How do pigments absorb light?
Metals are reflective because the electrons in metals are almost free, and have an infinitely large number of possible energy levels, and thus can reflect any photon. Answer 3: Most pigments work by absorbing certain wavelengths of light. Other wavelengths are reflected or scattered, which cause you to see those colours.
How do pigment molecules react to electromagnetic waves?
Dec 14, 2021 · Pigments in the light-harvesting complex pass light energy to two special chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center. The light excites an electron from the chlorophyll a pair, which passes to the primary electron acceptor. The excited electron must then be replaced.
What does it mean for a pigment molecule to get excited?
May 14, 2020 · The color of light absorbed by a pigment is merely the complementary color of that pigment. Thus, pure blue pigments absorb yellow light (which can be thought of as a combination of red and green light). Pure yellow pigments absorb blue light. Likewise, what is a pigment and how does it absorb light? A pigment is any substance that absorbs light. The …
How are pigments identified in photosynthesis?
Jul 09, 2015 · In order to understand how we study the universe, we need to talk a little bit about light. Light is a form of energy. Its wavelength tells us its energy and...
How does a pigment absorb light?
A pigment is any substance that absorbs light. The color of the pigment comes from the wavelengths of light that are reflected, or in other words, those wavelengths not absorbed. Chlorophyll, the green pigment common to all photosynthetic cells, absorbs all wavelengths of visible light except green, which it reflects.
How does a pigment react in light?
A pigment molecule in the photosystem absorbs one photon, a quantity or “packet” of light energy, at a time. A photon of light energy travels until it reaches a molecule of chlorophyll.
How do chlorophyll pigments absorb energy from light?
Pigments in plant cells absorb blue and red light, but much of the green light if reflected. How do chlorophyll pigments absorb energy from light ? A photon excites an electron in the chlorophyll to a higher energy state.Nov 28, 2021
Which part of a pigment absorbs light?
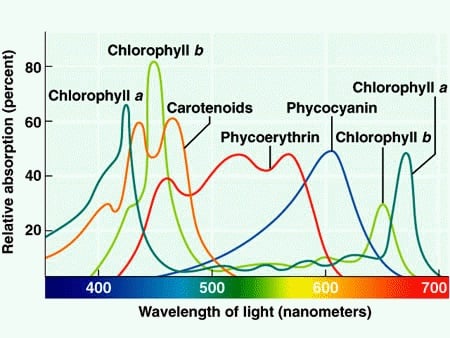
Chlorophyll aChlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not from green. Because green is reflected, chlorophyll appears green. Other pigment types include chlorophyll b (which absorbs blue and red-orange light) and the carotenoids.
Do pigments absorb light?
Pigments absorb light used in photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, the sun's energy is converted to chemical energy by photosynthetic organisms. However, the various wavelengths in sunlight are not all used equally in photosynthesis.
Why do pigments absorb light and other molecules don t?
Why do pigments absorb visible light and others don't? They have conjugated systems. Conjugated molecules, or molecules with unhybridized p-orbitals, can be excited by UV light. Best way to separate chloroplasts from buffer to extract pigments from chloroplasts?
Why can't chlorophyll absorb green light?
In conclusion, plant leaves are green because green light is less efficiently absorbed by chlorophylls a and b than red or blue light, and therefore green light has a higher probability to become diffusely reflected from cell walls than red or blue light. Chlorophylls do not reflect light.Dec 29, 2020
Does chlorophyll absorb green light?
Chlorophyll gives plants their green color because it does not absorb the green wavelengths of white light. That particular light wavelength is reflected from the plant, so it appears green.Sep 13, 2019
What happens to an electron when a pigment absorbs light it goes from a an?
When light strikes chlorophyll (or an accessory pigment) within the chloroplast, it energizes electrons within that molecule. These electrons jump up to higher energy levels; they have absorbed or captured, and now carry, that energy. ... The electrons replace those originally lost from chlorophyll.Mar 5, 2021
How is light absorbed?
A Quick Overview of Light Absorption In absorption, the frequency of the incoming light wave is at or near the energy levels of the electrons in the matter. The electrons will absorb the energy of the light wave and change their energy state.
How do plants absorb light energy?
Plants contain a molecule called chlorophyll, and the chlorophyll is what absorbs the sunlight. The chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light, and they reflect green light.Nov 24, 2021
Can light absorbed by other pigments be used in photosynthesis?
Different pigments respond to different wavelengths of visible light. Chlorophyll, the primary pigment used in photosynthesis, reflects green light and absorbs red and blue light most strongly. In plants, photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which contain the chlorophyll.
What molecules absorb light?
In plants, pigment molecules absorb only visible light for photosynthesis. The visible light seen by humans as white light actually exists in a rainbow of colors. Certain objects, such as a prism or a drop of water, disperse white light to reveal these colors to the human eye. The visible light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is perceived ...
What color does chlorophyll absorb?
Different kinds of pigments exist, and each absorbs only certain wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect the color of the wavelengths that they cannot absorb. All photosynthetic organisms contain a pigment called chlorophyll a, which humans see as the common green color associated with plants. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not from green. Because green is reflected, chlorophyll appears green.
What type of energy does the Sun emit?
Figure 3 The sun emits energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation . This radiation exists in different wavelengths, each of which has its own characteristic energy. Visible light is one type of energy emitted from the sun. Each type of electromagnetic radiation has a characteristic range of wavelengths.
How to determine the amount of energy of a wave?
Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its wavelength, the distance between two consecutive, similar points in a series of waves, such as from crest to crest or trough to trough ( Figure 2 ). Figure 2 The wavelength of a single wave is the distance between two consecutive points along the wave.
Which wave has the most energy?
Short, tight waves carry the most energy. This may seem illogical, but think of it in terms of a piece of moving rope. It takes little effort by a person to move a rope in long, wide waves. To make a rope move in short, tight waves, a person would need to apply significantly more energy.
Is visible light electromagnetic radiation?
Visible light constitutes only one of many types of electromagnetic radiation emitted from the sun. The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible wavelengths of radiation ( Figure 3 ). Each wavelength corresponds to a different amount of energy carried. Figure 3 The sun emits energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
Is the sun harmful to humans?
The sun emits a broad range of electromagnetic radiation, including X-rays and ultraviolet (UV) rays ( Figure 3) . The higher-energy waves are dangerous to living things; for example, X-rays and UV rays can be harmful to humans.
What pigment absorbs blue and red light?
Other pigment types include chlorophyll b (which absorbs blue and red-orange light) and the carotenoids. Each type of pigment can be identified by the specific pattern of wavelengths it absorbs from visible light, which is its absorption spectrum. Many photosynthetic organisms have a mixture of pigments; between them, ...
What molecules absorb light?
In plants, pigment molecules absorb only visible light for photosynthesis. The visible light seen by humans as white light actually exists in a rainbow of colors. Certain objects, such as a prism or a drop of water, disperse white light to reveal these colors to the human eye. The visible light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is perceived ...
What type of energy does the Sun emit?
Figure 3 The sun emits energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation . This radiation exists in different wavelengths, each of which has its own characteristic energy. Visible light is one type of energy emitted from the sun. Each type of electromagnetic radiation has a characteristic range of wavelengths.
How to determine the amount of energy of a wave?
Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its wavelength, the distance between two consecutive, similar points in a series of waves, such as from crest to crest or trough to trough ( Figure 2 ). Figure 2 The wavelength of a single wave is the distance between two consecutive points along the wave.
Which wave has the most energy?
Short, tight waves carry the most energy. This may seem illogical, but think of it in terms of a piece of moving rope. It takes little effort by a person to move a rope in long, wide waves. To make a rope move in short, tight waves, a person would need to apply significantly more energy.
Is the sun harmful to humans?
The sun emits a broad range of electromagnetic radiation, including X-rays and ultraviolet (UV) rays ( Figure 3) . The higher-energy waves are dangerous to living things; for example, X-rays and UV rays can be harmful to humans.
What color does chlorophyll absorb?
Different kinds of pigments exist, and each absorbs only certain wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect the color of the wavelengths that they cannot absorb. All photosynthetic organisms contain a pigment called chlorophyll a, which humans see as the common green color associated with plants. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectrum (blue and red), but not from green. Because green is reflected, chlorophyll appears green.
What Is Light Energy?
- The sun emits an enormous amount of electromagnetic radiation (solar energy). Humans can see only a fraction of this energy, which is referred to as “visible light.” The manner in which solar energy travels can be described and measured as waves. Scientists can determine the amount of energy of a wave by measuring its wavelength, the distance between two consecutive, similar po…
Absorption of Light
- Light energy enters the process of photosynthesis when pigments absorb the light. In plants, pigment molecules absorb only visible light for photosynthesis. The visible light seen by humans as white light actually exists in a rainbow of colors. Certain objects, such as a prism or a drop of water, disperse white light to reveal these colors to the human eye. The visible light portion of th…
Understanding Pigments
- Different kinds of pigments exist, and each absorbs only certain wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect the color of the wavelengths that they cannot absorb. All photosynthetic organisms contain a pigment called chlorophyll a, which humans see as the common green color associated with plants. Chlorophyll a absorbs wavelengths from either end of the visible spectru…
References
- Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax. Text adapted from: OpenStax, Concepts of Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 18, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
Popular Posts:
- 1. how to view course prerequisites for ivy tech
- 2. course hero how to see my unlocks
- 3. how many time can i retake a course at pierce college
- 4. randomly selecting someone who plays football. randomly selecting someone taking a calculus course.
- 5. what is the meanning fa class or course
- 6. how to register for iccoc course
- 7. how to login online course mcat prep for princeton
- 8. according to the course lessons, this is critical when you want to change a behavior:
- 9. what is pharm d course in india
- 10. astronomer what course of study is necessary to work in this field of science