How do you choose the best course of action?
1. Society’s wants are unlimited, but ALL resources are limited (scarcity). 2. Due to scarcity, choices must be made. Every choice has a cost (a trade-off). 3. Everyone’s goal is to make choices that maximize their satisfaction. Everyone acts in their own “self-interest.” 4. Everyone acts rationally by comparing the marginal
How do we select our preferred strategy and best course of action?
are all the alternatives that we give up whenever we choose one course of action over others. Opportunity Cost. the most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decison is known as opportunity cost. Thinking at the Margin. when you decide how much more or less to do, you are thinking at the margin. ...
Why does every choice involve an opportunity cost?
All the alternatives that we give up whenever we choose one course of action over another. In economics, it is expressed in terms of the opportunity cost of one potential choice, which is the loss of the best available alternative. Disincentives.
Is the right course of action so obvious?
Jan 14, 2013 · Once you have come up with an appropriate number of alternative ways of achieving your task you can evaluate each in turn and choose the best course of action. I find that 3 to 5 options is optimal. Contingency planning. The time spent on this process is not wasted as the courses you don’t choose become your contingency planning. There is an army phrase that …
What is the term for alternatives that people give up when they choose one course of action over another?
Trade offs are all the alternatives that we give up when we choose one course of actions over others, and opportunity cost is the most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision.
What is it called when a person gives up when making a decision?
Students should also be aware of opportunity cost—what a person gives up when a decision is made.
What is given up when choosing one option over another?
What Is Opportunity Cost? Opportunity costs represent the potential benefits an individual, investor, or business misses out on when choosing one alternative over another.
What is the opportunity of a decision?
The opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative foregone. Every decision necessarily means giving up other options, which all have a value. The opportunity cost is the value one could have derived from using the same resources another way, though this is not always easily quantifiable.
What is opportunity cost also known as?
Reduced cost aka 'opportunity cost' in linear programming.
How does opportunity cost affect decision-making?
Opportunity Costs Enhance Decision Making Incurring opportunity costs is not inherently bad, as they do not detract from business decisions; instead, opportunity costs often enhance the decision-making process. Weighing opportunity costs allows the business to make the best possible decision.
What are the opportunity cost of a student who decide to study college?
Answer: yes, but this is where opportunity cost comes in. Because you chose to go to college instead of working, your opportunity cost is actually the sum of your college expenses plus the money you could have earned had you chosen not to work. Your opportunity cost to attend college is $260k.Oct 11, 2020
What is the process of choosing which wants among several options will be satisfied?
The process of choosing which wants, among several options, will be satisfied is called economic decision making. In a traditional economy, goods and services are produced the way they have always been produced.
What is the difference between choice and opportunity?
is that opportunity is a chance for advancement, progress or profit while choice is an option; a decision; an opportunity to choose or select something.Jan 2, 2022
What is a opportunity cost example?
The opportunity cost is time spent studying and that money to spend on something else. A farmer chooses to plant wheat; the opportunity cost is planting a different crop, or an alternate use of the resources (land and farm equipment). A commuter takes the train to work instead of driving.Jan 29, 2020
Do all choices have an opportunity cost?
All choices, whether they are made by individuals or by groups of individuals such as governments, have a cost associated with them; economists call this an Opportunity Cost. Opportunity cost is the value of the benefits of the foregone alternative, of the next best alternative that could have been chosen, but was not.
What is the importance of opportunity cost in individual choice and decision-making?
The concept of Opportunity Cost helps us to choose the best possible option among all the available options. It helps us to use every possible resource tactfully, efficiently and hence, maximize economic profits.Sep 29, 2021
What is economic benefit?
Economic benefit (such as a tax allowance or duty rebate) or financial aid (such as a cash grant or soft loan) provided by a government to (1) support a desirable activity (such as exports), (2) keep prices of staples low, (3) maintain the income of the producers of critical or strategic products, (4) maintain employment levels, or (5) induce investment to reduce unemployment.
What is the theory of evolution?
A theory arising in the late nineteenth century that the laws of evolution, which Charles Darwin had observed in nature, also apply to society. It argued that social progress resulted from conflicts in which the fittest or best adapted individuals, or entire societies, would prevail. It gave rise to the slogan “survival of the fittest.”
What is the meaning of "money"?
An amount that has to be paid or given up in order to get something. It is usually a monetary valuation of (1) effort, (2) material, (3) resources, (4) time and utilities consumed, (5) risks incurred, and (6) opportunity forgone in production and delivery of a good or service.
What is a loan agreement?
An agreement under which a person borrows money to buy property, esp. a house, and the lender may take possession of the property if the borrower fails to repay the money.
What is Social Security Act?
A general term used to refer to the programs mandated in the United States by the Social Security Act of 1935. It consists of benefits for old age, survivors, and disability.
What is the key technique for selecting the best course of action?
A key technique for selecting the best course of action is to project the alternatives we are considering into the future to see what might happen if we implement each of these ideas.
What are negative criteria?
Negative criteria, which give reasons not to select an alternative, may include costs, risks, difficulty, hassle and trouble.
Brainstorming potential courses of action
We will be looking some more at the ‘cons’ in the next section on risk. But we will start here by looking to generate various courses of action so we can then evaluate them. We need a variety of options to examine and compare so at this stage we do some brainstorming.
Divergent thinking
There are many ways to help your creativity in thinking through a problem. Edward de Bono has written some excellent books on the topic such as Lateral Thinking and Six Thinking Hats . Malcolm Gladwell’s book ‘ Blink ’ and Tony Buzan’s work on Mind Mapping are other good resources that can help you.
Contingency planning
The time spent on this process is not wasted as the courses you don’t choose become your contingency planning. There is an army phrase that “no plan survives contact with the enemy.” In other words, there will always be unforeseen circumstances meaning you will have to adapt your ideas.
Making your choice
By this stage, you should have several courses of action that you could choose, Each option could achieve your aim. You will also have a feel for which option is the most attractive.
What is opportunity in education?
Don’t look for an industry, look for the opportunity. Opportunity is a set of circumstances that makes it possible to do something. The middle class looks for jobs to solve their problems. You need a job, but you also need opportunity. Senior students at MIT and Harvard right now don’t even know what opportunity means, ...
Can you see an opportunity if it hits you in the face?
This is why there is that saying, “You wouldn’t see an opportunity if it hit you in the face,” comes from. Opportunity can literally be right where you are but you’re blind to it.
What is a course of action?
1. Any sequence of activities that an individual or unit may follow.
What is the value of the next best opportunity?
action is what you must give up when you make that choice. Another way to say this is: it is the value of the next best opportunity. Opportunity cost is a direct implication of scarcity. People have to choose between different alternatives when deciding how to spend their money and their time. Milton Friedman, who won the Nobel Prize for
What is price setter?
Price Setter A company that has control over the prices of its products and services because its products and services are unique and there is little competition .
What is externality in economics?
In economics, an externality is a cost or benefit that is imposed on a third party who did not agree to incur that cost or benefit . For the purpose of these statements, overall cost and benefit to society is defined as the sum of the imputed monetary value of benefits and costs to all parties involved. The concept of externality was first developed by economist Arthur Pigou in the 1920s.
Why did the leaders of a powerful nation, most of whose citizens professed to be Christians, whipped
6 To give but one example, in the early 21st century the leaders of a powerful nation, most of whose citizens professed to be Christians, whipped up enmity against “Islamic terrorists” to justify invasion of a much weaker country that in fact posed no threat. Many believed the real reason was the leaders’ desire to gain control of the weaker country’s oil resources; but the stated ...
What is decision making in management?
Understand different types of decisions. Decision making refers to making choices among alternative courses of action —which may also include inaction. While it can be argued that management is decision making, half of the decisions made by managers within organizations ultimately fail.
What is the trade-off of a country?
• trade-off: the alternatives that we give up when we choose one course of action over another • “guns or butter”: a phrase expressing the idea that a country that decides to produce more military goods (“guns”) has fewer resources to produce consumer goods (“butter”) and vice versa • opportunity cost: the most desirable ...
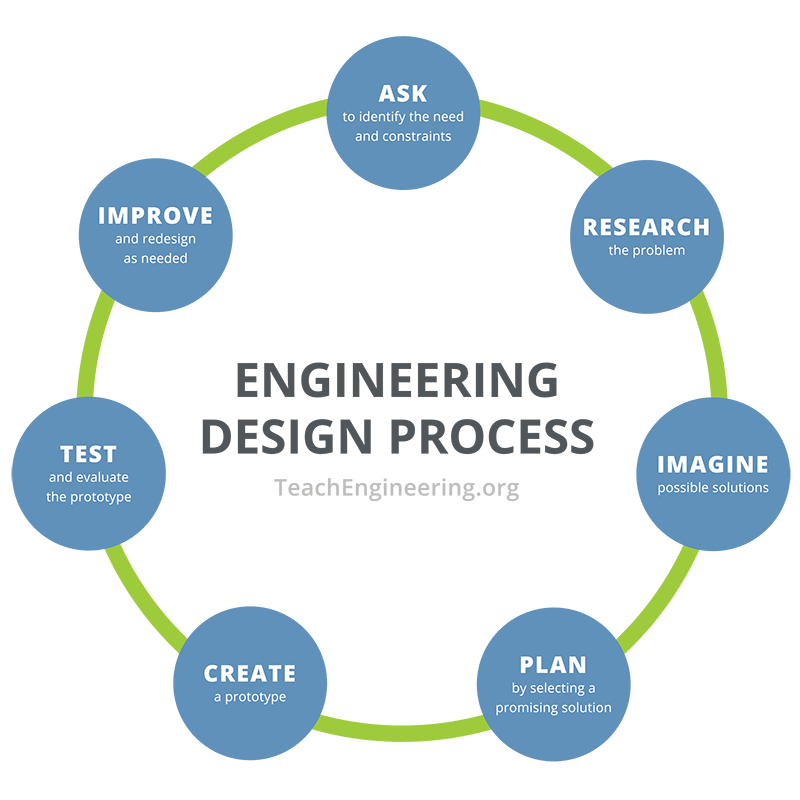
Criteria
- Selection is done through the application of some form ofcriteria, which may be consciously or subconsciously selected. These are reasonsfor or against taking the action, which will allow us to weigh up the pros andcons or the return on investment for each alternative. Negative criteria, which give reasons not to select analternative, may include costs, risks, difficulty, hassle and tro…
Negative Selection
- Remember when you last bought or rented a home. What youprobably did was to go along to a number of housing agents and come away withpiles of home details, then start your selection by sorting out the definite ‘nogood,’ the ‘maybe’ and the ‘interesting’ homes. The initial strategy that we commonly use when faced with alot of choices is to ‘sort the wheat from the chaff,’ rapidly el…
Forecasting and Risk Analysis
- A key technique for selecting the best course of action is toproject the alternatives we are considering into the future to see what mighthappen if we implement each of these ideas. In forecasting we make much use of our mental models to helpus grope forwards, weighing up the implications of each alternative, estimatingboth the possible outcomes an...
Positive Selection
- The final selection of the alternative that we will implementuses criteria in a more positive way, seeking to narrow down the short-list tothe item we will actually implement. This process is not always cool and rational, and even aftera long and drawn-out selection process, we sometimes change our minds for noapparent purpose, probably because our subconscious either objects i…
Popular Posts:
- 1. change leaders who change course
- 2. what is the course description for history alive's medieval world and beyonh?
- 3. game where youre sliding down a triangle and have to amke it down the course
- 4. indian mounds golf course jekyll island what is the cost per round
- 5. and of course, how is everyone doing
- 6. cystic fibrosis is characterized by which symptom course hero
- 7. how did charcters of macbeth developed/changed/ over the course of act
- 8. what is ipratropium bromide (atrovent) course hero
- 9. explain how 'forgery' is a real defense to an action by a holder in due course.
- 10. once purchased how long can i practise the course in udemy