational chart type mostly adopted by small companies and start-ups in their early stage. It’s almost impossible to use this model for larger companies with many projects and employees. The most important thing about this structure is that many levels of middle management are eliminated. This enables employees to make decisions quickly and independe…
Network Structure
- Network organizational structure helps visualize both internal and external relationships between managers and top-level management. They are not only less hierarchical but are also more decentralized and more flexible than other structures. The idea behind the network structure is based on social networks. Its structure relies on open communication and reliable partners; bot…
Divisional Structure
- Within a divisional types of organizational charts has its own division which corresponds to either products or geographies. Each division contains the necessary resources and functions needed to support the product line and geography. Another form of divisional org chart structure is the multi-divisional structure. It’s also known as M-form. It’s a legit structure in which one parent compan…
Line Organizational Structure
- Line organizational structure is one of the simplest types of organizational structures. Its authority flows from top to bottom. Unlike other structures, specialized and supportive services do not take place in these organizations. The chain of command and each department head has control over their departments. The self-contained department structure can be seen as its main characterist…
Team-Based Organizational Structure
- Team-based organizational structures are made of teams working towards a common goal while working on their individual tasks. They are less hierarchical and they have flexible structures that reinforce problem-solving, decision-making and teamwork. Team organization structures have changed the way many industries work. Globalization has allowed people in all industries aroun…
at A Glance
Flat Organization
- A flat organization is exactly as its name suggests. While individuals may hold an expertise, hierarchy and job titles are not stressed among general employees, senior managers, and executives. In a purely flat organization, everyone is equal. Flat organizations are also described as self-managed. The idea behind this organizational structure is to reduce bureaucracy and em…
Functional Organization
- Also referred to as a bureaucratic structure, a functional organization is one that divides a firm’s operations based on specialties. Ideally, there’s an individual in charge of a particular function. It’s like any typical business that consists of a sales department, human relationsCorporate DevelopmentCorporate development is the group at a corporation responsible for strategic deci…
Divisional Organization
- A divisional organization structures its activities around a market, product, or specific group of consumers. For instance, a firm can operate in the United States or Europe, or sell products focused on a specific group of customers. Gap Inc. is the perfect case in point. It runs three different retailers – Banana Republic, Gap, and Old Navy. Although each one operates as a separ…
Matrix Organization
- A matrix organizational structure is a bit more complex, in that there’s more than one line of reporting managers. It simply means that the employees are accountable to more than one boss. Most firms that take on this organizational structure often have two chains of command – functional and project managers. This type of organization works best for companies with large …
How to Choose from Different Types of Organizations
- A type of organization serves as a framework that a firm can use to establish communication structures and authority among employees. However, it is crucial that a company chooses a type that suits its needs best.
The Importance of Adopting Proper Types of Organizations
- 1. Better Communication
Keeping open channels of communication is crucial to the success of every organization. As such, an organization needs to be designed in such a way that individuals and departments are able to coordinate their efforts. - 2. Set Organizational Priorities
A sound organizational structure is essential for setting priorities. In a tall hierarchical structure, the managers and executives determine the most crucial objectives that need to be met first. The heads of departments can then determine how to allocate different resources and the specific t…
Summary
- Choosing a type of organizational structure is important to a company’s management. It’s therefore crucial that business owners pick the right organizational type to help operations run more smoothly. There are different types of organizations that a company can adopt, such as functional, flat, matrix, and divisional organizations. When determining which type of organizatio…
Additional Resources
- CFI offers the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)®CFI's Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today!certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep lear…
Popular Posts:
- 1. how can course work and certifications help you in healthcare administration
- 2. which of the following is a psychological factor course hero
- 3. what city built thefirst 18 hole golf course
- 4. 3 reason why taking a course in public speaking is imodium
- 5. how to say course credits in french
- 6. how to delete duolingo course someone else created with my email.
- 7. what does it mean to appeal a course grade
- 8. if you earn a b in a course with three credit hours, how many quality points do you earn
- 9. what are general study course
- 10. if you taught a college course what would it be