The course bearing from “C” to “D” is 30 degrees true and 34 degrees magnetic. To follow a bearing, point your kayak so your compass reads the course bearing and then paddle while keeping your compass pointed at that bearing. When marking a course bearing on your chart, you can mark true, magnetic or both.
Full Answer
How do you measure a relative bearing course?
$\begingroup$ Bearings are typically angles turned clockwise from North. Using the info given, you can sketch a triangle with two sides and the angle between them known. Then use Law of Cosines to get the missing side. $\endgroup$ –
What is a course bearing?
Dec 06, 2010 · To follow a bearing, point your kayak so your compass reads the course bearing and then paddle while keeping your compass pointed at that bearing. When marking a course bearing on your chart, you can mark true, magnetic or both. Stay consistent or label the bearings. You can also mark a back bearing, which is the bearing to take if traveling the course in the …
How to calculate the bearing of a line?
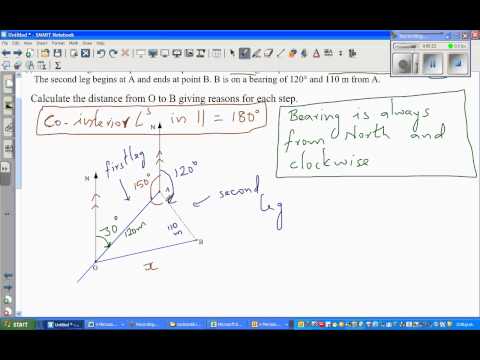
If given the bearing from B to A, the bearing from A to B can be found using interior angles. Subtract the bearing of B to A from 180° to find the missing interior angle, then use the fact that angles in a full turn add to 360° to find the bearing of A to B. For example, the bearing of B from A is 050°. Find the bearing of A from B.
How do you find the bearing of a longitude?
Dec 19, 2021 · 225 – 59 = 166°. Likewise, if you want to know the true bearing you can substitute other numbers. Let’s say you need to know the true bearing of Bruin Channel. The relative bearing is 325°. Your course is 135° T. According to the calculation relative bearing + heading = true bearing so 325 + 135 = 460.
How do you find the length of the bearing?
What is the formula for bearing?
| C r | basic dynamic radial load rating, [lbforce, N] |
|---|---|
| Fa | bearing axial load = axial component of the actual bearing load, [lbforce, N] |
| F r | bearing radial load = radial component of the actual bearing load[lbforce, N] |
| n | shaft rotates, [rpm] |
| L regr | required rating life, in 10 6 revolutions, [Mr] |
How do you find the length and bearing of a traverse?
...
HOW TO CALCULATE LENGTH AND BEARING OF OMITTING MEASUREMENT IN TRAVERSING.
How do you find the length of the bearings of a triangle?
How do you calculate bearings in surveying?
How do you solve a bearing question?
How do you calculate bearings from latitude and departure?
How is DMD calculated?
How do you find latitude and departure?
How do you work out bearings ks3?
How do you find a bearing from A to B?
How is course similar to bearing?
Course. Course is very similar to bearing in that it’s the desired direction for your route of flight. If you are going directly from one airport to the other, your course and bearing will be the same along the route of flight. If you are flying from an airport to a VOR to another airport, your course will change in each leg, as will your bearing.
Why is bearing confusing?
Bearing can be confusing sometimes because has some overlap with course. Bearing is simply the angle or direction between two points. A practical application of this is in VOR navigation. It’s a common thing to hear someone say “we are bearing 090 from the station”.
What is the difference between a track and a heading?
Heading is the direction the airplane is pointed, whereas track is the actual direction of the airplane tracking across the ground. Bearing is the angle between any two points, whereas course is your intended path of travel to your destination. In the rest of this post we’ll elaborate on each of these points and then also provide ...
What is heading in airplanes?
This does not factor for wind, or the actual movement of the airplane across the ground. It only refers to what the compass reads based on where the nose is pointed.
Why is the Earth not a perfect sphere?
This is indeed a very popular question and one that is a constant cause of confusion. The reason is that most people are looking for a simple and straight-forward answer. But there is none, because most people asking this question are not supplying enough information, simply because they are not aware that: 1 Earth is not a perfect sphere, since it is flattened/compressed by it poles 2 Because of (1) earth does not have a constant Radius, R. See here. 3 Earth is not perfectly smooth (variations in altitude) etc. 4 Due to tectonic plate movement, a geographic point's lat/lon position may change by several millimeters (at least), every year.
What are the different types of models?
Then the main models are: 1 Euclidian/Flat earth model: good for very short distances under ~10 km 2 Spherical model: good for large longitudinal distances, but with small latitudinal difference. Popular model:#N#Haversine: meter accuracy on [km] scales, very simple code. 3 Ellipsoidal models: Most accurate at any lat/lon and distance, but is still a numerical approximation that depend on what accuracy you need. Some popular models are:#N#Lambert: ~10 meter precision over 1000's of km.#N#Paul D.Thomas: Andoyer-Lambert approximation#N#Vincenty: millimeter precision and computational efficiency#N#Kerney: nanometer precision
What is bearing angle?
Bearing or heading angle is used to define navigation generally in the field of aircraft or marine or Vehicle navigation or while working for land surveying.
What is the difference between bearing and heading?
While Heading is an angle or direction where you are currently navigating in.
What is a compass for navigation?
Generally a ‘compass’ is an instrument, which gives you the direction information for navigation . You must refer Haversine distance formula before going through this post.

Heading
Track
- Track is the easiest of these four to understand in my mind,because it simply refers to how you are actually tracking over the ground. Whennavigating in the air, your track is really all that matters in terms ofgetting to where you want to go. If you need to go northeast to yourdestination, and have a significant wind from the west, your heading might beto the north in order to achieve a tr…
Bearing
- Bearing can be confusing sometimes because has some overlap with course. Bearing is simply the angle or direction between two points. A practical application of this is in VOR navigation. It’s a common thing to hear someone say “we are bearing 090 from the station”. This simply means that off of the VOR they are tracking on the 090 radial outbound from the station. In relation to th…
Course
- Course is very similar to bearing in that it’s the desireddirection for your route of flight. If you are going directly from one airportto the other, your course and bearing will be the same along the route of flight.If you are flying from an airport to a VOR to another airport, your course willchange in each leg, as will your bearing.
Example
- For this example we’re going to work backwards through the above mentioned directions. Assume you are departing an airport and your destination is directly eastbound. When you take off the course between the departing airport and destination airport is 090. In this instance the bearing of the destination airport off of your departing airport is also 090. This is also the direction you wan…
Does A GPS Use True Or Magnetic Heading?
- The above example assumes you are using the compass in yourairplane (hence why it requires so many steps to calibrate the differencebetween your true course all the way down to your actual compass heading). Butwhat about a GPS? By definition it’s not using earth’s magnetic fields as a wayof navigation, but rather positioning information provided by satellites. So ifit shows your “de…
Popular Posts:
- 1. how many chapters in each master craftsman course scottish rite
- 2. when a relationship has run its course
- 3. what is pharmacy course all about
- 4. how are the life course and spirituality related
- 5. when was bishop’s training course and self-help guide published
- 6. how to make your own mini golf course
- 7. how long is locating and evaluating information course for colllege
- 8. how to get my course on dailyom
- 9. how to audit course on udemy
- 10. how long does it take for a yeast infection to take its course in men