What is a crash course in organic chemistry?
In episode 37, we met a specific kind of EAS called Friedel-Crafts reactions, and we used them to add alkyl and acyl groups onto a benzene ring. Both reactions use an aluminium halide as a catalyst, commonly aluminium chloride. In Friedel-Crafts alkylation, an aromatic ring is reacted with an alkyl halide.
What are reactants and products in a dehydration synthesis reaction?
Sep 03, 2020 · This is the general model of a substitution reaction, with placeholders. We can add in some real atoms and molecules here: the substrate is 1-bromobutane, which switches its bromide dance partner for hydroxide. In this reaction, the leaving group is a bromide ion, and the nucleophile is a hydroxide ion.
What is the importance of dehydration synthesis?
2021-03-31 22:30. Even though all living things have a lot in common, different organisms can have very different reactions to the same organic chemicals. That means it’s really important for organic chemists to be able to purify chemicals and separate the products we want from reactions, from the side products we don’t. In this episode of Crash Course Organic Chemistry, …
How can I learn more about hydrolysis?
The Organic Chemistry Crash Course will be organised into four main topics: 1. Mechanisms (the "Why" of Organic Chemistry) Review the five mechanisms explicit in the syllabus, and concepts including the flow of electrons in organic reactions, the as well as the stability of intermediates and how they relate to major products.
How do you solve a synthesis problem?
How to approach synthesis problemsRelax!Understand that each step in a synthesis reactions can be broken down into two basic types of reactions; ... There are often times MANY routes to get to a final product. ... Sound out the problem. ... Practice, practice, practice! ... Sign up with StudyOrgo for help!Feb 9, 2016
How do you memorize reaction mechanisms?
2:187:13How to Memorize Organic Chemistry Mechanisms Through Active WritingYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipStart by looking at the mechanism. And copying. It you just look you basically cheat. And copy itMoreStart by looking at the mechanism. And copying. It you just look you basically cheat. And copy it over you see an alkene you draw the alkene you see an arrow you draw the arrow.
How do you perform a synthesis reaction in organic chemistry?
40:1551:13Organic Chemistry Synthesis Reactions - Retrosynthesis - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's going to grab one of the hydrogen's. And then a double bond is going to be formed and one ofMoreIt's going to grab one of the hydrogen's. And then a double bond is going to be formed and one of the BEA are just going to leave so this is going to be an e2 reaction.
What is a chemical reaction crash course?
0:333:50Chemical Changes: Crash Course Kids #19.2 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAs it burns it changes into burned wood and ash. We can't change this ash back into a match. SoMoreAs it burns it changes into burned wood and ash. We can't change this ash back into a match. So burning is an example of a chemical change that can't be undone.
Is Orgo memorization?
An introductory, undergrad course in Organic Chemistry does require a lot of memorization, but it is not all memorization. Nomenclature and learning about the different kind of reactions (there are a lot of them!)Oct 30, 2009
Does Lindlar's catalyst reduce alkenes?
Lindlar's catalyst is a palladium catalyst poisoned with traces of lead and quinoline, that reduce its activity such that it can only reduce alkynes, not alkenes. It always gives the cis-alkene, in contrast to Na/NH3, which gives the trans alkenes.Aug 19, 2011
What happens in a synthesis reaction?
Synthesis reactions are reactions that occur when two different atoms or molecules interact to form a different molecule or compound. Most of the time, when a synthesis reaction occurs, energy is released and the reaction is exothermic.
Can two elements be used as reactants for a synthesis reaction?
A synthesis reaction is when you Combined two or more things to get a single product. They ask if elements can be used as reactant and of compounds can be used and the answers are both yes.
What is a catalyst What is its role in organic synthesis reactions?
A catalyst is a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process. Catalysts typically speed up a reaction by reducing the activation energy or changing the reaction mechanism.
How do you name a crash course compound?
2:4710:42How to Speak Chemistrian: Crash Course Chemistry #11 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou just use the chemical symbol of its base element. And then add the charge as a superscript.MoreYou just use the chemical symbol of its base element. And then add the charge as a superscript. That's.
What are 20 examples of chemical changes?
burning of paper.cooking of food.burning of wood.ripening of fruits.rotting of fruits.frying egg.rusting of iron.mixing acid and base.More items...
What are the 4 types of chemical reactions?
The main four types of reactions are direct combination, analysis reaction, single displacement, and double displacement.Jan 24, 2020
What is the S N 1 reaction?
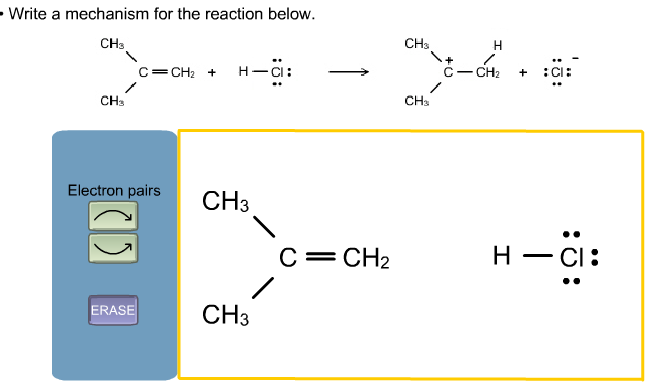
There are two steps to an S N 1 reaction: formation of a carbocation and nucleophilic attack. To see what this looks like in a reaction mechanism, let’s use a general model again.
What is substitution reaction?
In general chemistry, you might’ve heard substitution reactions called displacement reactions. Like two pairs of dance partners, two ionic compounds in water could swap ions when mixed, so the positive part of one compound ended up with the negative of the other. In organic chemistry, substitution reactions also involve switching partners, ...
What is the opposite of dehydration synthesis?
Now is a good time to mention hydrolysis, which is the opposite of dehydration synthesis. Rather than joining molecules together and releasing water as a product, hydrolysis uses water to split apart large molecules into their respective components. If you want to throw in some dry science humor, you might even say that hydrolysis is ...
What does it mean when you hear the word "dehydration"?
What Is Dehydration? When you hear the word dehydration, you undoubtedly think back to the last time you felt thirsty, dizzy, and generally off after a major loss of water (and insufficient water intake). Though we typically view the word dehydration in a negative light, the concept of dehydration synthesis is extremely valuable at ...
Is sucrose a macromolecule?
Disaccharide sugars, like sucrose, are carbohydrates and, as they are used in biological processes, are also considered biological macromolecules. If you’d like to delve a little deeper into the formation and characteristics of polymers, head over to our Polymers AP® Biology Crash Course Review when you’re done here.
Is water a polar molecule?
As you may have previously learned, water is arguably the most versatile, useful chemical in all of biology. If you’ve read our Hydrolysis AP® Biology Crash Course, you know that water is a polar molecule. Because of the charges at work, the two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in a water molecule are arranged in a familiar mouse-like fashion, ...
Popular Posts:
- 1. which of the following is not considered a benefit of byod course hero
- 2. how to use course unit folders video lms
- 3. what is the college course name for creating box for product
- 4. how to add a course ucsd
- 5. ccd refers to the ocean depth at which calcium carbonate is present only in solution. course hero
- 6. in what ways did african americans shape the course and consequences of the civil war essay
- 7. rs how to get to dorgesh-kaan agility course
- 8. how do i know if my morgagae points ar eover the course of the loan
- 9. what is course of pneumonia
- 10. how much is a hairdressing course